ASTM C577-19
(Test Method)Standard Test Method for Permeability of Refractories
Standard Test Method for Permeability of Refractories
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
3.1 This test method is used to measure the rate of flow of air or nitrogen through refractory brick and monoliths and to thus determine the permeability of tested products.
3.2 This test method is useful in research and development for establishing the relative permeability of products within comparable classes. It may also be used to identify acceptable products for design purposes and to establish permeability criteria for specification acceptance.
3.3 It must be recognized that permeability can vary in different directions and different parts of a refractory due to factors such as forming procedure, grain size and distribution, and heat treatment.
SCOPE
1.1 This test method covers determination of the permeability of refractory brick and monoliths, from which suitable specimens can be cut, at room temperature.
1.2 Units—The values stated in inch-pound units are to be regarded as standard. The values given in parentheses are mathematical conversions to SI units that are provided for information only and are not considered standard.
1.2.1 Exceptions—The apparatus used in this standard is only available in SI units (Section 4). Also, some of the calculations must use SI units only.
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety, health, and environmental practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
1.4 This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization established in the Decision on Principles for the Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
General Information
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization established in the Decision on Principles for the
Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
Designation: C577 − 19
Standard Test Method for
1
Permeability of Refractories
This standard is issued under the fixed designation C577; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope 3.2 This test method is useful in research and development
for establishing the relative permeability of products within
1.1 This test method covers determination of the permeabil-
comparable classes. It may also be used to identify acceptable
ity of refractory brick and monoliths, from which suitable
products for design purposes and to establish permeability
specimens can be cut, at room temperature.
criteria for specification acceptance.
1.2 Units—The values stated in inch-pound units are to be
3.3 It must be recognized that permeability can vary in
regarded as standard. The values given in parentheses are
different directions and different parts of a refractory due to
mathematical conversions to SI units that are provided for
factors such as forming procedure, grain size and distribution,
information only and are not considered standard.
and heat treatment.
1.2.1 Exceptions—The apparatus used in this standard is
only available in SI units (Section 4). Also, some of the
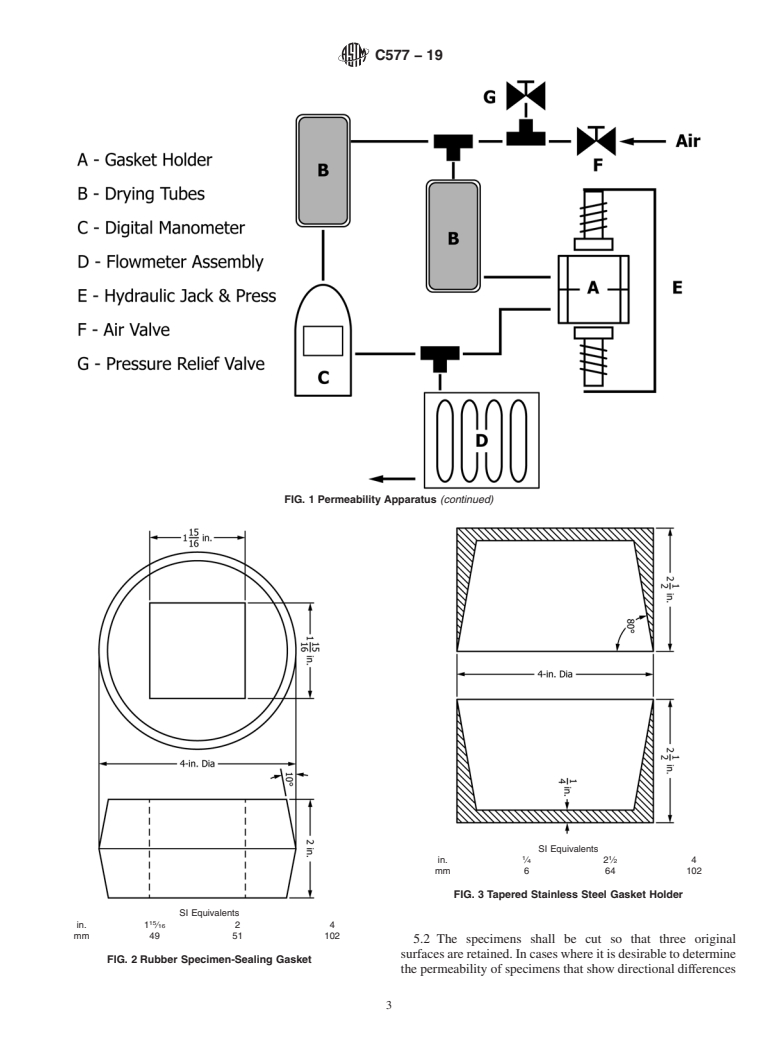
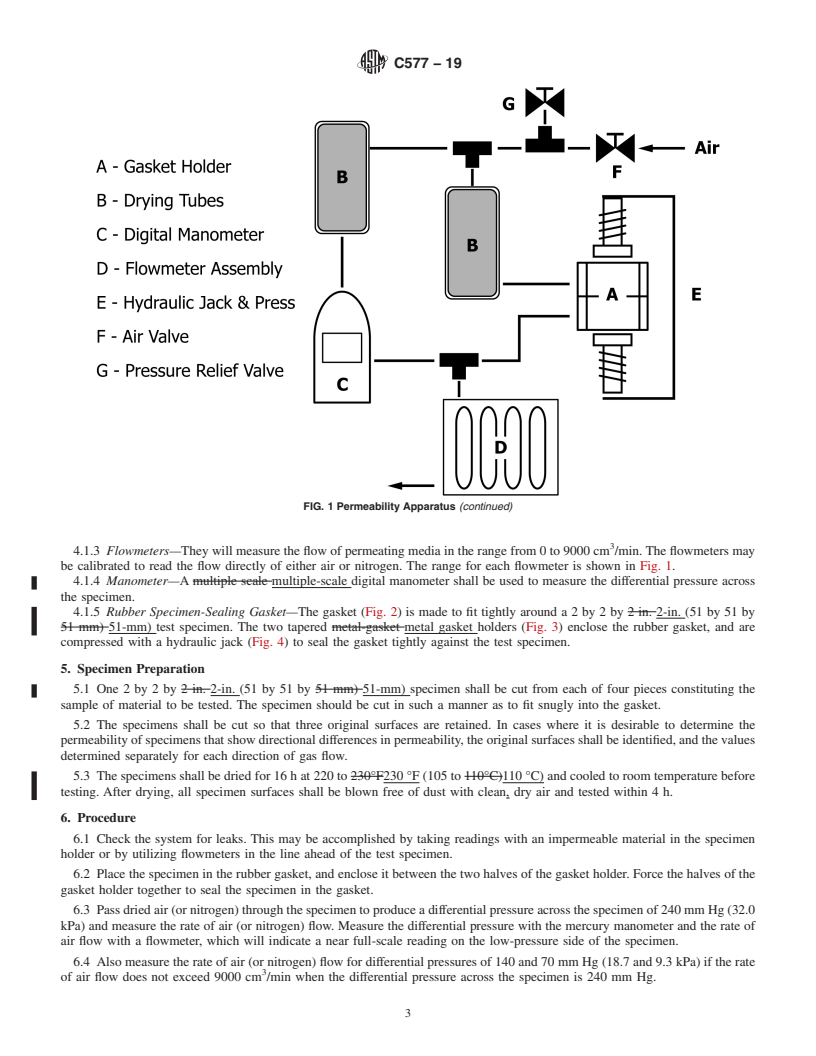
4. Apparatus
calculations must use SI units only.
4.1 The apparatus shall provide a leakproof system for
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the
testing 2-in. (51-mm) cubes held in a pressurized rubber
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
gasket, with means for controlling gas pressure and measuring
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
4
gas flow. Figs. 1-3 illustrate a suitable apparatus. The appa-
priate safety, health, and environmental practices and deter-
ratus consists of the following components:
mine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
4.1.1 Permeating Medium, air or nitrogen with regulator-
1.4 This international standard was developed in accor-
controlled inlet pressure.
dance with internationally recognized principles on standard-
4.1.2 Drier Tubes, each filled with a desiccant and strainer;
ization established in the Decision on Principles for the
used to remove any water or dirt from the gas before entering
Development of International Standards, Guides and Recom-
the flowmeters.
mendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical
4.1.3 Flowmeters—They will measure the flow of permeat-
Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
3
ing media in the range from 0 to 9000 cm /min. The flowme-
ters may be calibrated to read the flow directly of either air or
2. Referenced Documents
nitrogen. The range for each flowmeter is shown in Fig. 1.
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
4.1.4 Manometer—Amultiple-scale digital manometer shall
C1095 Practice for Calculating Precision Data on Refracto-
be used to measure the differential pressure across the speci-
ries (C08) From Interlaboratory Test Results (Withdrawn
men.
3
1998)
4.1.5 RubberSpecimen-SealingGasket—Thegasket(Fig.2)
3. Significance and Use is made to fit tightly arounda2by2by 2-in. (51 by 51 by
51-mm) test specimen. The two tapered metal gasket holders
3.1 This test method is used to measure the rate of flow of
(Fig. 3) enclose the rubber gasket, and are compressed with a
air or nitrogen through refractory brick and monoliths and to
hydraulic jack (Fig. 4) to seal the gasket tightly against the test
thus determine the permeability of tested products.
specimen.
1
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee C08 on
5. Specimen Preparation
Refractories and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee C08.03 on Physical
Properties.
5.1 One2by2by2-in.(51by51by51-mm)specimenshall
Current edition approved Nov. 1, 2019. Published December 2019. Originally
be cut from each of four pieces constituting the sample of
approved in 1965. Last previous edition approved in 2014 as C577 – 07 (2014).
material to be tested. The specimen should be cut in such a
DOI: 10.1520/C0577-19.
2
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
manner as to fit snugly into the gasket.
contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on
4
the ASTM website. The apparatus is described in Eusner, G. R., and Shapland, J. T., “Permeability
3
The last approved version of this historical standard is referenced on of Blast-Furnace Refractories,” Journal of the America
...
This document is not an ASTM standard and is intended only to provide the user of an ASTM standard an indication of what changes have been made to the previous version. Because
it may not be technically possible to adequately depict all changes accurately, ASTM recommends that users consult prior editions as appropriate. In all cases only the current version
of the standard as published by ASTM is to be considered the official document.
Designation: C577 − 07 (Reapproved 2014) C577 − 19
Standard Test Method for
1
Permeability of Refractories
This standard is issued under the fixed designation C577; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope
1.1 This test method covers determination of the permeability of refractory brick and monoliths, from which suitable specimens
can be cut, at room temperature.
1.2 Units—The values stated in inch-pound units are to be regarded as standard. The values given in parentheses are
mathematical conversions to SI units that are provided for information only and are not considered standard.
1.2.1 Exceptions—The apparatus used in this standard is only available in SI units (Section 4). Also, some of the calculations
must use SI units only.
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility
of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety safety, health, and healthenvironmental practices and determine the
applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
1.4 This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization
established in the Decision on Principles for the Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued
by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
2. Referenced Documents
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
3
C1095 Practice for Calculating Precision Data on Refractories (C08) From Interlaboratory Test Results (Withdrawn 1998)
3. Significance and Use
3.1 This test method is used to measure the rate of flow of air or nitrogen through refractory brick and monoliths and to thus
determine the permeability of tested products.
3.2 This test method is useful in research and development for establishing the relative permeability of products within
comparable classes. It may also be used to identify acceptable products for design purposes and to establish permeability criteria
for specification acceptance.
3.3 It must be recognized that permeability can vary in different directions and different parts of a refractory due to factors such
as forming procedure, grain size and distribution, and heat treatment.
4. Apparatus
4.1 The apparatus shall provide a leakproof system for testing 2 in. (51 mm) 2-in. (51-mm) cubes held in a pressurized rubber
4
gasket, with means for controlling gas pressure and measuring gas flow. Figs. 1-3 illustrate a suitable apparatus. The apparatus
consists of the following components:
4.1.1 Permeating Medium, air or nitrogen with regulator-controlled inlet pressure.
4.1.2 Drier Tubes, each filled with a desiccant and strainer; used to remove any water or dirt from the gas before entering the
flowmeters.
1
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee C08 on Refractories and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee C08.03 on Physical Properties.
Current edition approved March 1, 2014Nov. 1, 2019. Published March 2014December 2019. Originally approved in 1965. Last previous edition approved in 20072014
as C577 – 07.C577 – 07 (2014). DOI: 10.1520/C0577-07R14.10.1520/C0577-19.
2
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM Standards
volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on the ASTM website.
3
The last approved version of this historical standard is referenced on www.astm.org.
4
The apparatus is described in Eusner, G. R., and Shapland, J. T., “Permeability of Blast-Furnace Refractories,” Journal Am. Ceramic Soc.of the American Ceramic
Society, Vol.Vol 42, No. 10, 1959, pp. 459–464.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
C577 − 19
FIG. 1 Permeability Apparatus
2
---------------------- Page: 2 ----------------------
C577 − 19
FIG. 1 Permeability Apparatus (continued)
3
4.1.3 Flowmeters—They will measure the flow of permeating media in the range from 0 to 9000 cm /min. The flowmeters may
be calibrated to read the flow directly of either air or nitrogen. The range for each flowmeter is shown in Fig. 1.
4.1.4 Manometer—A multiple scal
...









Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.