ASTM D7667-21
(Test Method)Standard Test Method for Determination of Corrosiveness to Silver by Automotive Spark-Ignition Engine Fuel—Thin Silver Strip Method
Standard Test Method for Determination of Corrosiveness to Silver by Automotive Spark-Ignition Engine Fuel—Thin Silver Strip Method
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
5.1 Crude petroleum contains sulfur compounds, most of which are removed during refining. However, of the sulfur compounds remaining in the petroleum product or introduced into the fuel during storage and distribution, some can have a corroding action on various metals and this corrosivity is not necessarily related directly to the total sulfur content. The effect can vary according to the chemical types of sulfur compounds present. The silver strip corrosion test is designed to assess the relative degree of corrosivity of a petroleum product towards silver and silver alloys.
5.2 Under some circumstances, reactive sulfur compounds present in automotive spark-ignition engine fuels can tarnish or even corrode silver alloy fuel gauge in-tank sender units or silver-plated bearings (in 2-stroke cycle engines). To minimize or prevent the failure of silver alloy in-tank sender units by tarnish or corrosion, Specification D4814 requires that fuels shall pass a silver strip corrosion test.
SCOPE
1.1 This test method covers the determination of the corrosiveness to silver by automotive spark-ignition engine fuel (for example, gasoline), as defined by Specification D4814 or similar specifications in other jurisdictions, having a vapor pressure no greater than 124 kPa (18 psi) at 37.8 °C (100 °F) by one of two procedures.
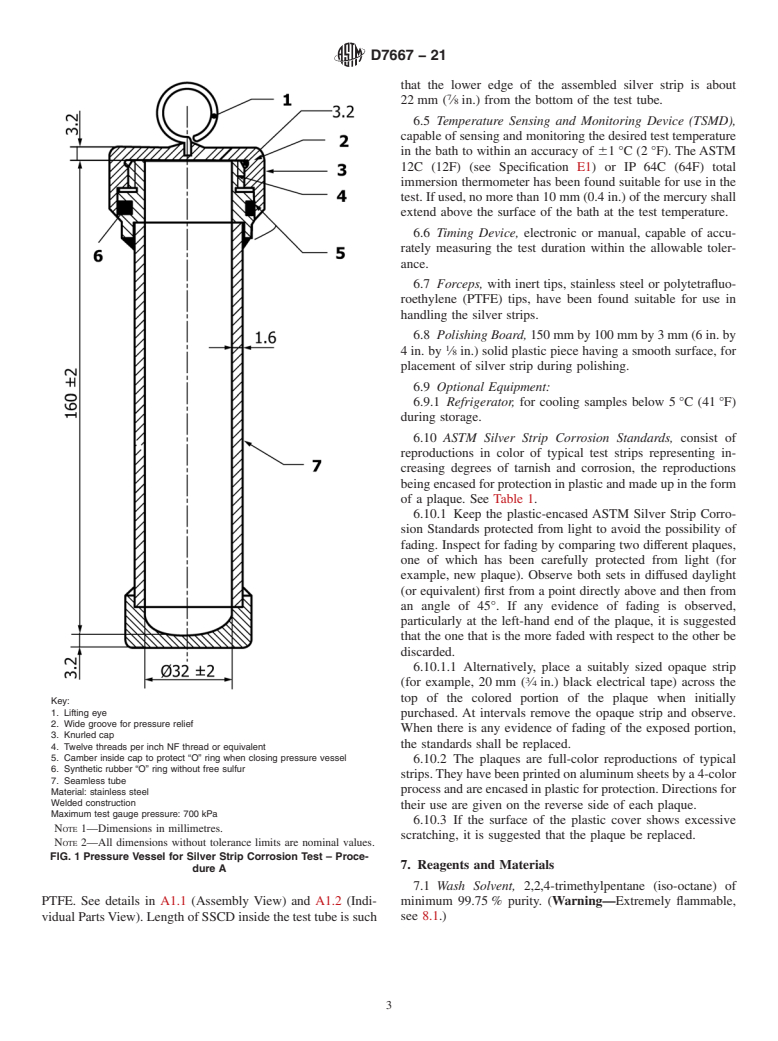
1.1.1 Procedure A—Involves the use of a pressure vessel.
1.1.2 Procedure B—Involves the use of a vented test tube.
1.2 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as the standard. The values in parentheses are for information only.
1.3 WARNING—Mercury has been designated by many regulatory agencies as a hazardous substance that can cause serious medical issues. Mercury, or its vapor, has been demonstrated to be hazardous to health and corrosive to materials. Use caution when handling mercury and mercury-containing products. See the applicable product Safety Data Sheet (SDS) for additional information. The potential exists that selling mercury or mercury-containing products, or both, is prohibited by local or national law. Users must determine legality of sales in their location.
1.4 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety, health, and environmental practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
1.5 This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization established in the Decision on Principles for the Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
General Information
Relations
Buy Standard
Standards Content (Sample)
This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization established in the Decision on Principles for the
Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
Designation: D7667 − 21
Standard Test Method for
Determination of Corrosiveness to Silver by Automotive
1
Spark-Ignition Engine Fuel—Thin Silver Strip Method
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D7667; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope* 2. Referenced Documents
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
1.1 This test method covers the determination of the corro-
D130 Test Method for Corrosiveness to Copper from Petro-
siveness to silver by automotive spark-ignition engine fuel (for
leum Products by Copper Strip Test
example, gasoline), as defined by Specification D4814 or
D3241 Test Method for Thermal Oxidation Stability of
similar specifications in other jurisdictions, having a vapor
Aviation Turbine Fuels
pressure no greater than 124 kPa (18 psi) at 37.8 °C (100 °F)
D4057 Practice for Manual Sampling of Petroleum and
by one of two procedures.
Petroleum Products
1.1.1 Procedure A—Involves the use of a pressure vessel.
D4177 Practice for Automatic Sampling of Petroleum and
1.1.2 Procedure B—Involves the use of a vented test tube.
Petroleum Products
D4814 Specification for Automotive Spark-Ignition Engine
1.2 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as the
Fuel
standard. The values in parentheses are for information only.
E1 Specification for ASTM Liquid-in-Glass Thermometers
3
1.3 WARNING—Mercury has been designated by many
2.2 Energy Institute Standards:
regulatory agencies as a hazardous substance that can cause
IP 227 Determination of Corrosiveness to Silver ofAviation
serious medical issues. Mercury, or its vapor, has been dem-
Turbine Fuels - Silver Strip Method
4
onstrated to be hazardous to health and corrosive to materials.
2.3 ASTM Adjuncts:
Use caution when handling mercury and mercury-containing
Color standard for tube deposit rating (5 aluminum strips)
products. See the applicable product Safety Data Sheet (SDS)
for additional information. The potential exists that selling
3. Terminology
mercury or mercury-containing products, or both, is prohibited
3.1 Abbreviations:
by local or national law. Users must determine legality of sales
3.1.1 PTFE—polytetrafluoroethylene
in their location.
3.1.2 PV—pressure vessel
1.4 This standard does not purport to address all of the
3.1.3 PVP—pressure vessel procedure
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
3.1.4 SSCD—silver strip centering device
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
3.1.5 TSMD—temperature sensing and monitoring device
priate safety, health, and environmental practices and deter-
mine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use. 3.1.6 VTTP—vented test tube procedure
1.5 This international standard was developed in accor-
4. Summary of Test Method
dance with internationally recognized principles on standard-
ization established in the Decision on Principles for the 4.1 Apolished, thin silver strip is immersed in 30 mLof the
sample being tested, and heated at 50 °C (122 °F) for 2 h. At
Development of International Standards, Guides and Recom-
the end of the heating period, the silver strip is removed,
mendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical
Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
2
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
1
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D02 on Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on
Petroleum Products, Liquid Fuels, and Lubricants and is the direct responsibility of the ASTM website.
3
SubcommitteeD02.05onPropertiesofFuels,PetroleumCokeandCarbonMaterial. Available from Energy Institute, 61 New Cavendish St., London, WIG 7AR,
Current edition approved Nov. 1, 2021. Published December 2021. Originally U.K., http://www.energyinst.org.uk.
4
approved in 2010. Last previous edition approved in 2015 as D7667 – 10 (2015). Available from ASTM International Headquarters. Order Adjunct No.
DOI: 10.1520/D7667-21. ADJD3241. Original adjunct produced in 1986.
*A Summary of Changes section appears at the end of this standard
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
D7667 − 21
washed, and the color and tarnish level assessed against the 6.3.1 Bath,shallbefittedwithsuitablesupportstoholdeach
...
This document is not an ASTM standard and is intended only to provide the user of an ASTM standard an indication of what changes have been made to the previous version. Because
it may not be technically possible to adequately depict all changes accurately, ASTM recommends that users consult prior editions as appropriate. In all cases only the current version
of the standard as published by ASTM is to be considered the official document.
Designation: D7667 − 10 (Reapproved 2015) D7667 − 21
Standard Test Method for
Determination of Corrosiveness to Silver by Automotive
1
Spark-Ignition Engine Fuel—Thin Silver Strip Method
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D7667; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope Scope*
1.1 This test method covers the determination of the corrosiveness to silver by automotive spark-ignition engine fuel (for example,
gasoline), as defined by Specification D4814 or similar specifications in other jurisdictions, having a vapor pressure no greater than
124 kPa (18 psi) at 37.8 °C (100 °F) by one of two procedures.
1.1.1 Procedure A—Involves the use of a pressure vessel.
1.1.2 Procedure B—Involves the use of a vented test tube.
1.2 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as the standard. The values in parentheses are for information only.
1.3 WARNING—Mercury has been designated by many regulatory agencies as a hazardous materialsubstance that can cause
central nervous system, kidney and liver damage. serious medical issues. Mercury, or its vapor, may has been demonstrated to be
hazardous to health and corrosive to materials. Caution should be taken Use caution when handling mercury and mercury
containing mercury-containing products. See the applicable product Material Safety Data Sheet (MSDS) for details and EPA’s
website—http://www.epa.gov/mercury/faq.htm—for additional information. Users should be aware (SDS) for additional informa-
tion. The potential exists that selling mercury and/or mercury containing products into your state or country may be prohibited by
law.or mercury-containing products, or both, is prohibited by local or national law. Users must determine legality of sales in their
location.
1.4 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility
of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety safety, health, and healthenvironmental practices and determine the
applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
1.5 This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization
established in the Decision on Principles for the Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued
by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
2. Referenced Documents
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
D130 Test Method for Corrosiveness to Copper from Petroleum Products by Copper Strip Test
1
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D02 on Petroleum Products, Liquid Fuels, and Lubricants and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee
D02.05 on Properties of Fuels, Petroleum Coke and Carbon Material.
Current edition approved Oct. 1, 2015Nov. 1, 2021. Published December 2015December 2021. Originally approved in 2010. Last previous edition approved in 20102015
ɛ2
as D7667 – 10 (2015). . DOI: 10.1520/D7667-10R15.10.1520/D7667-21.
2
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM Standards
volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on the ASTM website.
*A Summary of Changes section appears at the end of this standard
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
D7667 − 21
D3241 Test Method for Thermal Oxidation Stability of Aviation Turbine Fuels
D4057 Practice for Manual Sampling of Petroleum and Petroleum Products
D4177 Practice for Automatic Sampling of Petroleum and Petroleum Products
D4814 Specification for Automotive Spark-Ignition Engine Fuel
E1 Specification for ASTM Liquid-in-Glass Thermometers
3
2.2 Energy Institute Standards:
IP 227 Determination of Corrosiveness to Silver of Aviation Turbine Fuels - Silver Strip Method
4
2.3 ASTM Adjuncts:
Color standard for tube deposit rating (5 aluminum strips)
3. Terminology
3.1 Abbreviations:
PTFE = polytetrafluoroethylene
PV = pressure vessel
PVP = pressure vessel procedure
SSCD = silver strip centering device
TSMD = temperature sensing and monitoring device
VTTP = vented test tube procedure
3.1.1 PTFE—polytetrafluoroe
...










Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.