ASTM B956-10
(Specification)Standard Specification for Welded Copper and Copper-Alloy Condenser and Heat Exchanger Tubes with Integral Fins
Standard Specification for Welded Copper and Copper-Alloy Condenser and Heat Exchanger Tubes with Integral Fins
ABSTRACT
This specification establishes the requirements for forge-welded copper and copper alloy with integral fins for use in surface condenser, evaporator, and heat exchanger. The product shall be welded tube of one of the following Copper or Copper Alloy UNS Nos.: C12000, C12200, C19200, C23000, C44300, C44400, C44500, C68700, C70400, C70600, C70620, C71000, C71500, C71520, and C72200. The material heat identification or traceability shall be specified if required. The product shall be manufactured by cold forming to produce an integral enhanced surface for improved heat transfer and shall typically be furnished with unenhanced ends, but may be furnished with enhanced ends or stripped ends. Temper conditions (annealed, WO61 or light cold-worked, WC55) for the tubes and the enhanced and unenhanced sections of the tubes are given. The material shall conform to the chemical composition requirements prescribed for copper, tin, aluminum, nickel, cobalt, lead, iron, zinc, manganese, arsenic, antimony, phosphorus, chromium, and other elements such as carbon, sulfur, silicon, and titanium as determined by chemical analysis. Requirements for grain size, dimensions, mass, and mechanical properties including tensile strength and yield strength as determined by tension test are detailed. The performance requirements including expansion, flattening, and reverse bend tests; mercurous nitrate test or ammonia vapor test; and nondestructive tests such as eddy-current, hydrostatic, and pneumatic tests are detailed as well.
SCOPE
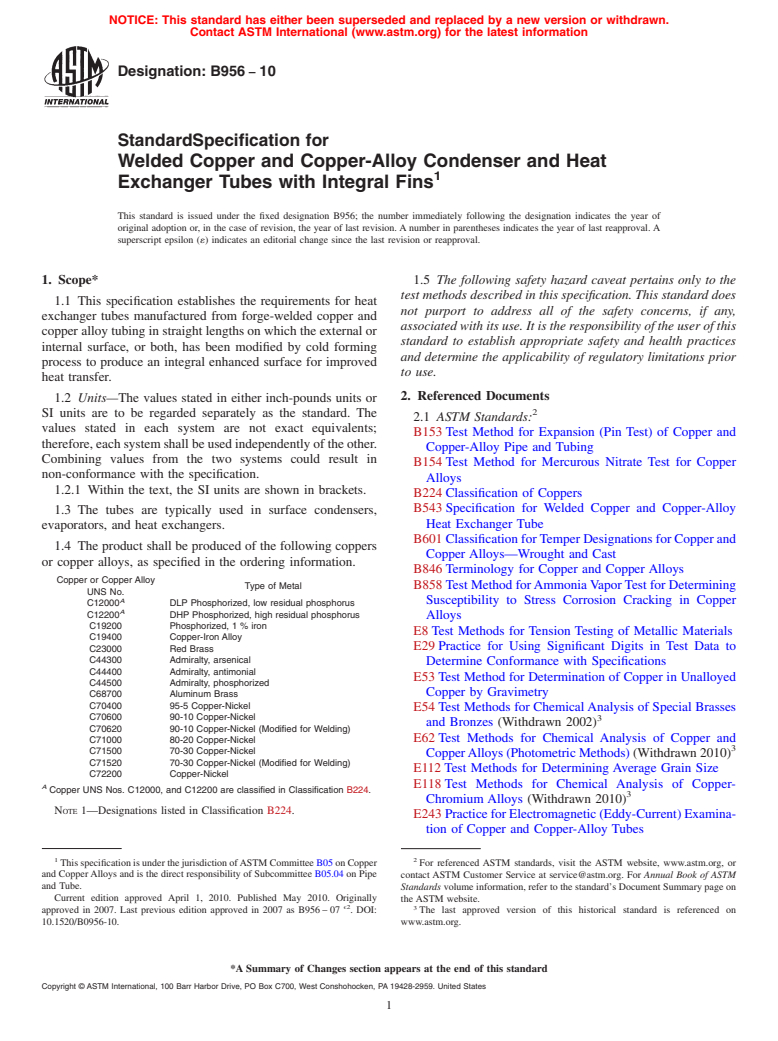
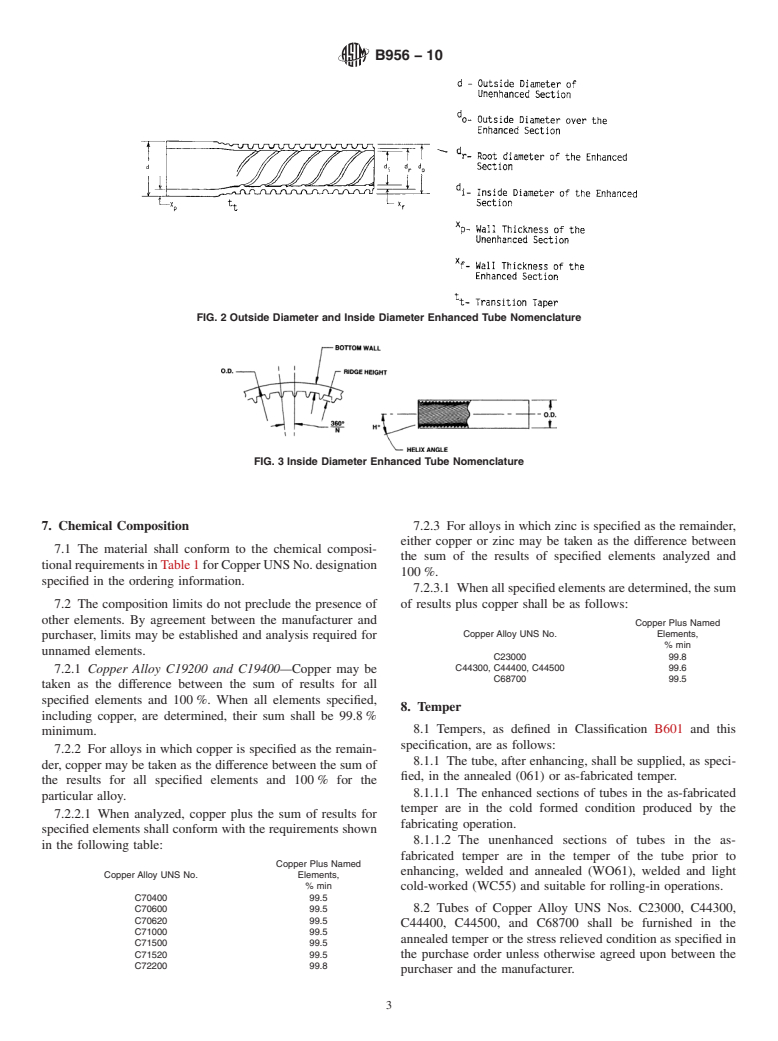
1.1 This specification establishes the requirements for heat exchanger tubes manufactured from forge-welded copper and copper alloy tubing in straight lengths on which the external or internal surface, or both, has been modified by cold forming process to produce an integral enhanced surface for improved heat transfer.
1.2 Units—The values stated in either inch-pounds units or SI units are to be regarded separately as the standard. The values stated in each system are not exact equivalents; therefore, each system shall be used independently of the other. Combining values from the two systems could result in non-conformance with the specification.
1.2.1 Within the text, the SI units are shown in brackets.
1.3 The tubes are typically used in surface condensers, evaporators, and heat exchangers.
General Information
Relations
Buy Standard
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Designation:B956 −10
StandardSpecification for
Welded Copper and Copper-Alloy Condenser and Heat
1
Exchanger Tubes with Integral Fins
This standard is issued under the fixed designation B956; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope* 1.5 The following safety hazard caveat pertains only to the
test methods described in this specification. This standard does
1.1 This specification establishes the requirements for heat
not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any,
exchanger tubes manufactured from forge-welded copper and
associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this
copper alloy tubing in straight lengths on which the external or
standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices
internal surface, or both, has been modified by cold forming
and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior
process to produce an integral enhanced surface for improved
to use.
heat transfer.
2. Referenced Documents
1.2 Units—The values stated in either inch-pounds units or
2
SI units are to be regarded separately as the standard. The
2.1 ASTM Standards:
values stated in each system are not exact equivalents;
B153 Test Method for Expansion (Pin Test) of Copper and
therefore,eachsystemshallbeusedindependentlyoftheother.
Copper-Alloy Pipe and Tubing
Combining values from the two systems could result in
B154 Test Method for Mercurous Nitrate Test for Copper
non-conformance with the specification.
Alloys
1.2.1 Within the text, the SI units are shown in brackets.
B224 Classification of Coppers
B543 Specification for Welded Copper and Copper-Alloy
1.3 The tubes are typically used in surface condensers,
Heat Exchanger Tube
evaporators, and heat exchangers.
B601 ClassificationforTemperDesignationsforCopperand
1.4 The product shall be produced of the following coppers
Copper Alloys—Wrought and Cast
or copper alloys, as specified in the ordering information.
B846 Terminology for Copper and Copper Alloys
Copper or Copper Alloy
Type of Metal B858 Test Method forAmmoniaVaporTest for Determining
UNS No.
A
Susceptibility to Stress Corrosion Cracking in Copper
C12000 DLP Phosphorized, low residual phosphorus
A
C12200 DHP Phosphorized, high residual phosphorus
Alloys
C19200 Phosphorized, 1 % iron
E8 Test Methods for Tension Testing of Metallic Materials
C19400 Copper-Iron Alloy
E29 Practice for Using Significant Digits in Test Data to
C23000 Red Brass
C44300 Admiralty, arsenical
Determine Conformance with Specifications
C44400 Admiralty, antimonial
E53 Test Method for Determination of Copper in Unalloyed
C44500 Admiralty, phosphorized
Copper by Gravimetry
C68700 Aluminum Brass
C70400 95-5 Copper-Nickel
E54 Test Methods for ChemicalAnalysis of Special Brasses
C70600 90-10 Copper-Nickel
3
and Bronzes (Withdrawn 2002)
C70620 90-10 Copper-Nickel (Modified for Welding)
E62 Test Methods for Chemical Analysis of Copper and
C71000 80-20 Copper-Nickel
3
C71500 70-30 Copper-Nickel
CopperAlloys(PhotometricMethods)(Withdrawn2010)
C71520 70-30 Copper-Nickel (Modified for Welding)
E112 Test Methods for Determining Average Grain Size
C72200 Copper-Nickel
E118 Test Methods for Chemical Analysis of Copper-
A
Copper UNS Nos. C12000, and C12200 are classified in Classification B224.
3
Chromium Alloys (Withdrawn 2010)
NOTE 1—Designations listed in Classification B224.
E243 PracticeforElectromagnetic(Eddy-Current)Examina-
tion of Copper and Copper-Alloy Tubes
1 2
ThisspecificationisunderthejurisdictionofASTMCommitteeB05onCopper For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
and CopperAlloys and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee B05.04 on Pipe contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
and Tube. Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on
Current edition approved April 1, 2010. Published May 2010. Originally the ASTM website.
ϵ2
3
approved in 2007. Last previous edition approved in 2007 as B956 – 07 . DOI: The last approved version of this historical standard is referenced on
10.1520/B0956-10. www.astm.org.
*A Summary of Changes section appears at the end of this standard
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
B956−10
E255 Practice for Sampling Copper and Copper Alloys for 5.2 The following options are available and shall be speci-
the Determination of Chemical Composition fied at the time placing the order, when required:
E478 Test Methods for ChemicalAnalysis of Co
...
This document is not anASTM standard and is intended only to provide the user of anASTM standard an indication of what changes have been made to the previous version. Because
it may not be technically possible to adequately depict all changes accurately, ASTM recommends that users consult prior editions as appropriate. In all cases only the current version
of the standard as published by ASTM is to be considered the official document.
´2
Designation:B956–07 Designation: B956 – 10
Standard Specification for
Welded Copper and Copper-Alloy Condenser and Heat
1
Exchanger Tubes with Integral Fins
This standard is issued under the fixed designation B956; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1
´ NOTE—Added table reference to Paragraph 5.2.4 in May 2008.
2
´ NOTE—Paragraph 8.3 editorially updated in December 2008.
1. Scope*
1.1 Thisspecificationestablishestherequirementsforheatexchangertubesmanufacturedfromforge-weldedcopperandcopper
alloy tubing in straight lengths on which the external or internal surface, or both, has been modified by cold forming process to
produce an integral enhanced surface for improved heat transfer.
1.2 Units—The values stated in either inch-pounds units or SI units are to be regarded separately as the standard. Within the
text, the SI units are shown in brackets. The values stated in each system are not exact equivalents; therefore, each system shall
beusedindependentlyoftheother.Combiningvaluesfromthetwosystemscouldresultinnon-conformancewiththespecification.
1.2.1 Within the text, the SI units are shown in brackets.
1.3 The tubes are typically used in surface condensers, evaporators, and heat exchangers.
1.4 The product shall be produced of the following coppers or copper alloys, as specified in the ordering information.
Copper or Copper Alloy
Type of Metal
UNS No.
A
C12000 DLP Phosphorized, low residual phosphorus
A
C12200 DHP Phosphorized, high residual phosphorus
C19200 Phosphorized, 1 % iron
C19400 Copper-Iron Alloy
C23000 Red Brass
C44300 Admiralty, arsenical
C44400 Admiralty, antimonial
C44500 Admiralty, phosphorized
C68700 Aluminum Brass
C70400 95-5 Copper-Nickel
C70600 90-10 Copper-Nickel
C70620 90-10 Copper-Nickel (Modified for Welding)
C71000 80-20 Copper-Nickel
C71500 70-30 Copper-Nickel
C71520 70-30 Copper-Nickel (Modified for Welding)
C72200 Copper-Nickel
A
Copper UNS Nos. C12000, and C12200 are classified in Classification B224.
NOTE 1—Designations listed in Classification B224.
1.5 The following safety hazard caveat pertains only to the test methods described in this specification. This standard does not
purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to
establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
2. Referenced Documents
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
B153 Test Method for Expansion (Pin Test) of Copper and Copper-Alloy Pipe and Tubing
B154 Test Method for Mercurous Nitrate Test for Copper Alloys
1
This specification is under the jurisdiction ofASTM Committee B05 on Copper and CopperAlloys and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee B05.04 on Pipe and
Tube.
Current edition approved Oct. 1, 2007. Published November 2007. DOI: 10.1520/B0956-07E02.
´2
Current edition approved April 1, 2010. Published May 2010. Originally approved in 2007. Last previous edition approved in 2007 as B956 – 07 . DOI:
10.1520/B0956-10.
2
For referencedASTM standards, visit theASTM website, www.astm.org, or contactASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM Standards
volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on the ASTM website.
*A Summary of Changes section appears at the end of this standard.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959, United States.
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
B956 – 10
B224 Classification of Coppers
B543 Specification for Welded Copper and Copper-Alloy Heat Exchanger Tube
B601 Classification for Temper Designations for Copper and Copper AlloysWrought and Cast
B846 Terminology for Copper and Copper Alloys
B858 Test Method for Ammonia Vapor Test for Determining Susceptibility to Stress Corrosion Cracking in Copper Alloys
E8 Test Methods for Tension Testing of Metallic Materials
E29 Practice for Using Significant Digits in Test Data to Determine Conformance with Specifications
E53 Test Method for Determination of Copper in Unalloyed Copper by Gravimetry
E54 Test Methods for Chemical Analysis of Special Brasses and Bronzes
E62 Test Methods for Chemical Analysis of Copper and Copper Alloys (Photometric Methods)
E112 Test Methods for Determining Av
...







Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.