ASTM E1999-23
(Test Method)Standard Test Method for Analysis of Cast Iron by Spark Atomic Emission Spectrometry
Standard Test Method for Analysis of Cast Iron by Spark Atomic Emission Spectrometry
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
5.1 The chemical composition of cast iron alloys shall be determined accurately in order to ensure the desired metallurgical properties. This procedure is suitable for manufacturing control and inspection testing.
SCOPE
1.1 This test method covers the analysis of cast iron by spark atomic emission spectrometry for the following elements in the ranges shown (Note 1):
Ranges, %
Elements
Applicable Range, %
Quantitative Range, %A
Carbon
1.9 to 3.8
1.90 to 3.8
Chromium
0 to 2.0
0.025 to 2.0
Copper
0 to 0.75
0.015 to 0.75
Manganese
0 to 1.8
0.03 to 1.8
Molybdenum
0 to 1.2
0.01 to 1.2
Nickel
0 to 2.0
0.02 to 2.0
Phosphorus
0 to 0.4
0.005 to 0.4
Silicon
0 to 2.5
0.15 to 2.5
Sulfur
0 to 0.08
0.01 to 0.08
Tin
0 to 0.14
0.004 to 0.14
Titanium
0 to 0.12
0.003 to 0.12
Vanadium
0 to 0.22
0.008 to 0.22
Note 1: The ranges of the elements listed have been established through cooperative testing of reference materials. These ranges can be extended by the use of suitable reference materials.
1.2 This test method covers analysis of specimens having a diameter adequate to overlap the bore of the spark stand opening (to effect an argon seal). The specimen thickness should be sufficient to prevent overheating during excitation. A heat sink backing may be used. The maximum thickness is limited only by the height that the stand will permit.
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety, health, and environmental practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
1.4 This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization established in the Decision on Principles for the Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
General Information
Buy Standard
Standards Content (Sample)
This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization established in the Decision on Principles for the
Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
Designation: E1999 − 23
Standard Test Method for
Analysis of Cast Iron by Spark Atomic Emission
1
Spectrometry
This standard is issued under the fixed designation E1999; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope mendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical
Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
1.1 This test method covers the analysis of cast iron by
spark atomic emission spectrometry for the following elements
2. Referenced Documents
in the ranges shown (Note 1):
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
Ranges, %
A
E29 Practice for Using Significant Digits in Test Data to
Elements Applicable Range, % Quantitative Range, %
Determine Conformance with Specifications
Carbon 1.9 to 3.8 1.90 to 3.8
E135 Terminology Relating to Analytical Chemistry for
Chromium 0 to 2.0 0.025 to 2.0
Metals, Ores, and Related Materials
Copper 0 to 0.75 0.015 to 0.75
Manganese 0 to 1.8 0.03 to 1.8
E305 Practice for Establishing and Controlling Spark
Molybdenum 0 to 1.2 0.01 to 1.2
Atomic Emission Spectrochemical Analytical Curves
Nickel 0 to 2.0 0.02 to 2.0
E406 Practice for Using Controlled Atmospheres in Atomic
Phosphorus 0 to 0.4 0.005 to 0.4
Silicon 0 to 2.5 0.15 to 2.5
Emission Spectrometry
Sulfur 0 to 0.08 0.01 to 0.08
E826 Practice for Testing Homogeneity of a Metal Lot or
Tin 0 to 0.14 0.004 to 0.14
Titanium 0 to 0.12 0.003 to 0.12 Batch in Solid Form by Spark Atomic Emission Spec-
3
Vanadium 0 to 0.22 0.008 to 0.22
trometry (Withdrawn 2023)
E1329 Practice for Verification and Use of Control Charts in
A
Quantitative range as directed in Practice E1601.
3
Spectrochemical Analysis (Withdrawn 2019)
NOTE 1—The ranges of the elements listed have been established
E1601 Practice for Conducting an Interlaboratory Study to
through cooperative testing of reference materials. These ranges can be
Evaluate the Performance of an Analytical Method
extended by the use of suitable reference materials.
E1763 Guide for Interpretation and Use of Results from
1.2 This test method covers analysis of specimens having a
Interlaboratory Testing of Chemical Analysis Methods
3
diameter adequate to overlap the bore of the spark stand
(Withdrawn 2015)
opening (to effect an argon seal). The specimen thickness
E1806 Practice for Sampling Steel and Iron for Determina-
should be sufficient to prevent overheating during excitation. A
tion of Chemical Composition
heat sink backing may be used. The maximum thickness is
E2972 Guide for Production, Testing, and Value Assignment
limited only by the height that the stand will permit.
of In-House Reference Materials for Metals, Ores, and
Other Related Materials
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
2.2 Other Documents:
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro- MNL 7 Manual on Presentation of Data and Control Chart
4
priate safety, health, and environmental practices and deter-
Analysis
mine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
3. Terminology
1.4 This international standard was developed in accor-
dance with internationally recognized principles on standard-
3.1 Definitions—For definitions of terms used in this test
ization established in the Decision on Principles for the
method, refer to Terminology E135.
Development of International Standards, Guides and Recom-
2
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
1
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee E01 on contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
Analytical Chemistry for Metals, Ores, and Related Materials and is the direct Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on
responsibility of Subcommittee E01.01 on Iron, Steel, and Ferroalloys. the ASTM website.
3
Current edition approved June 1, 2023. Published August 2023. Originally The last approved version of this historical standard is referenced on
approved in 1999. Last previous edition approved in 2018 as E1999 – 18. DOI: www.astm.org.
4
10.1520/E1999-23. ASTM Manual Series, ASTM International, 8th Edition, 2010.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
E1999 − 23
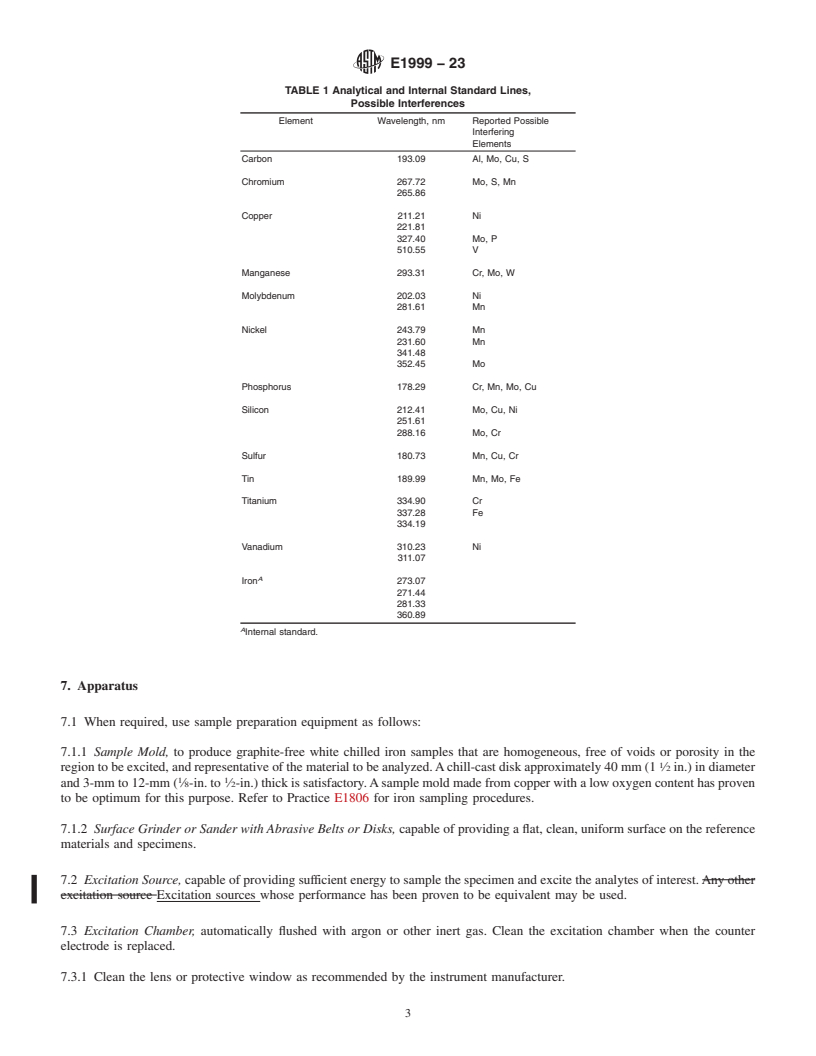
TABLE 1 Analytical and Internal Standard Lines,
4. Summary of Test Method
Possible Interferences
4.1 A capacitor disch
...
This document is not an ASTM standard and is intended only to provide the user of an ASTM standard an indication of what changes have been made to the previous version. Because
it may not be technically possible to adequately depict all changes accurately, ASTM recommends that users consult prior editions as appropriate. In all cases only the current version
of the standard as published by ASTM is to be considered the official document.
Designation: E1999 − 18 E1999 − 23
Standard Test Method for
Analysis of Cast Iron by Spark Atomic Emission
1
Spectrometry
This standard is issued under the fixed designation E1999; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope
1.1 This test method covers the analysis of cast iron by spark atomic emission spectrometry for the following elements in the
ranges shown (Note 1):
Ranges, %
A
Elements Applicable Range, % Quantitative Range, %
Carbon 1.9 to 3.8 1.90 to 3.8
Chromium 0 to 2.0 0.025 to 2.0
Copper 0 to 0.75 0.015 to 0.75
Manganese 0 to 1.8 0.03 to 1.8
Molybdenum 0 to 1.2 0.01 to 1.2
Nickel 0 to 2.0 0.02 to 2.0
Phosphorus 0 to 0.4 0.005 to 0.4
Silicon 0 to 2.5 0.15 to 2.5
Sulfur 0 to 0.08 0.01 to 0.08
Tin 0 to 0.14 0.004 to 0.14
Titanium 0 to 0.12 0.003 to 0.12
Vanadium 0 to 0.22 0.008 to 0.22
A
Quantitative range as directed in Practice E1601.
NOTE 1—The ranges of the elements listed have been established through cooperative testing of reference materials. These ranges can be extended by
the use of suitable reference materials.
1.2 This test method covers analysis of specimens having a diameter adequate to overlap the bore of the spark stand opening (to
effect an argon seal). The specimen thickness should be sufficient to prevent overheating during excitation. A heat sink backing
may be used. The maximum thickness is limited only by the height that the stand will permit.
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility
of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety, health, and environmental practices and determine the applicability of
regulatory limitations prior to use.
1.4 This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization
established in the Decision on Principles for the Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued
by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
1
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee E01 on Analytical Chemistry for Metals, Ores, and Related Materials and is the direct responsibility of
Subcommittee E01.01 on Iron, Steel, and Ferroalloys.
Current edition approved April 15, 2018June 1, 2023. Published June 2018August 2023. Originally approved in 1999. Last previous edition approved in 20112018 as
E1999 – 11.E1999 – 18. DOI: 10.1520/E1999-18.10.1520/E1999-23.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
E1999 − 23
2. Referenced Documents
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
E29 Practice for Using Significant Digits in Test Data to Determine Conformance with Specifications
E135 Terminology Relating to Analytical Chemistry for Metals, Ores, and Related Materials
E305 Practice for Establishing and Controlling Spark Atomic Emission Spectrochemical Analytical Curves
E406 Practice for Using Controlled Atmospheres in Atomic Emission Spectrometry
E826 Practice for Testing Homogeneity of a Metal Lot or Batch in Solid Form by Spark Atomic Emission Spectrometry
3
(Withdrawn 2023)
3
E1329 Practice for Verification and Use of Control Charts in Spectrochemical Analysis (Withdrawn 2019)
E1601 Practice for Conducting an Interlaboratory Study to Evaluate the Performance of an Analytical Method
E1763 Guide for Interpretation and Use of Results from Interlaboratory Testing of Chemical Analysis Methods (Withdrawn
3
2015)
E1806 Practice for Sampling Steel and Iron for Determination of Chemical Composition
E2972 Guide for Production, Testing, and Value Assignment of In-House Reference Materials for Metals, Ores, and Other
Related Materials
2.2 Other Documents:
4
MNL 7 Manual on Presentation of Data and Control Chart Analysis
3. Terminology
3.1 Definitions—For definitions of terms used in this test method, refer to Terminology E135.
4. Summary of Test Method
4.1 A capacitor discharge is produced between the flat, groundprepared surface of the disk specimen and a conically shaped
electrode. The discharge is terminated at a predetermined intensity of a selected iron line, or at a predetermined time, and the
relative radiant energies of the analytical lines are recorde
...









Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.