ASTM D3944-12(2017)
(Test Method)Standard Test Method for Solidification Point of Petroleum Wax
Standard Test Method for Solidification Point of Petroleum Wax
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
5.1 The related methods of determining the melt point of petroleum wax are relatively time-consuming. This method endeavors to reduce the duration of testing significantly and at the same time maintain a reasonable precision. This method can be useful for quality control of petroleum waxes as well as research and product development work on these waxes.
5.2 For methods used for testing melt points of petroleum waxes, see Tests Method D87, D127, including Petrolatum and Test Method D938.
SCOPE
1.1 This test method covers a procedure for rapidly determining the solidification point of petroleum wax.
Note 1: This test method is also applicable to similar materials such as synthetic waxes but the precision may vary.
1.2 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as the standard. .
1.2.1 Exception—The values given in parentheses are for information only
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety problems, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
1.4 This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization established in the Decision on Principles for the Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
General Information
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization established in the Decision on Principles for the
Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
Designation: D3944 − 12 (Reapproved 2017)
Standard Test Method for
Solidification Point of Petroleum Wax
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D3944; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope 3.1.1 solidification point of petroleum wax, n—that tempera-
ture in the cooling curve of the wax where the slope of the
1.1 This test method covers a procedure for rapidly deter-
curve first changes significantly as the wax sample changes
mining the solidification point of petroleum wax.
from a liquid to a solid state.
NOTE 1—This test method is also applicable to similar materials such as
synthetic waxes but the precision may vary.
4. Summary of Test Method
1.2 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as the
4.1 A 50 mg sample of wax is placed in a test tube at
standard.
ambient temperature and heated above the solidification point
1.2.1 Exception—The values given in parentheses are for
of the wax sample. A thermocouple probe, attached to a
information only
recorder, is inserted into the wax sample, which is allowed to
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the
cool at room temperature. The thermocouple response of the
safety problems, if any, associated with its use. It is the
cooling wax traces a curve on the chart paper of the recorder.
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
The first significant change in the slope of the curve is the
priate safety and health practices and determine the applica-
solidification point.
bility of regulatory limitations prior to use.
1.4 This international standard was developed in accor-
5. Significance and Use
dance with internationally recognized principles on standard-
5.1 The related methods of determining the melt point of
ization established in the Decision on Principles for the
petroleum wax are relatively time-consuming. This method
Development of International Standards, Guides and Recom-
endeavors to reduce the duration of testing significantly and at
mendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical
the same time maintain a reasonable precision. This method
Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
can be useful for quality control of petroleum waxes as well as
research and product development work on these waxes.
2. Referenced Documents
5.2 For methods used for testing melt points of petroleum
2.1 ASTM Standards:
waxes, see Tests Method D87, D127, including Petrolatum and
D87 Test Method for Melting Point of Petroleum Wax
Test Method D938.
(Cooling Curve)
D127 Test Method for Drop Melting Point of Petroleum
6. Apparatus
Wax, Including Petrolatum
D938 Test Method for Congealing Point of Petroleum
6.1 Thermocouple, with an iron-constantan junction.
Waxes, Including Petrolatum
6.2 Recorder, capable of recording voltage and equipped
E1 Specification for ASTM Liquid-in-Glass Thermometers
with a time-base module. The recorder should have the
following minimum specifications:
3. Terminology
6.2.1 Span, 0 mV to 10 mV or other suitable ranges.
3.1 Definitions of Terms Specific to This Standard:
6.2.2 Accuracy, 0.25 % of full scale.
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D02 on
Petroleum Products, Liquid Fuels, and Lubricants and is the direct responsibility of
Subcommittee D02.10 on Properties of Petroleum Waxes and Alternative Wax-like Suitable thermocouples are available from: Claud S. Gordon Co., 5710
Materials. Kenosha St., Richmond, IL 60071, (815) 678-2211. For “J” (iron-constantan)
Current edition approved June 1, 2017. Published July 2017. Originally approved junction the following is suitable: Xactpak Type MM Assembly, Catalog No.
in 1980. Last previous edition approved in 2012 as D3944 – 12. DOI: 10.1520/ 402-1101.
D3944-12R17. Junction: grounded (G)
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or Transition fitting: TH 2780-020
contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM Thermocouple wire: J30-1-305
Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on L (length of metal sheath)
the ASTM website. E (lead length): specify length desired.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
D3944 − 12 (2017)
FIG. 1 Solidification Point Apparatus
6.2.3 Step Response Time, 1 s full scale, 3 s full scale is also 7. Procedure
appropriate.
7.1 Calibrate the recorder at least every 60 days when in
6.2.4 Zero Junction/Reference Junction/Temperature Com-
frequent use (see Annex A1).
pensated Junction—Must be included.
7.2 Obtain a wax sample representative of the material to be
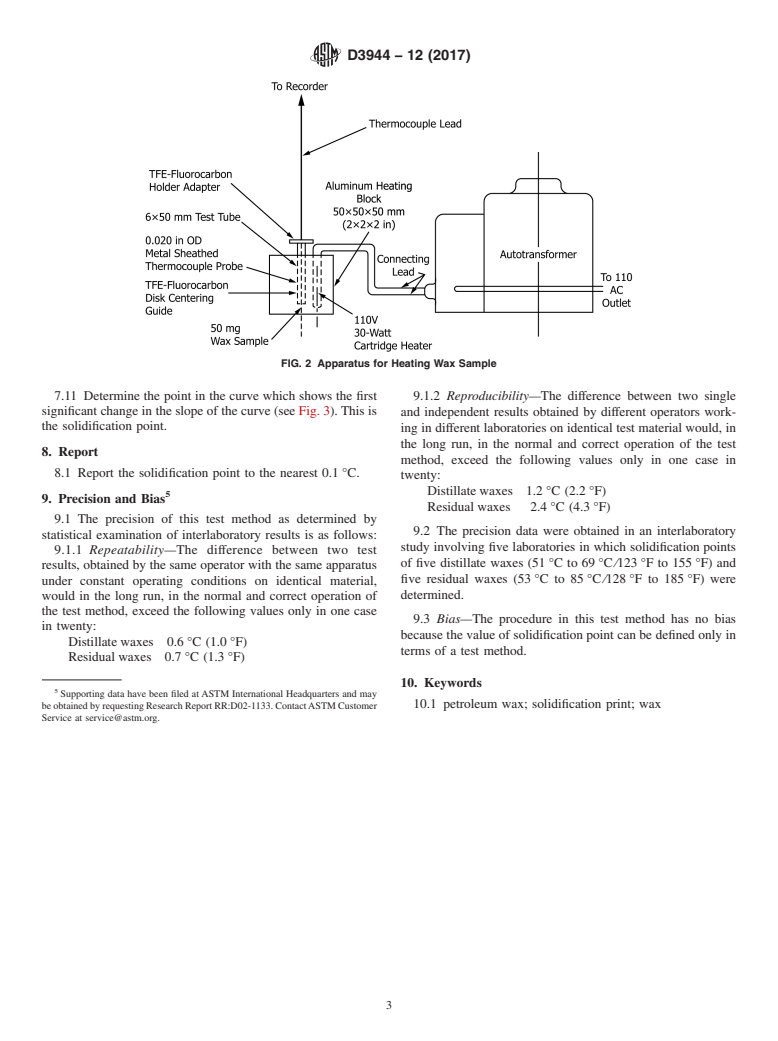
6.3 TFE-Fluorocarbon Holder Adapter—See Fig. 1 and Fig.
tested.
2.
7.3 Using a balance accurate to at least 1 mg, weigh
6.4 TFE-Fluorocarbon Disk Centering Guide—See Fig. 1
50 mg 6 5 mg of sample by putting a few tiny pieces of solid
and Fig. 2.
wax into a tared 6 mm by 50 mm test tube.
6.5 Test Tubes, 6 mm by 50 mm.
7.4 Start the temperature recorder. A horizontal pen speed of
about 150 mm (5 in.) ⁄10 min for a X-Y recorder or a chart
6.6 Vial, 25 mm by 52 mm.
speed of about 150 mm (5 in.) ⁄10 min for a strip chart recorder
6.7 Apparatus for Calibrating Temperature Recorder:
is usually appropriate.
6.7.1 Stainless Steel Beaker, 1000 mL.
7.5 Heat the sample by any convenient method, such as by
6.7.2 Heating Mantle, to fit 6.7.1.
6.7.3 Autotransformer to control heat to 6.7.2. use of:
7.5.1 A hot air blower.
6.7.4 Variable-Speed-Stirrer.
6.7.5 Thermometer, or other te
...







Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.