ASTM D1351-20
(Specification)Standard Specification for Thermoplastic Polyethylene Insulation for Electrical Wire and Cable
Standard Specification for Thermoplastic Polyethylene Insulation for Electrical Wire and Cable
ABSTRACT
This specification covers thermoplastic polymer insulation consisting substantially of polyethylene considered suitable for use on electrical wire or cable with specified maximum conductor sizes that will be used for continuous operation at specified conductor temperatures and maximum voltage ratings for power application or series lighting. Since the insulation material cannot be tested unless it has been formed around a conductor, tests shall then be done on insulated wire or cable in this specification are solely to determine the relevant property of the insulation material and not to test the insulated conductor or completed cable. Materials shall conform to physical properties as to unaged tensile strength and elongation at rupture, tensile strength and elongation at rupture after air oven aging, absorption coefficient, and insulation thickness. Insulations shall also be tested for their electrical performance in terms of AC and DC voltage, partial discharge, and insulation resistance.
SCOPE
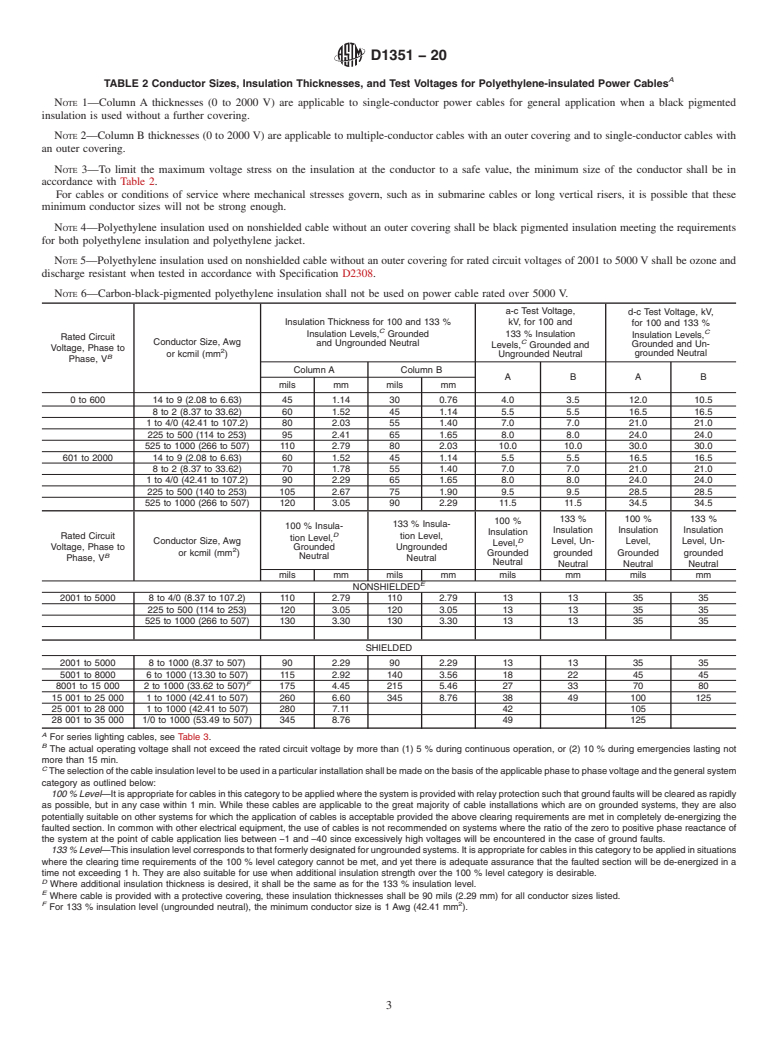
1.1 This specification covers a thermoplastic insulation which consists substantially of polyethylene.
1.2 This type of insulation is considered suitable for use on wire or cable that will be used for continuous operation at conductor temperatures up to 75 °C with a maximum conductor size of 1000 kcmil (507 mm2). The maximum voltage rating shall not exceed 35 000 V for power application or 9 000 V for series lighting.
1.3 In many instances the insulation material cannot be tested unless it has been formed around a conductor. Therefore, tests done on insulated wire or cable in this specification are solely to determine the relevant property of the insulation material and not to test the insulated conductor or completed cable.
1.4 Whenever two sets of values are stated, in different units, the values in the first set are regarded as standard, while the values in parentheses are provided for information only and are not considered standard.
1.5 This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization established in the Decision on Principles for the Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
General Information
Buy Standard
Standards Content (Sample)
This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization established in the Decision on Principles for the
Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
Designation:D1351 −20
Standard Specification for
Thermoplastic Polyethylene Insulation for Electrical Wire
1
and Cable
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D1351; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope* D2308 Specification for Thermoplastic Polyethylene Jacket
for Electrical Wire and Cable
1.1 This specification covers a thermoplastic insulation
D2633 Test Methods for Thermoplastic Insulations and
which consists substantially of polyethylene.
Jackets for Wire and Cable
1.2 This type of insulation is considered suitable for use on
D3349 Test Method for Absorption Coefficient of Ethylene
wire or cable that will be used for continuous operation at
Polymer Material Pigmented with Carbon Black
conductor temperatures up to 75 °C with a maximum conduc-
3
2.2 ICEA Standard:
2
torsizeof1000kcmil(507mm ).Themaximumvoltagerating
T-24-380 Guide for Partial-Discharge Procedure
shall not exceed 35 000Vfor power application or 9 000Vfor
series lighting.
3. Terminology
1.3 In many instances the insulation material cannot be
3.1 Definitions:
testedunlessithasbeenformedaroundaconductor.Therefore,
3.1.1 Refer to Terminology D1711 for definitions of terms
tests done on insulated wire or cable in this specification are
used in this specification.
solely to determine the relevant property of the insulation
3.2 Definitions of Terms Specific to This Standard:
material and not to test the insulated conductor or completed
3.2.1 aging (act of), n—exposure of materials to air at a
cable.
temperature of 100 °C for 48 h.
1.4 Whenever two sets of values are stated, in different
4. High Voltage Hazard
units, the values in the first set are regarded as standard, while
thevaluesinparenthesesareprovidedforinformationonlyand
4.1 High Voltage:
are not considered standard. 4.1.1 Lethal voltages are a potential hazard during the
performance of this test. It is essential that the test apparatus,
1.5 This international standard was developed in accor-
and all associated equipment electrically connected to it, be
dance with internationally recognized principles on standard-
properly designed and installed for safe operation.
ization established in the Decision on Principles for the
4.1.2 Solidly ground all electrically conductive parts which
Development of International Standards, Guides and Recom-
it is possible for a person to contact during the test.
mendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical
4.1.3 Provide means for use at the completion of any test to
Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
ground any parts which were at high voltage during the test or
have the potential for acquiring an induced charge during the
2. Referenced Documents
test or retaining a charge even after disconnection of the
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
voltage source.
D1248 Specification for Polyethylene Plastics Extrusion
4.1.4 Thoroughly instruct all operators as to the correct
Materials for Wire and Cable
procedures for performing tests safely.
D1711 Terminology Relating to Electrical Insulation
4.1.5 When making high voltage tests, particularly in com-
pressed gas or in oil, it is possible for the energy released at
breakdown to be sufficient to result in fire, explosion, or
1
This specification is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D09 on
rupture of the test chamber. Design test equipment, test
Electrical and Electronic Insulating Materials and is the direct responsibility of
Subcommittee D09.07 on Electrical Insulating Materials. chambers, and test specimens so as to minimize the possibility
Current edition approved Oct. 1, 2020. Published October 2020. Originally
of such occurrences and to eliminate the possibility of personal
approved in 1954. Last previous edition approved in 2014 as D1351 – 14. DOI:
injury. If the potential for fire exists, have fire suppression
10.1520/D1351-20.
2
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
3
Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on Available from The Insulated Cable Engineers Association, Inc. (ICEA), P.O.
the ASTM website. Box 2694, Alpharetta, GA 30023, http://www.icea.net.
*A Summary of Changes section appears at the end of this standard
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ---------
...
This document is not an ASTM standard and is intended only to provide the user of an ASTM standard an indication of what changes have been made to the previous version. Because
it may not be technically possible to adequately depict all changes accurately, ASTM recommends that users consult prior editions as appropriate. In all cases only the current version
of the standard as published by ASTM is to be considered the official document.
Designation: D1351 − 14 D1351 − 20
Standard Specification for
Thermoplastic Polyethylene Insulation for Electrical Wire
1
and Cable
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D1351; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope*
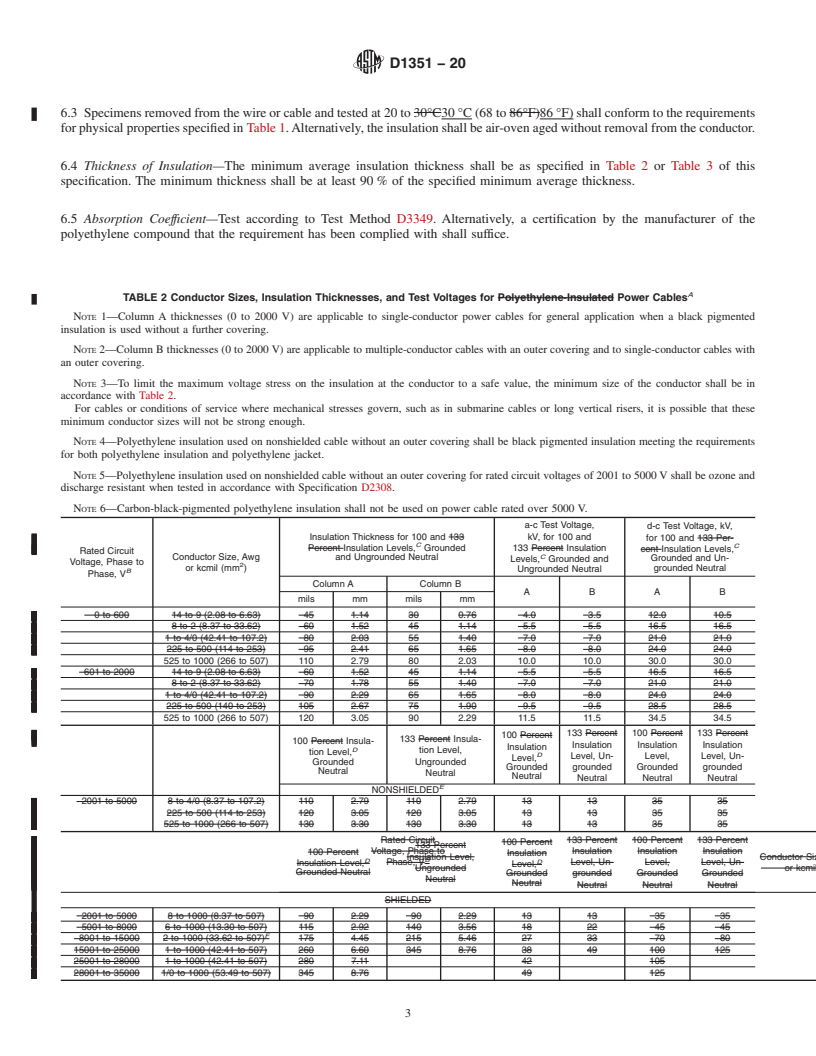
1.1 This specification covers a thermoplastic insulation which consists substantially of polyethylene.
1.2 This type of insulation is considered suitable for use on wire or cable that will be used for continuous operation at conductor
2
temperatures up to 75°C 75 °C with a maximum conductor size of 1000 kcmil (507 mm ). The maximum voltage rating shall not
exceed 35 000 V for power application or 9 000 V for series lighting.
1.3 In many instances the insulation material cannot be tested unless it has been formed around a conductor. Therefore, tests done
on insulated wire or cable in this specification are solely to determine the relevant property of the insulation material and not to
test the insulated conductor or completed cable.
1.4 Whenever two sets of values are presented,stated, in different units, the values in the firstfirst set are the regarded as standard,
while those the values in parentheses are provided for information only. only and are not considered standard.
1.5 This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization
established in the Decision on Principles for the Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued
by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
2. Referenced Documents
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
D1248 Specification for Polyethylene Plastics Extrusion Materials for Wire and Cable
D1711 Terminology Relating to Electrical Insulation
D2308 Specification for Thermoplastic Polyethylene Jacket for Electrical Wire and Cable
D2633 Test Methods for Thermoplastic Insulations and Jackets for Wire and Cable
D3349 Test Method for Absorption Coefficient of Ethylene Polymer Material Pigmented with Carbon Black
3
2.2 ICEA Standard:
T-24-380 Guide for Partial-Discharge Procedure
3. Terminology
3.1 Definitions:
1
This specification is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D09 on Electrical and Electronic Insulating Materials and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee
D09.07 on Electrical Insulating Materials.
Current edition approved March 1, 2014Oct. 1, 2020. Published April 2014October 2020. Originally approved in 1954. Last previous edition approved in 20082014 as
D1351 – 08.D1351 – 14. DOI: 10.1520/D1351-14.10.1520/D1351-20.
2
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM Standards
volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on the ASTM website.
3
Available from The Insulated Cable Engineers Association, Inc. (ICEA), P.O. Box 1568, Carrollton,2694, Alpharetta, GA 30112,30023, http://www.icea.net.
*A Summary of Changes section appears at the end of this standard
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
D1351 − 20
3.1.1 Refer to Terminology D1711 for definitions of terms used in this specification.
3.2 Definitions of Terms Specific to This Standard:
3.2.1 aging (act of), n—exposure of materials to air at a temperature of 100°C 100 °C for 48 h.
4. High Voltage Hazard
4.1 High Voltage:
4.1.1 Lethal voltages are a potential hazard during the performance of this test. It is essential that the test apparatus, and all
associated equipment electrically connected to it, be properly designed and installed for safe operation.
4.1.2 Solidly ground all electrically conductive parts which it is possible for a person to contact during the test.
4.1.3 Provide means for use at the completion of any test to ground any parts which were at high voltage during the test or have
the potential for acquiring an induced charge during the test or retaining a charge even after disconnection of the voltage source.
4.1.4 Thoroughly instruct all operators as to the correct procedures for performing tests safely.
4.1.5 When making high voltage tests, particularly in compressed gas or in oil, it is possible for the energy released at brea
...









Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.