ASTM D2786-91(2016)
(Test Method)Standard Test Method for Hydrocarbon Types Analysis of Gas-Oil Saturates Fractions by High Ionizing Voltage Mass Spectrometry (Withdrawn 2023)
Standard Test Method for Hydrocarbon Types Analysis of Gas-Oil Saturates Fractions by High Ionizing Voltage Mass Spectrometry (Withdrawn 2023)
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
5.1 A knowledge of the hydrocarbon composition of process streams and petroleum products boiling within the range of 205 °C to 540 °C (400 °F to 1000 °F) is useful in following the effect of changes in process variables, diagnosing the source of plant upsets and in evaluating the effect of changes in composition on product performance properties.
5.2 This test method, when used together with Test Method D3239, provides a detailed analysis of the hydrocarbon composition of such materials.
SCOPE
1.1 This test method2 covers the determination by high ionizing voltage mass spectrometry of seven saturated hydrocarbon types and one aromatic type in saturate petroleum fractions having average carbon numbers 16 through 32. The saturate types include alkanes (0-rings), single-ring naphthenes, and five fused naphthene types with 2, 3, 4, 5, and 6 rings. The nonsaturate type is monoaromatic. Noncondensed naphthenes are analyzed as single rings. Samples must be nonolefinic and must contain less than 5 volume % monoaromatic. Composition data are in volume percent.
1.2 The values stated in acceptable SI units are to be regarded as the standard. The values given in parentheses are provided for information purposes only.
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
WITHDRAWN RATIONALE
This test method covered the determination by high ionizing voltage mass spectrometry of seven saturated hydrocarbon types and one aromatic type in saturate petroleum fractions having average carbon numbers 16 through 32. The saturate types included alkanes (0-rings), single-ring naphthenes, and five fused naphthene types with 2, 3, 4, 5, and 6 rings. The nonsaturate type was monoaromatic. Noncondensed naphthenes were analyzed as single rings. Samples must have been nonolefinic and must have contained less than 5 % by volume monoaromatic. Composition data were in volume percent.
Formerly under the jurisdiction of Committee D02 on Petroleum Products, Liquid Fuels, and Lubricants, this test method was withdrawn without replacement in March 2023. This test method was created in 1969. Test method has a precision statement but no referenced research report. ASTM archives do not have a research report on file. The Form and Syle Manual requires a research report. The test method was originally developed for specific types of magnetic sector mass spectrometers and published calculations were based on such instrumentation. As a result, there is no easy mechanism to update the test method without method development. In addition, Committee D02 understands that this method may not be performed by many, if any, laboratories. ASTM will continue to provide copies of the test method for those that may need it. Committee D02.04M encourages members to submit potential replacement test method(s), based on newer technologies (e.g. MS-FIMS, GC-FIMS, NOISE, GC/MS etc.) that can be developed into ASTM approved test method(s).
General Information
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Designation: D2786 − 91 (Reapproved 2016)
Standard Test Method for
Hydrocarbon Types Analysis of Gas-Oil Saturates Fractions
1
by High Ionizing Voltage Mass Spectrometry
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D2786; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope Quantitative Analysis from a Batch Inlet (Withdrawn
4
1992)
2
1.1 This test method covers the determination by high
ionizing voltage mass spectrometry of seven saturated hydro-
3. Terminology
carbon types and one aromatic type in saturate petroleum
3.1 Definitions of Terms Specific to This Standard:
fractions having average carbon numbers 16 through 32. The
3.1.1 Characteristic Mass Groupings:
saturate types include alkanes (0-rings), single-ring
3.1.1.1
naphthenes, and five fused naphthene types with 2, 3, 4, 5, and
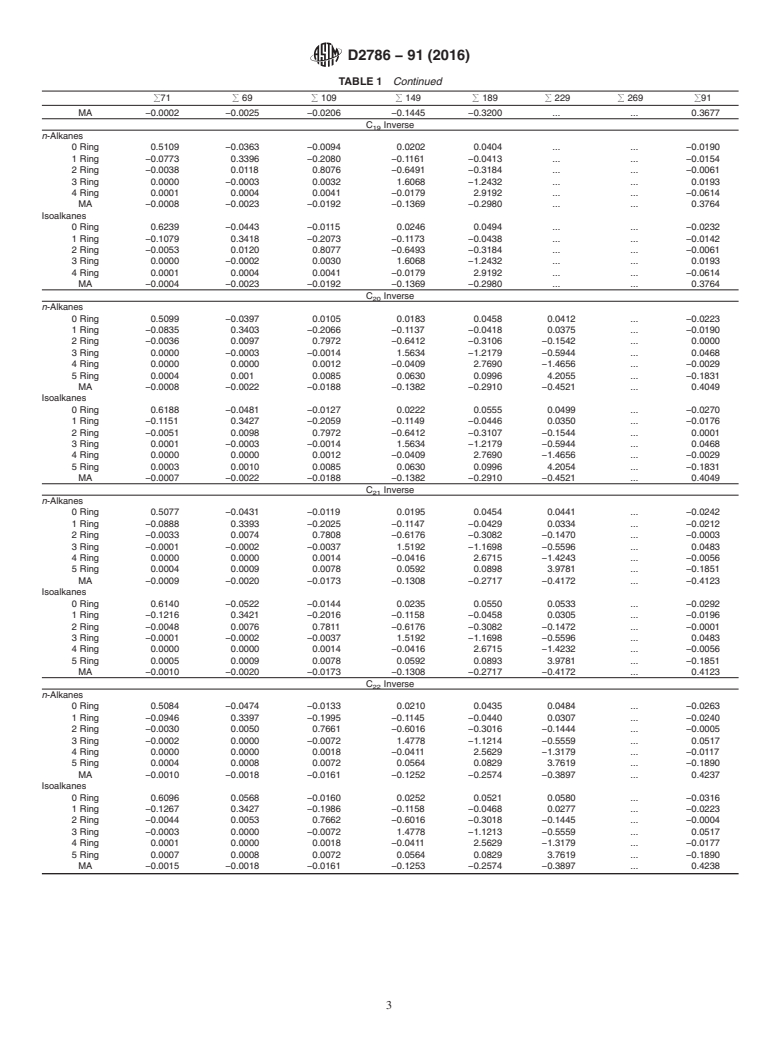
715 711851991113 ~alkanes!. (1)
6 rings. The nonsaturate type is monoaromatic. Noncondensed
(
naphthenes are analyzed as single rings. Samples must be
3.1.1.2
nonolefinic and must contain less than 5 volume % monoaro-
695 69183197111111251139 ~1 2 ring!. (2)
matic. Composition data are in volume percent.
(
3.1.1.3
1.2 The values stated in acceptable SI units are to be
regarded as the standard. The values given in parentheses are
1095 109112311371151116511791193 ~2 2 ring!. (3)
(
provided for information purposes only.
3.1.1.4
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the
1495 1491163117711911205121912331247 3 2 ring .
~ !
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
(
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro- (4)
priate safety and health practices and determine the applica-
3.1.1.5
bility of regulatory limitations prior to use.
1895 1891203121712311245125912731287
(
2. Referenced Documents
1301 4 2 ring . (5)
~ !
3
2.1 ASTM Standards:
3.1.1.6
D2549 Test Method for Separation of Representative Aro-
2295 22912431257127112851299131313271341
(
matics and Nonaromatics Fractions of High-Boiling Oils
1355 ~5 2 ring!. (6)
by Elution Chromatography
D3239 Test Method for Aromatic Types Analysis of Gas-Oil
3.1.1.7
Aromatic Fractions by High Ionizing Voltage Mass Spec-
2695 269128312971311132513391353136713811395
(
trometry
1409 6 2 ring . (7)
E137 Practice for Evaluation of Mass Spectrometers for ~ !
3.1.1.8
915 911105111711191129113111331143114511471157
1 (
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D02 on
11591171 ~monoaromatic!. (8)
Petroleum Products, Liquid Fuels, and Lubricants and is the direct responsibility of
Subcommittee D02.04.0M on Mass Spectroscopy.
4. Summary of Test Method
Current edition approved Oct. 1, 2016. Published November 2016. Originally
approved in 1969. Last previous edition approved in 2011 as D2786 – 91 (2011).
4.1 The relative abundance of alkanes (0-ring), 1-ring,
DOI: 10.1520/D2786-91R16.
2
2-ring, 3-ring, 4-ring, 5-ring, and 6-ring naphthenes in petro-
Hood, A., and O’Neal, M. J., Advances in Mass Spectrometry, AMSPA,
Waldron, 1959, p. 175.
leum saturate fractions is determined by mass spectrometry
3
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
4
Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on The last approved version of this historical standard is referenced on
the ASTM website. www.astm.org.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
D2786 − 91 (2016)
using a summation of mass fragment groups most characteris- 6.2 Sample Inlet System—Any inlet system may be used that
tic of each molecular type. Calculations are carried out by the
permits the introduction of the sample without loss,
use of inverted matrices (derived from ion intensity calibration
contamination, or change in composition. The system must
sensitivities) that are specific for any average carbon number.
function in the range from 125 °C to 350 °C to provide an
The saturate fraction is obtained by liquid elution
appropriate sampling device.
chromatography, see Test Method D2549.
6.3 Microburet or Constant-Volume Pipet.
5. Significance and Use
7. Reagents
5.1 A knowledge of the hydrocarbon composition of process
streams and petroleum products boiling within the range of
7.1 n-Hexadecane. (Warning—Combustible. Vapor harm-
205 °C to 540 °C (400 °F to 1000 °F) is useful in following the
ful.)
effect of changes in process variables, diagnosing the source of
plant upsets and in evaluating the effect
...








Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.