ASTM C927-80(2019)e1
(Test Method)Standard Test Method for Lead and Cadmium Extracted from the Lip and Rim Area of Glass Tumblers Externally Decorated with Ceramic Glass Enamels
Standard Test Method for Lead and Cadmium Extracted from the Lip and Rim Area of Glass Tumblers Externally Decorated with Ceramic Glass Enamels
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
5.1 The heavy metals, lead and cadmium, are known to cause serious health effects in man if consumed in excess. It is, therefore, important to measure the amount that may be extracted from an area of the glass drinking vessel in contact with the lip. Even though the amount of lead and cadmium extracted by this test method is in no way representative of the amount of the metals extracted by actual lip contact, the relative magnitude of metals extracted from one test specimen in relation to another test specimen provides an effective tool for discrimination.
SCOPE
1.1 This test method covers the determination of lead and cadmium extracted by acetic acid from the lip and rim area of glassware used for drinking and which is exteriorly decorated with ceramic glass enamels. The procedure of extraction may be expected to accelerate the release of lead and cadmium from the decorated area and to serve, therefore, as a severe test that is unlikely to be matched under the actual conditions of usage of such glassware. This test method is specific for lead and cadmium.
Note 1: For additional information see Test Method C738.
1.2 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as standard. No other units of measurement are included in this standard.
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety, health, and environmental practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
1.4 This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization established in the Decision on Principles for the Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
General Information
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization established in the Decision on Principles for the
Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
´1
Designation: C927 − 80 (Reapproved 2019)
Standard Test Method for
Lead and Cadmium Extracted from the Lip and Rim Area of
Glass Tumblers Externally Decorated with Ceramic Glass
Enamels
This standard is issued under the fixed designation C927; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
ε NOTE—Eq 1 and 2 were revised editorially in February 2019.
1. Scope 2. Referenced Documents
2.1 ASTM Standards:
1.1 This test method covers the determination of lead and
C738 Test Method for Lead and Cadmium Extracted from
cadmium extracted by acetic acid from the lip and rim area of
Glazed Ceramic Surfaces
glassware used for drinking and which is exteriorly decorated
with ceramic glass enamels. The procedure of extraction may
3. Terminology
beexpectedtoacceleratethereleaseofleadandcadmiumfrom
3.1 Definitions:
the decorated area and to serve, therefore, as a severe test that
3.1.1 ceramic glass decorations—ceramic glass enamels
is unlikely to be matched under the actual conditions of usage
fused to glassware at temperatures above 425°C (800°F) to
of such glassware. This test method is specific for lead and
produce a decoration.
cadmium.
3.1.2 ceramic glass enamels (also ceramic enamels or glass
NOTE 1—For additional information see Test Method C738.
enamels)—predominately colored, silicate glass fluxes used to
decorate glassware.
1.2 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as
standard. No other units of measurement are included in this
3.1.3 lip and rim area—that part of a drinking vessel which
standard.
extends 20 mm below the rim on the outside of the specimen.
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the
4. Summary of Test Method
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
4.1 Lead and cadmium are extracted from the lip and rim
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
area of the article under test by leaching with a 4 % acetic acid
priate safety, health, and environmental practices and deter-
solution at 20 to 24°C (68 to 75°F) for 24 h and are measured
mine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
by atomic absorption spectrophotometry using specific hollow
1.4 This international standard was developed in accor-
cathode or electrodeless discharge lamps for lead and cadmium
dance with internationally recognized principles on standard-
respectively. Results are reported as micrograms per millilitre
ization established in the Decision on Principles for the
(ppm) extracted relative to the internal volume of the glass
Development of International Standards, Guides and Recom-
article.
mendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical
Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
5. Significance and Use
5.1 The heavy metals, lead and cadmium, are known to
cause serious health effects in man if consumed in excess. It is,
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee C14 on Glass
therefore, important to measure the amount that may be
and Glass Products and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee C14.10 on
extracted from an area of the glass drinking vessel in contact
Glass Decoration. It was developed jointly byASTM Committee C-14 and C-21 on
Ceramic Whitewares and Related Products, the Society of Glass Decorators A-20
Subcommittee on Ceramic Enameled Decorated Glass Tumblers, and an Inter-
agency Task Force consisting of FDA, EPA, and CPSC of the U.S. Government. For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
Current edition approved Feb. 1, 2019. Published February 2019. Originally contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
approved in 1980. Last previous edition approved in 2014 as C927 – 80 (2014). Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on
DOI: 10.1520/C0927-80R19E01. the ASTM website.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
´1
C927 − 80 (2019)
with the lip. Even though the amount of lead and cadmium 8.4 Cadmium Standard Stock Solution (1000 µg/mL of
extracted by this test method is in no way representative of the cadmium)—Dissolve 0.9273 g of anhydrous cadmium sulfate
amount of the metals extracted by actual lip contact, the in 250 mL of 1 % HCl (8.6) and dilute to 500 mL with 1 %
relative magnitude of metals extracted from one test specimen HCl. Commercially available standard cadmium solutions may
in relation to another test specimen provides an effective tool also be used.
for discrimination.
8.5 Detergent Rinse—Add 2 mL of hand dishwashing de-
tergent to 1 L of lukewarm tap water.
6. Interferences
8.6 Hydrochloric Acid (1 weight %)—Mix 1 volume of
6.1 Since specific hollow cathode lamps or electrodeless
concentrated hydrochloric acid (HCl, sp gr 1.19) with 37
discharge lamps for lead and cadmium are used, there are no
volumes of water.
interferences.
8.7 Lead Standard Stock Solution (1000 µg/mL)—Dissolve
7. Apparatus
1.598 g of lead nitrate (Pb(NO ) ) in 4 % acetic acid and dilute
3 2
to 1 L with 4 % acetic acid. Commercially available standard
7.1 Atomic Absorption Spectrophotometer (AAS), equipped
lead solutions may also be used.
with a 102-mm single slot or Boling burner head and digital
concentration readout attachment (DCR) if available. This
9. Sampling
instrument should have a sensitivity of about 0.5 µg/mLof lead
9.1 Continuous Process—Since the amount of metal re-
for 1 % absorption and a sensitivity of about 0.025 µg/mL of
leased from a decoration can be affected by the firing
cadmium for 1 % absorption. Use the operating conditions as
conditions, which may not be uniform across the width of the
specified in the instrument manufacturer’s analytical methods
lehr, a minimum of six samples should be taken representing
manual.
both sides and the center of the lehr.
7.2 Hollow Cathode or Electrodeless Discharge Lead
9.2 Load or Pile—A minimum of six samples should be
Lamp, set at 283.3 nm.
randomly selected from throughout the load.
7.3 Hollow Cathode or Electrodeless Discharge Cadmium
10. Preparation of Standards
Lamp, set at 228.8 nm.
10.1 Lead Standard Working Solutions—Dilute lead nitrate
7.4 Glassware of chemically resistant borosilicate glass for
solution(8.7)withaceticacid(8.3)toobtainworkingstandards
use in preparing and storing reagents and solutions, and for use
having final lead concentrations of 0, 5, 10, 15, and 20 µg/mL.
as test specimen containers.
10.2 Cadmium Standard Working Solutions—Dilute cad-
7.5 Detection limits of lead and cadmium shall be deter-
mined and reported for individual instruments. In this test mium stock solution (8.4) with acetic acid (8.3) to obtain
working standards having final cadmium concentrations of 0.0,
method, the detection limit shall be defined as twice the mean
noise level at 0 µ
...







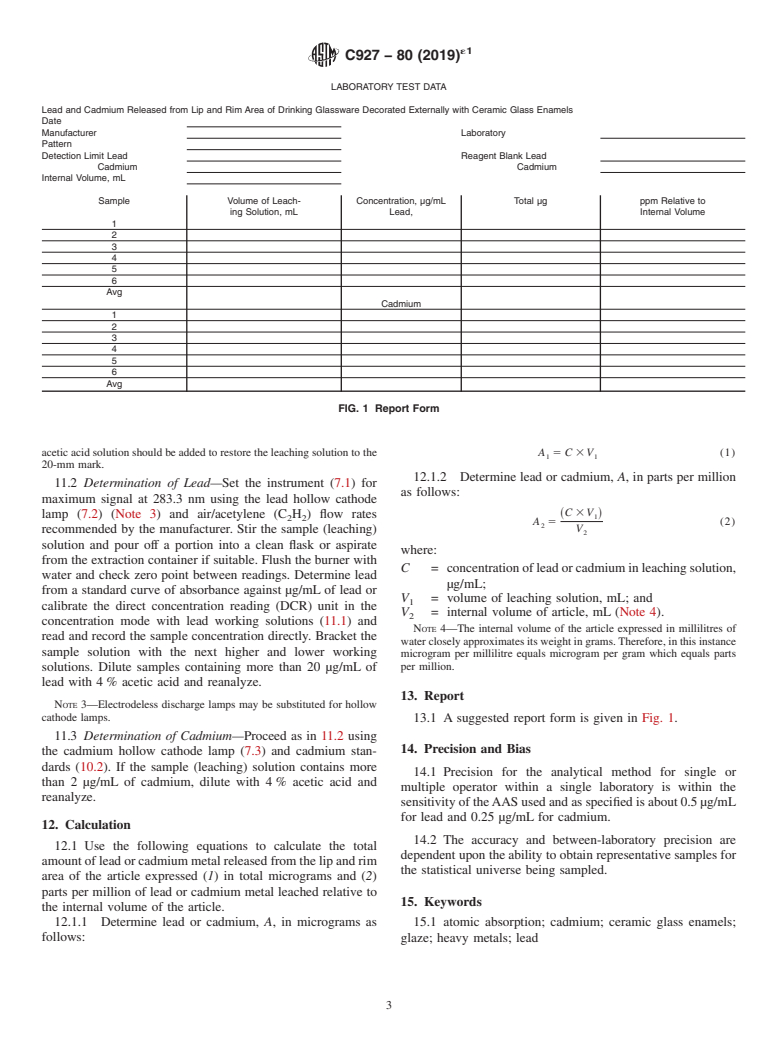
Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.