ASTM D3037-93
(Test Method)Standard Test Methods for Carbon Black—Surface Area by Nitrogen Adsorption (Withdrawn 1999)
Standard Test Methods for Carbon Black—Surface Area by Nitrogen Adsorption (Withdrawn 1999)
SCOPE
1.1 These test methods cover the determination of the surface area of carbon blacks. The test methods appear in the following order: SectionsTest Method A—Surface Area by Ni-Count-1 Apparatus9-14Test Method B—Surface Area by Model 2200 Automatic Automatic Surface Area Analyzer15-20Test Method C—Surface Area by Continuous Flow Chromatography21-27Test Method D—Surface Area by Monosorb Surface Area Analyzer28-35
1.2 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as the standard. The values given in parentheses are for information only.
1.3 Goal values for the standard reference blacks were determined by using Test Methods D4820.
1.4 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety problems, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use. For specific precautionary statement, see Note 3.
General Information
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn. Contact ASTM
International (www.astm.org) for the latest information.
Designation:D3037–93
Standard Test Methods for
Carbon Black—Surface Area By Nitrogen Adsorption
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D3037; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision.Anumber in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval.A
superscript epsilon (e) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
This standard has been approved for use by agencies of the Department of Defense.
1. Scope D4483 Practice for Determining Precision forTest Method
Standards in the Rubber and Carbon Black Industries
1.1 These test methods cover the determination of the
D4820 Test Methods for Carbon Black—Surface Area by
surface area of carbon blacks. The test methods appear in the
Multipoint B.E.T. Nitrogen Adsorption
following order:
Sections
3. Significance and Use
Test Method A—Surface Area by Ni-Count-1 Apparatus 9-14
3.1 These test methods are used to measure the surface area
Test Method B—Surface Area by Model 2200 Automatic 15-20
of carbon black that is available to the nitrogen molecule.
Surface Area Analyzer
Test Method C—Surface Area by Continuous Flow Chro- 21-27
4. Reagents
matography
Test Method D—Surface Area by Monosorb Surface Area 28-35
4.1 Purity of Reagents—Reagent grade chemicals shall be
Analyzer
used in all tests. Unless otherwise indicated, it is intended that
1.2 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as the
all reagents shall conform to the specifications of the Commit-
standard. The values given in parentheses are for information
tee onAnalytical Reagents of theAmerican Chemical Society,
only.
where such specifications are available. Other grades may be
1.3 Goal values for the standard reference blacks were
used, provided it is first ascertained that the reagent is of
determined by using Test Methods D4820.
sufficiently high purity to permit its use without lessening the
1.4 This standard does not purport to address all of the
accuracy of the determination.
safety problems, if any, associated with its use. It is the
4.2 Purity of Water—Unlessotherwiseindicated,references
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
towatershallbeunderstoodtomeandistilledwaterorwaterof
priate safety and health practices and determine the applica-
equal purity.
bility of regulatory limitations prior to use. For specific
5. ASTM D-24 Standard Reference Blacks
precautionary statement, see Note 3.
5.1 The apparatus shall be checked initially for correct
2. Referenced Documents
calibration by testing the ASTM D-24 Standard Reference
2.1 ASTM Standards:
Blacks. These blacks shall be tested regularly, along with
D1799 Practice for Carbon Black—Sampling Packaged
sample blacks, as described inTest MethodsAthrough D.The
Shipments
standardvalueandrangeforeachofthestandardblacks,when
D1900 Practice for Carbon Black—Sampling Bulk Ship-
tested by these test methods, is given in Practice D3324.
ments
5.1.1 InTestMethodsAthroughD,allsamplesandstandard
D3324 Practice for Carbon Black—Improving Test Repro-
blacks shall be dried for1hat 125°C before weighing. Cool
ducibility Using ASTM Reference Blacks
and keep blacks in a well-maintained desiccator before taking
These test methods are under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D-24 on
Carbon Black and are the direct responsibility of Subcommittee D24.21 on “ReagentChemicals,AmericanChemicalSocietySpecifications,”Am.Chemi-
Adsorptive Properties of Carbon Black. cal Soc., Washington, DC. For suggestions on the testing of reagents not listed by
Current edition approved March 15, 1993. Published May 1993. Originally theAmericanChemicalSociety,see“ReagentChemicalsandStandards,”byJoseph
published as D3037–71T. Last previous edition D3037–92a. Rosin, D. Van Nostrand Co., Inc., New York, NY, and the “United States
Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 09.01. Pharmacopeia.”
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959, United States.
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn. Contact ASTM
International (www.astm.org) for the latest information.
D3037–93
the weight. This precaution will minimize inaccuracies due to 7.5.2 Reproducibility—The reproducibility, (R), of the ni-
adsorbed water and other materials. trogen surface area adsorption has been established as 4.59%.
Twosingletestresults(ordeterminations)producedinseparate
6. Sampling
laboratoriesthatdifferbymorethan4.59%mustbeconsidered
as suspect and dictates that appropriate investigation or
6.1 Samples shall be taken in accordance with Practice
technical/commercial actions be taken.
D1799 or D1900.
7.6 Bias—In test method terminology, bias is the difference
7. Precision and Bias between an average test value and the reference (true) test
property value. Reference values do not exist for these test
7.1 Thisprecisionandbiashasbeenpreparedinaccordance
methods since the value or level of the test property is
with Practice D4483. Refer to this practice for terminology
exclusively defined by these test methods. Bias, therefore,
and other statistical details.
cannot be determined.
7.2 The precision results in this precision and bias give an
estimate of the precision as described below. The precision
8. Keywords
parameters should not be used for acceptance/rejection testing
8.1 carbon black; continuous flow chromatography; sur-
of any group of materials without documentation stating that
face area analyzer; surface area by nitrogen absorption
theyareapplicabletothoseparticularmaterialsandthespecific
testing protocols that include this test method.
TEST METHOD A—SURFACE AREA BY
7.3 A Type 1 interlaboratory precision program was con-
NI-COUNT-1 APPARATUS
ducted. Both repeatability and reproducibility represent short
term testing conditions. Six laboratories tested the six standard
9. Apparatus
reference blacks (A4 to F4) twice on each of two different
9.1 Ni-Count-1 Specific Surface Area Apparatus (Fig. 1,
days. Therefore, p=6, q =6, and n =4. A test result is the
value obtained from a single determination.Acceptable differ- Fig. 2, and Fig. 3), or an equivalent one-point adsorption
apparatus. (See Fig. 4 for installation diagram.)
ence values were not measured.
7.4 The results of the precision calculations are given in 9.2 Heater and Voltage Control Device, to maintain a
temperature of 300 6 10°C for degassing the samples. The
Table 1 with the materials arranged in ascending mean level
order of the surface area by nitrogen adsorption. heater (Fig. 1) is furnished with the Ni-Count-1 apparatus.
9.3 Vacuum Pump, capable of ultimate pressure of 1.3 Pa
7.5 The precision for the pooled values for surface area by
−2
nitrogen adsorption may be expressed as follows: (1 310 mm Hg abs).
9.4 Dewar Flask,265-cm capacity,approximately145mm
7.5.1 Repeatability—The repeatability, (r), of the nitrogen
surface area adsorption has been established as 1.62%. Two high (supplied with the Ni-Count-1 apparatus).
9.5 Nitrogen Vapor Pressure Thermometer, a part of the
single test results (or determinations) that differ by more than
Ni-Count-1 apparatus (Fig. 2).
1.62% must be considered suspect and dictates that some
9.6 Sample Tubes (Fig. 5).
appropriate investigative action be taken.
The Ni-Count-1 is developed by Phillips Petroleum Co. and is available from
Supporting data are available from ASTM Headquarters. Request RR:
Chandler Engineering Co., 7707 E. 38th St., Tulsa, OK.
D24–1021.
A
TABLE 1 Precision Values—Type 1
NOTE 1—Symbols are defined as follows:
Sr =within laboratory standard deviation,
r =repeatability, measurement units
(r) =repeatability,%
SR =between laboratory standard deviation,
R =reproducibility, measurement units
(R) =repeatability, %
B B
Within Laboratories Between Laboratories
Mean Level,
Material
3 2 2
10 m /kg (m /g)
Sr r (r) SR R (R)
D-4 (N 762) 24.31 0.123 0.349 1.452 0.343 0.971 4.046
E-4 (N 660) 34.85 0.270 0.764 2.193 0.579 1.638 4.700
F-4 (N 683) 38.62 0.205 0.580 1.502 0.707 2.000 5.180
B-4 (N 330) 75.40 0.529 1.498 1.997 0.770 2.180 2.906
A-4 (N 326) 77.83 0.263 0.744 0.956 0.586 1.660 2.133
C-4 (N 121) 126.61 0.547 1.549 1.223 2.091 5.917 4.673
Pooled or Aver- 62.94 0.36 1.02 1.62 1.02 2.89 4.59
aged Values
A
This is short-term precision (days) where: p=6, q = 6, and n=4.
B
Report repeatability and reproducibility in percent.
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn. Contact ASTM
International (www.astm.org) for the latest information.
D3037–93
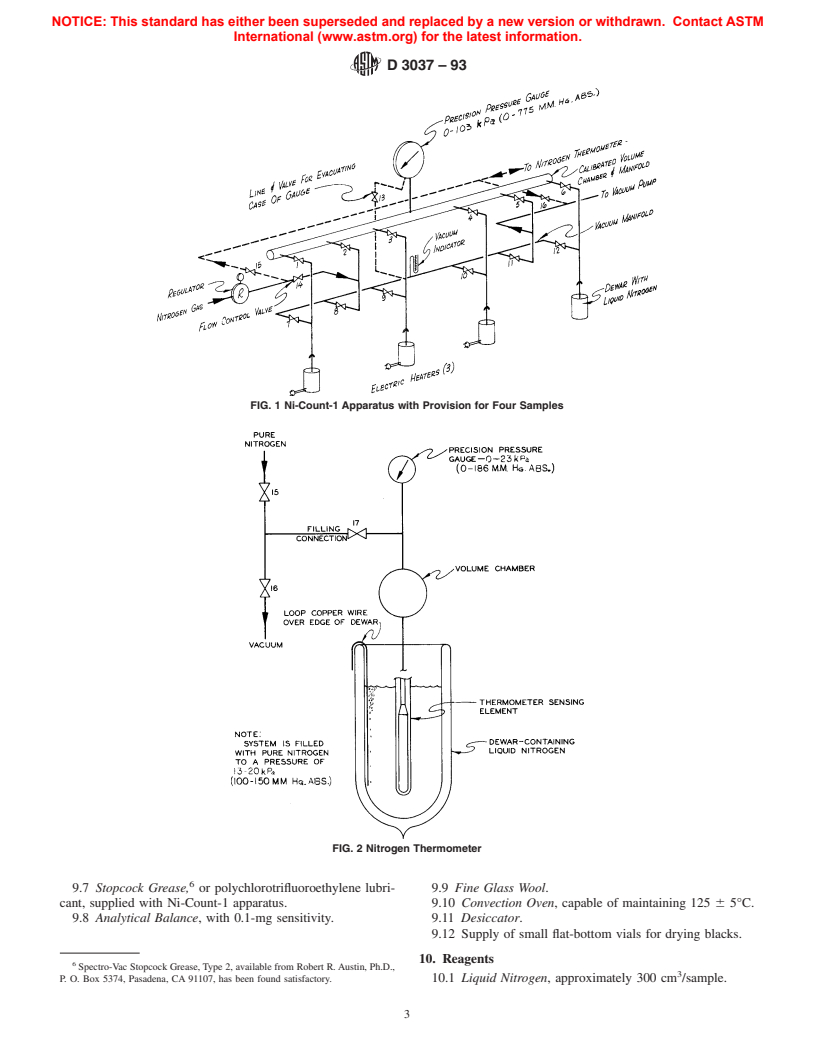
FIG. 1 Ni-Count-1 Apparatus with Provision for Four Samples
FIG. 2 Nitrogen Thermometer
9.7 Stopcock Grease, or polychlorotrifluoroethylene lubri- 9.9 Fine Glass Wool.
cant, supplied with Ni-Count-1 apparatus. 9.10 Convection Oven, capable of maintaining 125 6 5°C.
9.8 Analytical Balance, with 0.1-mg sensitivity. 9.11 Desiccator.
9.12 Supply of small flat-bottom vials for drying blacks.
10. Reagents
Spectro-Vac Stopcock Grease, Type 2, available from Robert R.Austin, Ph.D.,
P. O. Box 5374, Pasadena, CA 91107, has been found satisfactory. 10.1 Liquid Nitrogen, approximately 300 cm /sample.
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn. Contact ASTM
International (www.astm.org) for the latest information.
D3037–93
FIG. 3 Ni-Count-1 Apparatus
FIG. 4 Installation of the Surface Area Apparatus
10.2 Nitrogen Gas, cylinder or other source of prepurified lines to the sample valve, and the volume in the bellows of the
nitrogen gas.
pressure gage so positioned that the gage indicates 66.7 kPa
(500 mm Hg abs pressure). The tables of surface area versus
11. Preparation and Calibration of Apparatus
pressure furnished with the Ni-Count-1 will yield accurate
specific surface areas, if the internal volume of the instrument
11.1 The all metal Ni-Count-1 apparatus has an adjusted
3 3
internalvolumeof139.5cm .Thisinternalvolumeincludesall has been accurately adjusted at the factory to 139.5 cm .
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn. Contact ASTM
International (www.astm.org) for the latest information.
D3037–93
ReferenceBlack(onewhichisareasonablesurfaceareamatch
for the sample blacks to be run). Proceed in accordance with
instructions, skipping 12.1.1 and substituting the word “stan-
dard” for the word “sample” in 12.2-14.1.2.
12.1.1 Using the data in Table 2 as a guide, select a sample
tube and fill it with the suggested mass of pre-dried black. If
the identity of the black is not known, make a preliminary run
to determine the mass of black to give an adsorption pressure
between 20.0 and 33.3 kPa (150 and 250 mm Hg abs).
12.2 Prepare a tuft of glass wool of suitable size to support
the filler tube in the sample tube stem. Record the mass to 0.1
mg.
12.3 Prepareacleandrysampletubewithitsfillerandglass
wool tuft. Record the mass to 0.1 mg.
12.4 Roughly weigh the amount of sample to be placed in
the sample tube. (This mass will not be used.)
12.5 Placethesampleinthetube,introducethetuftofglass
wool, and shove in the filler rod to its proper position.
12.6 Lubricate the ball joint of the sample tube sparingly
with high-vacuum grease, taking care not to place lubricant
inside the stem. Wring the sample tube ball into the mating
metal receptacle on the Ni-Count-1 apparatus and retain the
sample tube in place with the metal spring clip.
12.7 Start the evacuation of the sample tube and raise the
heater into place around the tube.
12.8 Several times during the evacuation, purge the sample
FIG. 5 Loading Funnel and Glass Sample Tube
momentarily with the nitrogen gas.
12.9 Close the vacuum valve and observe the leak detector
Checking the ASTM D-24 Standard Reference Blacks, pre-
to determine whether gases are still evolving from the sample.
sentedinPracticeD3324,isanessentialsteptoconfirminitial
When the sample is properly degassed, the leak indicator
instrument calibration and is required each time a set of
should not show a change of pressure greater than 0.1 kPa (1
samples is to be run, as described in Section 12.
mm Hg) in 5 min.
11.2 TheNi-Count-1apparatusshouldbepreparedasspeci-
12.10 Isolate the degassed sample from the vacuum mani-
fied in the instructions furnished with the apparatus. This
fold by closing the valve. Remove the heater.
includes filling the vapor pressure thermometer with prepuri-
12.11 Fill the purged reservoir, gage, and manifold with
fiednitrogengas,evacuatingthecaseofthelargepressuregage
nitrogengasto66.6kPa(500mmHgabspressure),iftheroom
and closing the case valve, flushing the reservoir and vacuum
temperature is 27°C. If the room temperature is not 27°C, add
manifolds with nitrogen several times until any air is elimi-
0.222 kPa (1.67 mm Hg) pressure for each degree C above
nated, and setting the voltage on the heaters to maintain a
27°C.Subtractthecorrectionifthetemperatureisbelow27°C.
temperatureof300 610°Casmeasuredwithathermometerin
12.12 Open the valve to the sample tube from the reservoir
the heater well.
and gage.
12.13 Place the Dewar flask filled with liquid nitrogen
12. Procedure
around the sample tube.
12.1 In order to standardize results, use the data in Table 2
12.14 Permit the adsorption to proceed until the pressure
as a guide, select a sample tube, and place in it the suggested
becomes constant. Observe and record the pressure to the
weight of the appropriate pre-dried (see 5.2) D-24 Standard
nearest 1 mm Hg (see 12.9).
12.15 Lower the Dewar flask of liquid nitrogen away from
TABLE 2 Recommended Sample Tube Volumes and Sample
the sample tube and place it around the sensing element of the
Masses for Common Grades of Pressed and Pelleted Carbon
nitrogen thermometer.
Blacks
12.16 Observe the pressure gage on the nitrogen thermom-
Approximate
Tube Volume
ASTM Sample
Surface
eter and record the pressure to the nearest 0.1 kPa (1 mm Hg).
Series No. Mass, g
3 3
Pressed, cm Pelleted, cm
Area, m /g
12.17 Allow the sample tube to warm up above the tem-
N-900 20to6 15to30 10to25 10to15
perature of water vapor condensation on the tube. A heat gun
N-600 30 22 11 5.3
may be used to hasten the warming process.
N-500 44 18 9 3.6
N-300 80 10 5.5 2.0
12.18 Add nitrogen gas to the reservoir and sample tube
N-200 110 7.5 4.5 1.5
until the pressure gage reads approximately 1.3 kPa (10 mm
N-100 140 5.0 3.5 1.1
Hg) above the barometric pressure.
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a n
...







Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.