ASTM D5235-97
(Test Method)Standard Test Method for Microscopical Measurement of Dry Film Thickness of Coatings on Wood Products (Withdrawn 2006)
Standard Test Method for Microscopical Measurement of Dry Film Thickness of Coatings on Wood Products (Withdrawn 2006)
SCOPE
1.1 This test method covers the measurement of dry film thickness of coatings applied to a smooth, textured or curved rigid substrate of wood or a wood-based product.
1.2 This test method covers the preparation of wood or wood-based specimens for the purpose of microscopical measurement of dry film thickness.
1.3 This test method suggests an interpretation of dry film thickness of coatings on wood or wood-based products when porous substrates are coated.
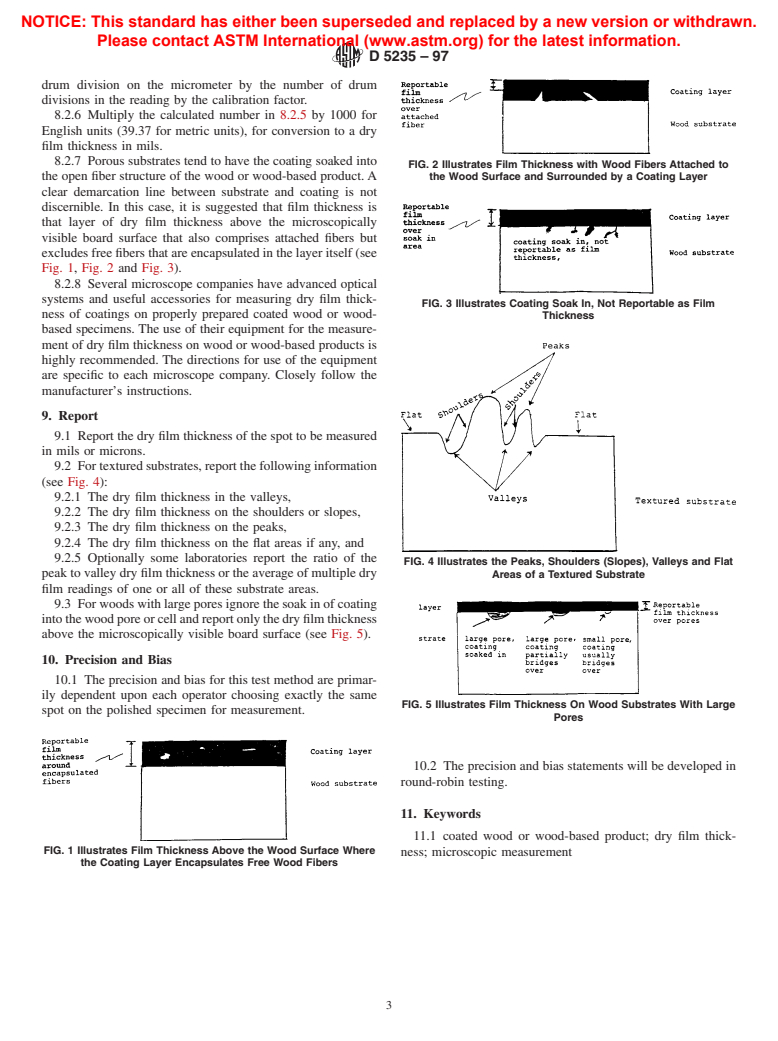
1.4 This test method suggests an interpretation of dry film thickness of coatings on wood or wood-based products when substrate attached or non-attached fibers occur in the dry film.
1.5 The values stated in inch-pound units are to be regarded as the standard. The values given in parentheses are for information only.
1.6 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use. Specific hazard statements are given in Section 7.
WITHDRAWN RATIONALE
This test method covers the measurement of dry film thickness of coatings applied to a smooth, textured or curved rigid substrate of wood or a wood-based product.
Formerly under the jurisdiction of Committee D01 on Paint and Related Coatings, Materials, and Applications, this test method was withdrawn in February 2006 in accordance with section 10.5.3.1 of the Regulations Governing ASTM Technical Committees, which requires that standards shall be updated by the end of the eighth year since the last approval date.
General Information
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Please contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information.
Designation:D5235–97
Standard Test Method for
Microscopical Measurement of Dry Film Thickness of
Coatings on Wood Products
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D 5235; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (ϵ) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope 2.1.3 soak in—refers to a coating on a porous substrate
where the coating does not lie essentially on the surface of the
1.1 This test method covers the measurement of dry film
wood or wood-based product, but has penetrated into the fiber
thickness of coatings applied to a smooth, textured or curved
structure of the wood or wood-based material.
rigid substrate of wood or a wood-based product.
2.1.3.1 Discussion—Woodorwood-basedproductsaregen-
1.2 This test method covers the preparation of wood or
erally of a porous nature; sometimes exhibiting uniform
wood-based specimens for the purpose of microscopical mea-
absorption of coatings. Frequently absorption of coatings is of
surement of dry film thickness.
a nonuniform nature and influenced by localized surface
1.3 This test method suggests an interpretation of dry film
density differences or wood pore size. These conditions of
thickness of coatings on wood or wood-based products when
coating absorption are commonly referred to as soak in.
porous substrates are coated.
1.4 This test method suggests an interpretation of dry film
3. Summary of Test Method
thickness of coatings on wood or wood-based products when
3.1 A specimen of coated wood or wood-based product is
substrate attached or non-attached fibers occur in the dry film.
cut to convenient size and edge polished with sandpaper.
1.5 The values stated in inch-pound units are to be regarded
3.2 The polished edge of the specimen is viewed through a
as the standard. The values given in parentheses are for
calibrated microscope in order to measure dry film thickness.
information only.
3.3 Suggestions regarding interpretation of dry film thick-
1.6 This standard does not purport to address all of the
ness on porous wood or wood-based material are offered.
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
3.4 Suggestions regarding interpretation of dry film thick-
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
ness on wood or wood-based material that have attached or
priate safety and health practices and determine the applica-
encapsulated fibers in the coating are offered.
bility of regulatory limitations prior to use. Specific hazard
statements are given in Section 7.
4. Significance and Use
2. Terminology 4.1 The dry film thickness of coatings on wood or wood-
based products is specified in written product warranties for
2.1 Definitions of Terms Specific to This Standard:
proper decorative and protective performance of coatings on
2.1.1 dry film thickness—that layer of thickness of dried
wood or wood-based products.
coating above the microscopically visible board surface that
4.2 The minimum and maximum dry film thickness of
also comprises attached fibers but excludes free fibers that are
coatingsisrecommendedbycoatingcompaniesforsatisfactory
encapsulated in the layer itself.
decorative and protective performance on wood or wood-based
2.1.2 edge face—That part of the specimen that is a plane
products.
perpendicular to the surface showing a cross section of the
4.3 The average dry film thickness of coatings on wood or
coating and substrate.
wood-based material may be used by manufacturing compa-
nies to calculate theoretical cost of applied coatings. By
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D-1 on Paint
comparison with actual cost, utilization efficiency may be
and Related Coatings, Materials, andApplications and is the direct responsibility of
calculated.
Subcommittee D01.52 on Factory-Coated Wood Products.
4.4 Theratioofpeaktovalleydryfilmthicknessontextured
Current edition approved Feb. 10, 1997. Published September 1997. Originally
published as D 5235 – 92. Last previous edition D 5235 – 92. products is used as an indication of coating uniformity.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959, United States.
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Please contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information.
D5235–97
4.5 Specific coated product requirements may dictate cer- 8.1.2 Cut this specimen to a length that is at least ⁄2-in.
tain film thickness determinations to be made. Discussions (12.7 mm) less than the inside diameter of the mold to be used.
between buyer and seller may be advisable to accommodate
8.1.3 Place the specimen, with the sample edge to be
product needs relative to dry film thickness.
measured, face down and approximately centered in the mold.
8.1.4 Prepare the sanding adhesive according to the manu-
5. Apparatus 5
facturer’s direction for use. A dispersed pigment may be
5.1 Calibrated Monocular Microscope, equipped with an
added to the adhesive for better microscopic contrast between
opticalsystem providingsufficientresolutionof0.1-mil(2.54-
the dry film and the adhesive.
µm) dry film thickness. One system consisting of a 16-mm
8.1.5 Pour the sanding adhesive around the sample in the
objective and a 10-power filar micrometer eyepiece, resulting
mold and allow to harden according to the manufacturer’s
in a magnification of at least 100 diameters, has been found
directions.
satisfactory. Other combinations of objectives and eyepieces
8.1.6 Remove the mold from the hardened and encapsulated
and other magnifications may also be suitable, although mag-
specimen edge.
nifications above 200 diameters may result in distortion of the
8.1.7 Using a disc sander, belt sander or 200-grit sandpaper
viewed cross section.
mounted on a glass plate, sand the edge face of the encapsu-
5.2 Source of Oblique Illumination, for the microscope.
lated specimen to be measured until the edge face is relatively
5.3 Cutoff Saw.
smooth. Maintain the edge face of the specimen as flat as
5.4 Belt or Disc Sander.
possible during sanding. Avoid heat buildup of the sanding
5.5 C-Type Clamp.
adhesive by intermittent sanding if necessary.
8.1.8 Polish the edge face of the rough sanded specimen as
6. Materials
follows:
6.1 200 and 600-Grit Sand Paper.
8.1.8.1 Mount a piece of 600-grit sandpaper on a flat glass
6.2 Mold, such as a paper cup, aluminum weighing dish, or
plate. Rub the edge face of the rough sanded specimen over the
a 2-in. (50.8-mm) or larger diameter plastic pipe that is at least
600-grit sandpaper in one direction, then reverse direction by
1-in. (25.4-mm) high.
180° for several more rubs. Zinc stearate powder can be
6.3 Source of Sanding Adhesive, which is used as encapsu-
sprinkled on the 600-grit sandpaper or the 600-grit sandpaper
lating medium such as:
can be wetted with mineral oil to produce a highly polished
6.3.1 Hot Melt Glue,
edge face free of scratches.
6.3.2 Fast-Cure Acrylic Mounting Kit, and
8.1.9 To improv
...







Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.