ASTM D3935-94
(Specification)Standard Specification for Polycarbonate (PC) Unfilled and Reinforced Material
Standard Specification for Polycarbonate (PC) Unfilled and Reinforced Material
SCOPE
1.1 This specification covers unfilled and reinforced polycarbonate and polycarbonate copolymer materials suitable for injection molding, blow molding, and extrusion. Some of these compositions may also find use for compression molding or application from solution.
1.2 The properties in this specification are those required for identifying the compositions covered. There may be other requirements necessary for identifying particular characteristics important to specific applications. Those may be specified by using the suffixes in accordance with Section 5.
1.3 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as the standard.
Note 1—This specification is similar to ISO 7391 - 1987 in title only. The technical content is significantly different.
1.4 The following hazards caveat pertains only to the test methods portion, Section 12, of this specification. This standard does not purport to address all safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability or regulatory limitations prior to use.
General Information
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or discontinued.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information.
Designation: D 3935 – 94 An American National Standard
Standard Specification for
Polycarbonate (PC) Unfilled and Reinforced Material
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D 3935; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (e) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope and Reinforced Plastics and Electrical Insulating Materi-
als
1.1 This specification covers unfilled and reinforced poly-
D 792 Test Method for Specific Gravity (Relative Density)
carbonate and polycarbonate copolymer materials suitable for
and Density of Plastics by Displacement
injection molding, blow molding, and extrusion. Some of these
D 883 Terminology Relating to Plastics
compositions may also find use for compression molding or
D 1238 Test Method for Flow Rates of Thermoplastics by
application from solution.
Extrusion Plastometer
1.2 This specification is not intended for the selection of
D 1600 Terminology for Abbreviated Terms Relating to
materials, but only as a means to call out plastic materials to be
Plastics
used for the manufacture of parts. The selection of these
D 1897 Practice for Injection Molding Test Specimens of
materials is to be made by personnel with expertise in the
Thermoplastic Molding and Extrusion Materials
plastics field in which the environment, inherent properties of
D 2584 Test Method for Ignition Loss of Cured Reinforced
the materials, performance of the parts, part design, manufac-
Resins
turing process, and economics are considered.
D 3892 Practice for Packaging/Packing of Plastics
1.3 The properties in this specification are those required for
D 4000 Classification System for Specifying Plastic Mate-
identifying the compositions covered. There may be other
rials
requirements necessary for identifying particular characteris-
E 29 Practice for Using Significant Digits in Test Data to
tics important to specific applications. Those may be specified
Determine Conformance with Specifications
by using the suffixes in accordance with Section 5.
E 169 Practices for General Techniques of Ultraviolet
1.4 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as the
Quantitative Analysis
standard.
2.2 ISO Standard:
NOTE 1—This specification is similar to ISO 7391 – 1987 in title only.
ISO 7391–1987 Plastics—Polycarbonate Molding and Ex-
The technical content is significantly different.
trusion Materials (Part 1: Designation—1987) (Part 2:
Preparation of Test Specimens and Determination of
2. Referenced Documents
Properties)
2.1 ASTM Standards:
D 256 Test Methods for Impact Resistance of Plastics and
3. Terminology
Electrical Insulating Materials
3.1 Definitions—The terminology used in this specification
D 638 Test Method for Tensile Properties of Plastics
is in accordance with Terminologies D 883 and D 1600. The
D 648 Test Method for Deflection Temperature of Plastics
polycarbonate materials will be designated PC as specified in
Under Flexural Load
Terminology D 1600.
D 790 Test Methods for Flexural Properties of Unreinforced
4. Classification
1 4.1 Unfilled polycarbonate materials are classified into
This specification is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D-20 on
groups according to their composition. These groups are
Plastics and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee D20.15 on Thermoplastic
Materials.
subdivided into classes and grades as shown in Table PC
Current edition approved Oct. 15, 1994. Published December 1994. Originally
published as D 3935 – 80. Last previous edition D 3935 – 87 (1992).
Significant changes to the content of this specification have been made. New
grades and recycle grades, recommended molding conditions, an ISO equivalency Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 08.02.
statement, revised inspection and certification criteria, and a keywords section have Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 08.03.
all been added. Modifications to the tables have been made to allow the callout of Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 14.02.
the new materials. Almost every section of the specification has been affected either Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 14.01.
technically or in an editorial manner. Available from American National Standards Institute, 11 W. 42nd St., 13th
Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 08.01. Floor, New York, NY 10036.
D 3935
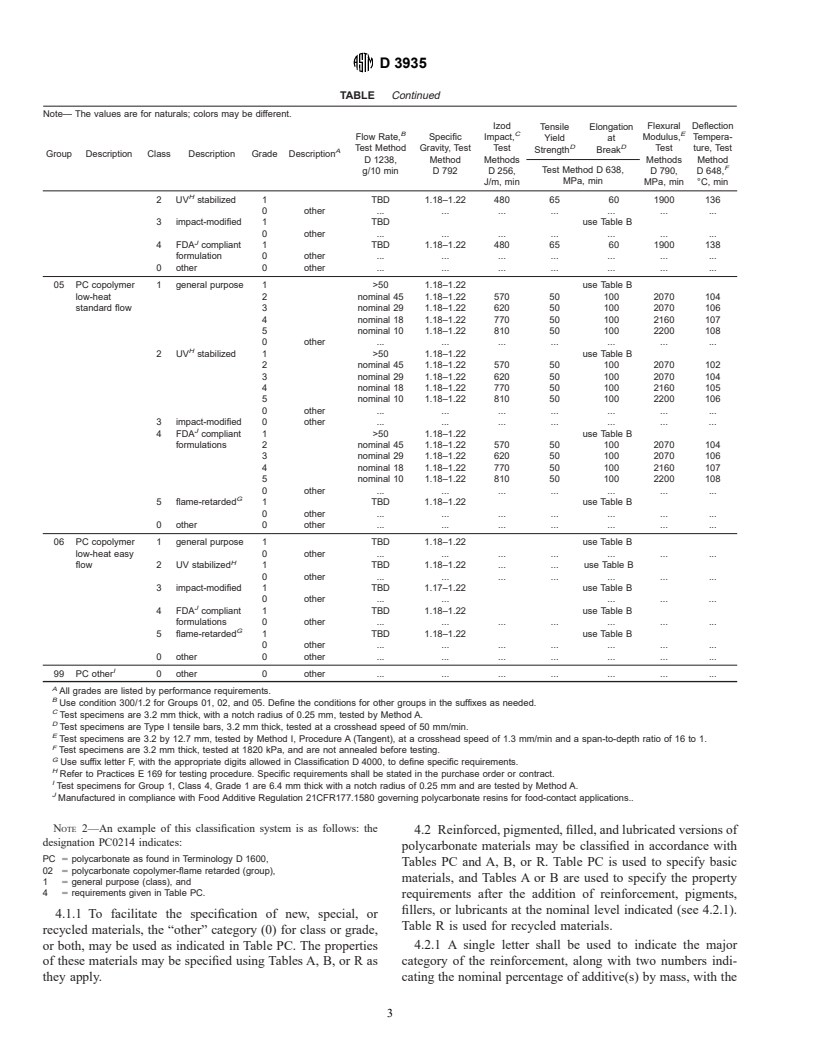
TABLE PC Polycarbonate Materials and Detail Requirements
Note— The values are for naturals; colors may be different.
Izod Flexural Deflection
Tensile Elongation
B C E
Flow Rate, Specific Impact, Modulus, Tempera-
Yield at
D D
Test Method Gravity, Test Test Test ture, Test
Strength Break
A
Group Description Class Description Grade Description
D 1238, Method Methods Methods Method
F
Test Method D 638,
g/10 min D 792 D 256, D 790, D 648,
MPa, min
J/m, min MPa, min °C, min
01 PC 1 general purpose 1 >24 1.19–1.22 use Table B
2 15 to 30 1.19–1.22 use Table B
3 12 to 20 1.19–1.22 640 55 100 2000 126
4 9 to 18 1.19–1.22 750 60 105 2100 126
5 6 to 13 1.19–1.22 750 60 110 2200 128
6 4 to 8 1.19–1.22 750 60 110 2200 128
7 <5 1.19–1.22 780 60 110 2200 130
0 other . . . . . . .
G
2 flame-retarded 1 >24 1.19–1.22 use Table B
2 15 to 30 1.19–1.22 use Table B
3 12 to 20 1.19–1.22 640 55 100 2000 126
4 9 to 18 1.19–1.22 640 60 100 2100 126
5 6 to 13 1.19–1.22 640 60 105 2200 128
6 4 to 8 1.19–1.22 640 60 110 2200 128
7 <5 1.19–1.22 640 60 110 2200 130
0 other . . . . . . .
H
3UV stabilized 1 >24 1.19–1.22 use Table B
2 15 to 30 1.19–1.22 use Table B
3 12 to 20 1.19–1.22 640 55 100 2000 124
4 9 to 18 1.19–1.22 750 60 105 2100 124
5 6 to 13 1.19–1.22 750 60 110 2100 126
6 4 to 8 1.19–1.22 750 60 110 2200 126
7 <5 1.19–1.22 750 60 110 2200 128
0 other . . . . . . .
I
4 impact-modified 1 6to15 1.18–1.22 375 50 90 1900 121
0 other . . . . . . .
J
5 FDA compliant 1 >24 1.19–1.22 use Table B
formulations 2 15 to 30 1.19–1.22 use Table B
3 12 to 20 1.19–1.22 640 55 100 2000 126
4 9 to 18 1.19–1.22 750 60 105 2100 126
5 6 to 13 1.19–1.22 750 60 110 2200 128
6 4 to 8 1.19–1.22 750 60 110 2200 128
7 <5 1.19–1.22 780 60 110 2200 130
0 other . . . . . . .
0 other 0 other . . . . . . .
02 PC copolymer- 1 general purpose 1 >24 1.22–1.26 use Table B
flame retarded 2 15 to 30 1.22–1.26 use Table B
3 12 to 20 1.22–1.26 80 60 100 2100 128
4 9 to 18 1.22–1.26 80 60 110 2200 128
5 6 to 13 1.22–1.26 90 60 110 2200 130
6 4 to 8 1.22–1.26 90 60 110 2200 130
7 <5 1.22–1.26 90 60 110 2200 132
0 other . . . . . . .
H
2UV stabilized 1 >24 1.22–1.26 use Table B
2 15 to 30 1.22–1.26 use Table B
3 12 to 20 1.22–1.26 80 60 100 2100 126
4 9 to 18 1.22–1.26 80 60 110 2200 126
5 6 to 13 1.22–1.26 90 60 110 2200 128
6 4 to 8 1.22–1.26 90 60 110 2200 130
7 <5 1.22–1.26 90 60 110 2200 130
0 other . . . . . . .
0 other 0 other . . . . . . .
03 PC copolymer 1 general purpose 1 TBD 1.18–1.22 80 63 40 1700 150
high-heat resin 0 other . . . . . . .
H
2UV stabilized 1 TBD 1.18–1.22 80 63 40 1700 148
0 other . . . . . . .
3 impact-modified 1 TBD use Table B
0 other . . . . . . .
J
4 FDA compliant 1 TBD 1.18–1.22 80 63 40 1700 150
formulation 0 other . . . . . . .
0 other 0 other . . . . . . .
04 PC copolymer 1 general purpose 1 TBD 1.18–1.22 480 65 60 1900 138
homopolymer 0 other . . . . . . .
intermediate
heat blends
D 3935
TABLE Continued
Note— The values are for naturals; colors may be different.
Izod Flexural Deflection
Tensile Elongation
B C E
Flow Rate, Specific Impact, Modulus, Tempera-
Yield at
D D
Test Method Gravity, Test Test Test ture, Test
A Strength Break
Group Description Class Description Grade Description
D 1238, Method Methods Methods Method
F
Test Method D 638,
g/10 min D 792 D 256, D 790, D 648,
MPa, min
J/m, min MPa, min °C, min
H
2UV stabilized 1 TBD 1.18–1.22 480 65 60 1900 136
0 other . . . . . . .
3 impact-modified 1 TBD use Table B
0 other . . . . . . .
J
4 FDA compliant 1 TBD 1.18–1.22 480 65 60 1900 138
formulation 0 other . . . . . . .
0 other 0 other . . . . . . .
05 PC copolymer 1 general purpose 1 >50 1.18–1.22 use Table B
low-heat 2 nominal 45 1.18–1.22 570 50 100 2070 104
standard flow 3 nominal 29 1.18–1.22 620 50 100 2070 106
4 nominal 18 1.18–1.22 770 50 100 2160 107
5 nominal 10 1.18–1.22 810 50 100 2200 108
0 other . . . . . . .
H
2UV stabilized 1 >50 1.18–1.22 use Table B
2 nominal 45 1.18–1.22 570 50 100 2070 102
3 nominal 29 1.18–1.22 620 50 100 2070 104
4 nominal 18 1.18–1.22 770 50 100 2160 105
5 nominal 10 1.18–1.22 810 50 100 2200 106
0 other . . . . . . .
3 impact-modified 0 other . . . . . . .
J
4 FDA compliant 1 >50 1.18–1.22 use Table B
formulations
2 nominal 45 1.18–1.22 570 50 100 2070 104
3 nominal 29 1.18–1.22 620 50 100 2070 106
4 nominal 18 1.18–1.22 770 50 100 2160 107
5 nominal 10 1.18–1.22 810 50 100 2200 108
0 other . . . . . . .
G
5 flame-retarded 1 TBD 1.18–1.22 use Table B
0 other . . . . . . .
0 other 0 other . . . . . . .
06 PC copolymer 1 general purpose 1 TBD 1.18–1.22 use Table B
low-heat easy 0 other . . . . . . .
H
flow 2 UV stabilized 1 TBD 1.18–1.22 . . use Table B
0 other . . . . . . .
3 impact-modified 1 TBD 1.17–1.22 use Table B
0 other . . . . .
J
4 FDA compliant 1 TBD 1.18–1.22 use Table B
formulations 0 other . . . . . . .
G
5 flame-retarded 1 TBD 1.18–1.22 use Table B
0 other . . . . . . .
0 other 0 other . . . . . . .
I
99 PC other 0 other 0 other . . . . . . .
A
All grades are listed by performance requirements.
B
Use condition 300/1.2 for Groups 01, 02, and 05. Define the conditions for other groups in the suffixes as needed.
C
Test specimens are 3.2 mm thick, with a notch radius of 0.25 mm, tested by Method A.
D
Test specimens are Type I tensile bars, 3.2 mm thick, tested at a crosshead speed of 50 mm/min.
E
Test specimens are 3.2 by 12.7 mm, tested by Method I, Procedure A (Tangent), at a crosshead speed of 1.3 mm/min and a span-to-depth ratio of 16 to 1.
F
Test specimens are 3.2 mm thick, tested at 1820 kPa, and are not annealed before testing.
G
Use suffix letter F, with the appropriate digits allowed in Classification D 4000, to define specific requirements.
H
Refer to Practices E 169 for testing procedure. Specific requirements shall be stated in the purchase order or contract.
I
Test specimens for Group 1, Class 4, Grade 1 are 6.4 mm thick with a notch radius of 0.25 mm and are tested by Method A.
J
Manufactured in compliance with Food Additive Regulation 21CFR177.1580 governing polycarbonate resins for food-contact applications.
NOTE 2—An example of this classification system is as follows: the
4.2 Reinforced, pigmented, filled, and lubricated versions of
designation PC0214 indicates:
polycarbonate materials may be classified in accordance with
PC 5 polycarbonate as found in Terminology D 1600,
Tables PC and A, B, or R. Table PC is used to specify basic
02 5 polycarbonate copolymer-flame retarded (group),
materials, and Tables A or B are used to specify the property
1 5 general purpose (class), and
4 5 requirements given in Table PC.
requirements after the addition of reinforcement, pigments,
fillers, or lubricants at the nominal level indicated (see 4.2.1).
4.1.1 To facilitate the specification of new, special, or
Table R is used for recycled materials.
recycled materials, the “other” category (0) for class or grade,
4.2.1 A single letter shall be used to indicate the major
or both, may be used as indicated in Table PC. The properties
of these materials may be specified using Tables A, B, or R as category of the reinforcement, along with two numbers indi-
they apply. cating the nominal percentage of additive(s) by mass, with the
D 3935
tolerances as tabulated as follows:
0 5 unspecified.
Tolerance
4.4 The short- and long-term mechanical properties of
Category Material
(Based on the Total Mass)
polycarbonate materials can be affected adversely by their prior
C carbon and graphite fiber- 62 percentage points
reinforced processing as well as end-use exposure to chemicals, weather-
G glass-reinforced
ing, and secondary finishing steps. Efforts to reuse materials
<15 % glass content 62 percentage points
may include direct feedback into the system from which they
>15 % glass content 63 percentage points
L lubricants (such as PTFE, depends on material and are generated, or they could involve isolation for reuse at other
graphite, silicone, and molyb- process—to be specified
times into other processes or parts. Most manufacturer’s
denum disulfide)
literature contains recommendations regarding direct feedback
M mineral-reinforced 62 percentage points
R combination/mixtures of rein- 63 percentage points based on practices to aid the user in maintaining the properties of the
forcements or other fillers/ total reinforcement
original materials as much as possible. When polycarbonate
reinforcements
resins are isolated and reprocessed in conjunction with fillers,
NOTE 3—If necessary, additional requirements may be specified using
additives, colorants, etc., there is a special risk that the
suffixes, in accordance with Section 5. Special agreements on tolerances
properties of the final products may not be equal to those
may be required when levels are below 5 %. The ash content of filled or
obtained when “virgin” resins are used. While the test speci-
reinforced materials may be determined using Test Method D 2584 where
men properties called out in this specification may be used to
applicable.
screen these materials, the user should take precautions to
4.2.2 Specific requirements for reinforced, filled, or lubri-
ensure that parts made from these materials meet the desired
cated polycarbonate materials shall be shown by a six-
parameters. Group and class designations from Table PC, used
character designation that will consist of the letter A or B and
in conjunction with Grade Designation 0, allow line callouts to
the five digits comprising the cell numbers for the property
be defined for recycled resins. The group, class, and grades
requirements in the order in which they occur in Tables A or B.
given should be used with the property ranges from Table R, as
4.2.2.1 Although the values listed in Tables A and B are
appropriate. Table R lists two impact and two tensile
...







Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.