ASTM E2111-12(2018)
(Test Method)Standard Quantitative Carrier Test Method to Evaluate the Bactericidal, Fungicidal, Mycobactericidal, and Sporicidal Potencies of Liquid Chemicals
Standard Quantitative Carrier Test Method to Evaluate the Bactericidal, Fungicidal, Mycobactericidal, and Sporicidal Potencies of Liquid Chemicals
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
5.1 This test method is fully quantitative and it also avoids any loss of viable organisms through wash off, making it possible to produce statistically valid data using many fewer test and control carriers than other quantitative methods based on most probable numbers (MPN).
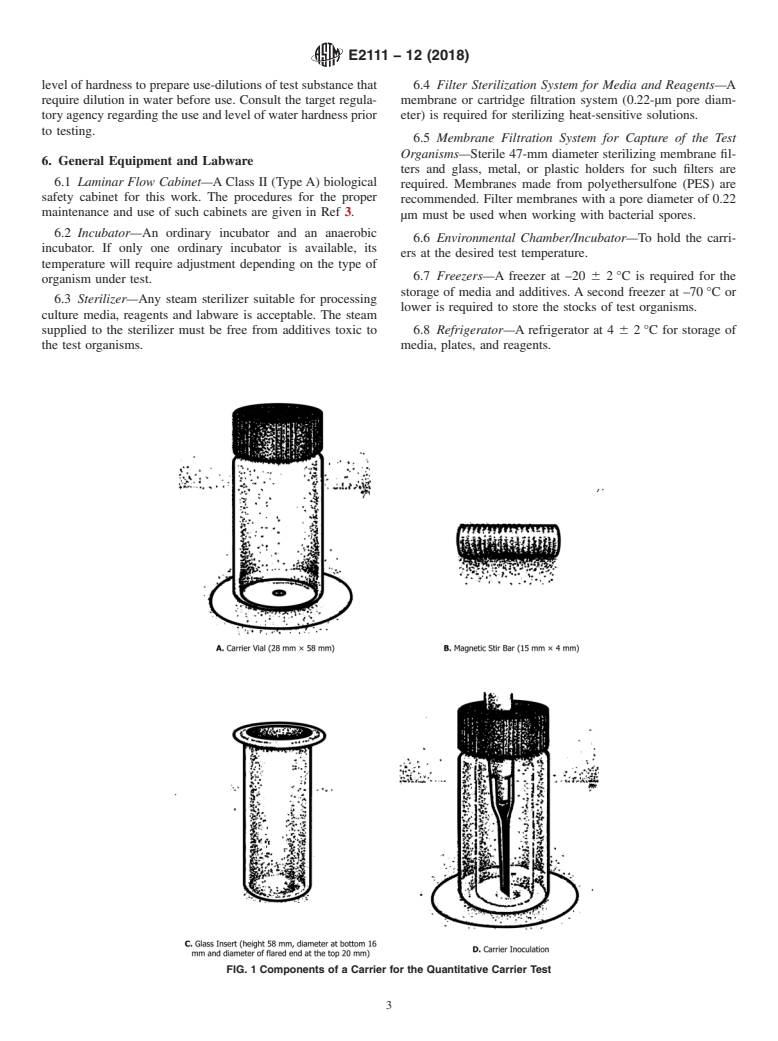
5.2 The design of the carriers makes it possible to place into each a precisely measured volume of the test suspension. The use of the threaded stir bars allows for efficient recovery of the inoculum even after its exposure for several hours to strong fixatives such as glutaraldehyde.
5.3 The membrane filtration step allows processing of the entire eluate from the test carriers and therefore the capture and subsequent detection of even low numbers of viable organisms that may be present.
5.4 This test can be performed with or without a soil load to determine the effect of such loading on microbicide performance. Consult the target regulatory agency on the need, type(s), and acceptable level(s) of soil load prior to testing. One type of soil load (Quantitative Disk Carrier Test Method E2197) to consider for this test is a mixture of three types of proteins (high molecular weight proteins, low molecular weight peptides, and mucous material) to represent the body secretions, excretions, or other extraneous substances that chemical microbicides may encounter under field conditions. It is suitable for working with the various test organisms included here. The components of the soil load are readily available and subject to much less variability than animal sera.
5.5 If distilled water or other diluent is not to be specified on the product label, the diluent for the test substance is assumed to be tap water. Since the quality of tap water varies considerably both geographically and temporally, this test method incorporates the use of water with a specified and documented level of hardness to prepare use-dilutions of test substance that require dilution in water before use. Consult the tar...
SCOPE
1.1 This test method is designed for use in product development and for the generation of product potency data. This test method permits the loading of each carrier with a known volume of the test organism. The incorporation of controls can also determine the initial load of colony forming units (CFU) of organisms on the test carriers and any loss in CFU after the mandatory drying of the inoculum.
1.2 This test method is designed to have survivors and also to be used with a performance standard. The surviving microorganisms on each test carrier are compared to the mean of no less than three control carriers to determine if the performance standard has been met. To allow proper statistical evaluation of results, the size of the test inoculum should be sufficiently large to take into account both the performance standard and the experimental variation in the results. For example, if an arbitrary performance standard of 6-log10 reduction in the viability titer of the test organism is used, and an inoculum size of 107 CFU, then theoretically a maximum of ten survivors per carrier is permitted; however, because of experimental variability, the exact target may need to be higher than 106 CFU/carrier, thus fewer survivors would be permitted.
1.3 This test method should be performed by persons with training in microbiology and in facilities designed and equipped for work with infectious agents at the appropriate biosafety level (3).
1.4 In this test method, SI units are used for all applications, except for distance, in which case inches are used and SI units follow.
1.5 It is the responsibility of the investigator to determine whether Good Laboratory Practice Regulations (GLPs) are required and to follow them where appropriate (40 CFR Part 160 for EPA submissions and 21 CFR Part 58 for FDA submissions).
1.6 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It ...
General Information
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization established in the Decision on Principles for the
Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
Designation: E2111 − 12 (Reapproved 2018)
Standard Quantitative Carrier Test Method to
Evaluate the Bactericidal, Fungicidal, Mycobactericidal, and
1
Sporicidal Potencies of Liquid Chemicals
This standard is issued under the fixed designation E2111; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision.Anumber in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval.A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
INTRODUCTION
2
The need for better tests to assess the microbicidal activity of chemicals was recognized (1) and
severalsimplerandquantitativetestmethodshavebeendevelopedforworkingwithawidevarietyof
microorganisms (2). The test method described here uses glass vials as carriers; the same basic set of
materials and procedures can be used to test the potency of liquid microbicides against vegetative
bacteria,fungi,mycobacteria,andbacterialspores.However,thetestmethodisnotappropriateforuse
with viruses because of the relatively high levels of eluate dilutions required and the need for
membrane filtration. Further evaluation of products under more stringent test conditions may be
necessary for their registration. Performance standards for the categories of products to be tested and
the specific types of organism(s) to be used may also vary depending on the regulatory agency.
1. Scope carrier is permitted; however, because of experimental
6
variability, the exact target may need to be higher than 10
1.1 This test method is designed for use in product devel-
CFU/carrier, thus fewer survivors would be permitted.
opment and for the generation of product potency data. This
test method permits the loading of each carrier with a known
1.3 This test method should be performed by persons with
volume of the test organism.The incorporation of controls can training in microbiology and in facilities designed and
also determine the initial load of colony forming units (CFU)
equipped for work with infectious agents at the appropriate
of organisms on the test carriers and any loss in CFU after the biosafety level (3).
mandatory drying of the inoculum.
1.4 Inthistestmethod,SIunitsareusedforallapplications,
1.2 This test method is designed to have survivors and also
except for distance, in which case inches are used and SI units
to be used with a performance standard. The surviving micro-
follow.
organisms on each test carrier are compared to the mean of no
1.5 It is the responsibility of the investigator to determine
less than three control carriers to determine if the performance
whether Good Laboratory Practice Regulations (GLPs) are
standardhasbeenmet.Toallowproperstatisticalevaluationof
required and to follow them where appropriate (40 CFR Part
results,thesizeofthetestinoculumshouldbesufficientlylarge
160 for EPA submissions and 21 CFR Part 58 for FDA
to take into account both the performance standard and the
submissions).
experimental variation in the results. For example, if an
1.6 This standard does not purport to address all of the
arbitrary performance standard of 6-log reduction in the
10
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
viabilitytiterofthetestorganismisused,andaninoculumsize
7
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
of10 CFU,thentheoreticallyamaximumoftensurvivorsper
priate safety, health, and environmental practices and deter-
mine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
1
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee E35 on
1.7 This international standard was developed in accor-
Pesticides, Antimicrobials, and Alternative Control Agents and is the direct
dance with internationally recognized principles on standard-
responsibility of Subcommittee E35.15 on Antimicrobial Agents.
Current edition approved Sept. 15, 2018. Published March 2019. Originally
ization established in the Decision on Principles for the
approved in 2000. Last previous edition approved in 2012 as E2111–12. DOI:
Development of International Standards, Guides and Recom-
10.1520/E2111–12R18.
2 mendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical
Theboldfacenumbersinparenthesesrefertothelistofreferencesattheendof
this standard. Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
E2111 − 12 (2018)
2. Referenced Documents a soil load. The contamination of the inside surface of the
3 carrier with microaerosols is avoided by the use of glass
2.1 ASTM Standard
...








Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.