ASTM C652-04
(Specification)Standard Specification for Hollow Brick (Hollow Masonry Units Made From Clay or Shale)
Standard Specification for Hollow Brick (Hollow Masonry Units Made From Clay or Shale)
SCOPE
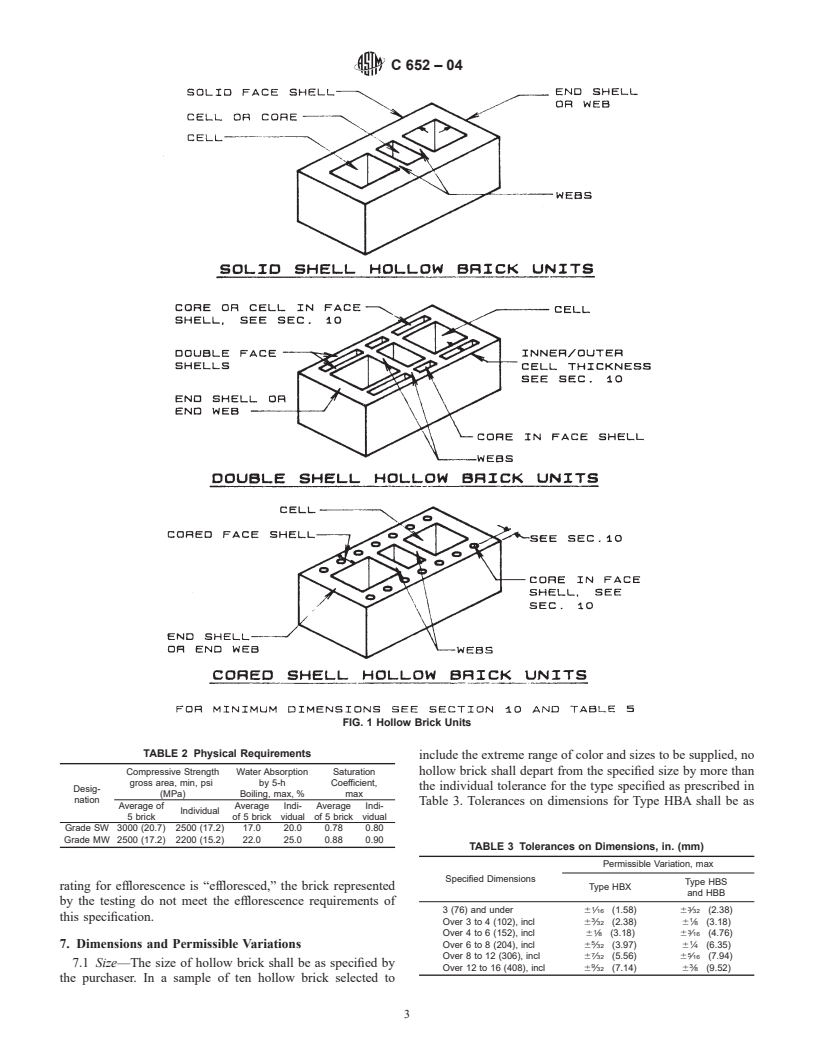
1.1 This specification covers hollow building brick and hollow facing brick made from clay, shale, fire clay, or mixtures thereof, and fired to incipient fusion. Four types of hollow brick in each of two grades and two classes are covered. In this specification the term hollow brick shall be understood to mean hollow clay masonry units whose net cross-sectional area (solid area) in any plane parallel to the surface, containing the cores, cells, or deep frogs, is less than 75 % of its gross cross-sectional area measured in the same plane (see ). This specification does not cover brick intended for use as paving brick (see Specification C 902).
1.2 The property requirements of this standard apply at the time of purchase. The use of results from testing of brick extracted from masonry structures for determining conformance or nonconformance to the property requirements (Section ) of this standard is beyond the scope of this standard.
1.3 Brick covered by this specification are manufactured from clay, shale, or similar naturally occurring substances and subjected to a heat treatment at elevated temperatures (firing). The heat treatment shall develop sufficient fired bond between the particulate constituents to provide the strength and durability requirements of this specification. (See "firing" and "firing bond" in Terminology C 43.)
1.4 Hollow brick differ from unglazed structural clay tile (Specifications C 34 and C 212) and solid brick (Specifications C 62 and C 216). Hollow brick require greater shell and web thicknesses and higher minimum compressive strength than structural clay tile, but permit greater void area and lesser distance from exposed edge to core hole than solid brick. Therefore, environmental and structural performance may be different in elements constructed of hollow brick from those constructed of structural clay tile or solid brick.
1.5 The text of this standard references notes and footnotes which provide explanatory material. These notes and footnotes (excluding those in tables and figures) shall not be considered as requirements of the standard.
1.6 The values stated in inch-pound units are to be regarded as the standard. The values given in parentheses are for information only.
General Information
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Designation: C 652 – 04
Standard Specification for
Hollow Brick (Hollow Masonry Units Made From Clay or
1
Shale)
This standard is issued under the fixed designation C 652; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (e) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
This standard has been approved for use by agencies of the Department of Defense.
1. Scope* 1.5 The text of this standard references notes and footnotes
which provide explanatory material. These notes and footnotes
1.1 This specification covers hollow building brick and
(excluding those in tables and figures) shall not be considered
hollow facing brick made from clay, shale, fire clay, or
as requirements of the standard.
mixtures thereof, and fired to incipient fusion. Four types of
1.6 The values stated in inch-pound units are to be regarded
hollow brick in each of two grades and two classes are covered.
as the standard. The values given in parentheses are for
In this specification the term hollow brick shall be understood
information only.
to mean hollow clay masonry units whose net cross-sectional
area (solid area) in any plane parallel to the surface, containing
2. Referenced Documents
the cores, cells, or deep frogs, is less than 75 % of its gross
2.1 ASTM Standards:
cross-sectional area measured in the same plane (see 3.3). This
C 34 Specification for Structural Clay Load-Bearing Wall
specification does not cover brick intended for use as paving
Tile
brick (see Specification C 902).
C 43 Terminology of Structural Clay Products
1.2 The property requirements of this standard apply at the
C 62 Specification for Building Brick (Solid Masonry Units
time of purchase. The use of results from testing of brick
Made from Clay or Shale)
extracted from masonry structures for determining conform-
C 67 Test Methods for Sampling and Testing Brick and
ance or nonconformance to the property requirements (Section
Structural Clay Tile
5) of this standard is beyond the scope of this standard.
C 212 Specification for Structural Clay Facing Tile
1.3 Brick covered by this specification are manufactured
C 216 Specification for Facing Brick (Solid Masonry Units
from clay, shale, or similar naturally occurring substances and
Made from Clay or Shale)
subjected to a heat treatment at elevated temperatures (firing).
C 902 Specification for Pedestrian and Light Traffic Paving
The heat treatment shall develop sufficient fired bond between
Brick
the particulate constituents to provide the strength and dura-
E 835/E 835M Guide for Modular Coordination of Clay
bility requirements of this specification. (See “firing” and
and Concrete Masonry Units
“firing bond” in Terminology C 43.)
1.4 Hollow brick differ from unglazed structural clay tile
3. Classification
(Specifications C 34 and C 212) and solid brick (Specifications
3.1 Grades—Two grades of hollow brick are covered:
C 62 and C 216). Hollow brick require greater shell and web
3.1.1 Grade SW—Hollow brick intended for use where a
thicknesses and higher minimum compressive strength than
high and uniform degree of resistance to frost action and
structural clay tile, but permit greater void area and lesser
disintegration by weathering is desired and the exposure is
distance from exposed edge to core hole than solid brick.
such that the hollow brick may be frozen when permeated with
Therefore, environmental and structural performance may be
water.
different in elements constructed of hollow brick from those
3.1.2 Grade MW—Hollow brick intended for use where a
constructed of structural clay tile or solid brick.
moderate and somewhat nonuniform degree of resistance to
frost action is permissible or where they are unlikely to be
1
This specification is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee C15 on
permeated with water when exposed to temperatures below
Manufactured Masonry Units and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee
freezing.
C15.02 on Brick and Structural Clay Tile.
3.2 Types—Four types of hollow brick are covered:
Current edition approved January 1, 2004. Published February 1, 2004. Origi-
3.2.1 Type HBS—Hollow brick for general use in masonry.
nally approved in 1970. Last previous edition approved in 2001 as C 652–01a.
*A Summary of Changes section appears at the end of this standard.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959, United States.
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
C652–04
3.2.2 Type HBX—Hollow brick for general use in masonry ments in Table 2, test the unit with the compressive force
where a higher degree of precision and lower permissible perpendicular to the bed surface of the
...







Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.