ASTM E882-87(2003)
(Guide)Standard Guide for Accountability and Quality Control in the Chemical Analysis Laboratory
Standard Guide for Accountability and Quality Control in the Chemical Analysis Laboratory
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
An accountability and quality control system is established by laboratory management to improve the quality of its results. It provides documented records which serve to assure users of the laboratory’services that a specified level of precision is achieved in the routine performance of its measurements and that the data reported were obtained from the samples submitted. The system also provides for: early warning to analysts when methods or equipment begin to develop a bias or show deterioration of precision; the protection and retrievability of data (results); traceability and control of samples as they are processed through the laboratory; good communication of sample information between submitters, analysts, and supervision; and information on sample processing history. This guide describes such a system. Other accountability and quality control programs can be developed. Such programs can be equivalent to the program in this guide if they provide all of the benefits mentioned above.
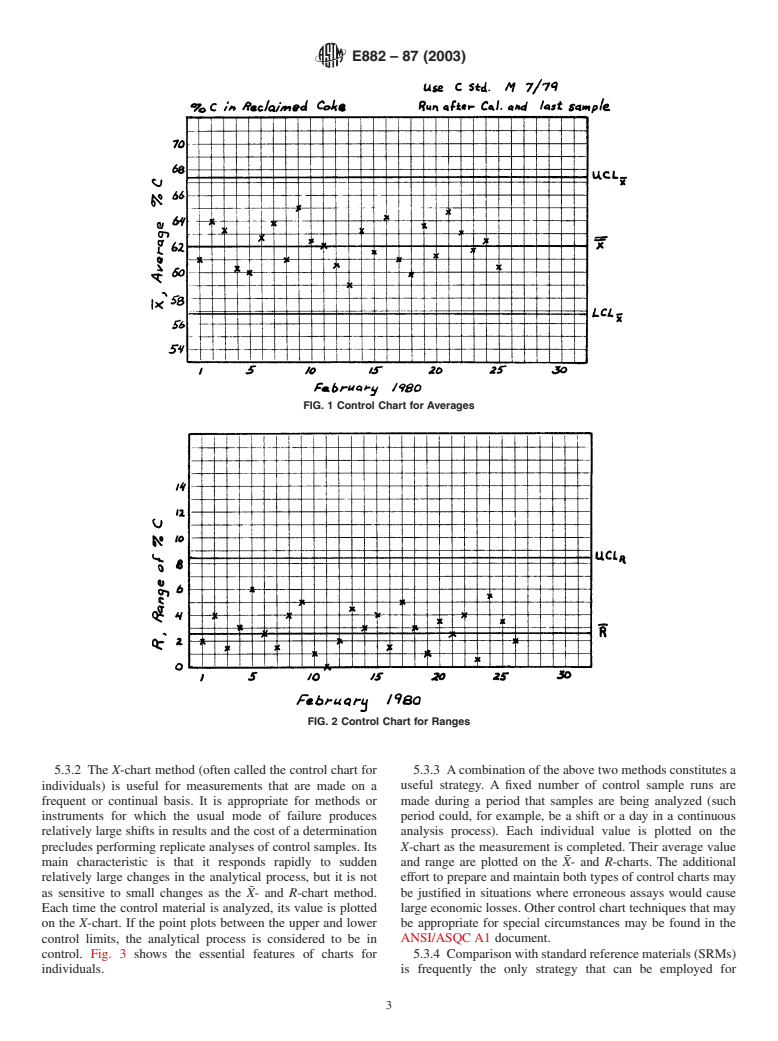
SCOPE
1.1 This guide covers the essential aspects of an accountability and quality control program for a chemical analysis laboratory. The reasons for establishing and operating such a program are discussed.
General Information
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Designation:E882–87 (Reapproved 2003)
Standard Guide for
Accountability and Quality Control in the Chemical
1
Analysis Laboratory
This standard is issued under the fixed designation E882; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope programs can be equivalent to the program in this guide if they
provide all of the benefits mentioned above.
1.1 This guide covers the essential aspects of an account-
ability and quality control program for a chemical analysis
4. Accountability
laboratory. The reasons for establishing and operating such a
4.1 Accountability means assurance that the results reported
program are discussed.
refer directly to the samples submitted.
2. Referenced Documents 4.2 Prior to submitting samples to the laboratory, the pro-
spective user should consult with laboratory personnel con-
2.1 ASTM Standards:
cerning his needs and the capability of the laboratory to satisfy
MNL 7 Manual on Presentation of Data and Control Chart
2
them. It is the responsibility of the originator of the samples to
Analysis
select and identify proper samples for submission to the
2.2 ANSI Document:
laboratory, to decide what information is required (especially,
ANSI/ASQC A1 Definitions, Symbols, Formulas, and
3
to define the use to be made of the information), and, after
Tables for Control Charts
consulting with laboratory personnel, to submit the samples in
3. Significance and Use suitable containers, properly labeled, and accompanied by
written instructions identifying the samples, their nature, and
3.1 An accountability and quality control system is estab-
the information sought through chemical analysis. This should
lished by laboratory management to improve the quality of its
be done formally, using a well-defined document for informa-
results. It provides documented records which serve to assure
tion transfer to initiate work in the laboratory.
users of the laboratory’s services that a specified level of
4.3 Laboratory management establishes a written account-
precision is achieved in the routine performance of its mea-
ability system to be used throughout the laboratory at all times.
surements and that the data reported were obtained from the
This implies traceability and documentation of all reported
samples submitted. The system also provides for: early warn-
results through the laboratory back to the submitted sample.
ing to analysts when methods or equipment begin to develop a
This system should have the following general characteristics:
bias or show deterioration of precision; the protection and
4.3.1 Each nonroutine job submitted by a user of the
retrievability of data (results); traceability and control of
laboratory’s services is assigned an internal laboratory identi-
samples as they are processed through the laboratory; good
fication number (ID), which is used to correlate all samples,
communication of sample information between submitters,
work, time and cost accounting, consultation, and reports and
analysts, and supervision; and information on sample process-
other paperwork associated with that job. The final report that
ing history.This guide describes such a system. Other account-
is returned to the originator will always bear the number (ID)
ability and quality control programs can be developed. Such
for future reference. Moreover, it is convenient for laboratory
data to be filed according to sequential ID numbers. For
example, “86/0428” might identify the associated work as the
1
This guide is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee E01 on Analytical
428th request submitted in the year 1986. The Data Record
Chemistry for Metals, Ores, and Related Materials and is the direct responsibility of
shouldprovidealldatageneratedduringtheanalyses,namesof
Subcommittee E01.22 on Laboratory Quality.
persons performing the analyses, dates the analyses were
Current edition approved Oct. 1, 2003. Published November 2003. Originally
approved in 1982. Last previous edition approved in 1998 as E882 – 98. DOI:
performed, and any unusual occurrences that happened during
10.1520/E0882-87R03.
the analyses. Accountability for production control samples is
2
ASTM Manual Series, ASTM, 6th Edition, 1990.
3
normally maintained separately from the nonroutine records
Available from American National Standards Institute (ANSI), 25 W. 43rd St.,
4th Floor, New York, NY 10036. because results from production control samples are usually
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959, United States.
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
E8
...







Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.