ASTM C1138-97
(Test Method)Standard Test Method for Abrasion Resistance of Concrete (Underwater Method)
Standard Test Method for Abrasion Resistance of Concrete (Underwater Method)
SCOPE
1.1 This test method covers a procedure for determining the relative resistance of concrete (including concrete overlays and impregnated concrete) to abrasion under water (see Note 1). This procedure simulates the abrasive action of waterborne particles (silt, sand, gravel, and other solids).
Note 1-Other procedures are available for measuring abrasion resistance of concrete surfaces not under water. These include Test Methods C 418, C 779, and C 944.
1.2 The values stated in acceptable metric units are to be regarded as the standard.
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
General Information
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn. Contact ASTM
International (www.astm.org) for the latest information.
Designation:C1138–97
Standard Test Method for
Abrasion Resistance of Concrete (Underwater Method)
This standard is issued under the fixed designation C 1138; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (e) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope ported solid objects that produce abrasion of concrete and
cause potholes and related effects.
1.1 This test method covers a procedure for determining the
3.2 This test method should provide a relative evaluation of
relative resistance of concrete (including concrete overlays and
the resistance of concrete to such action.
impregnated concrete) to abrasion under water (see Note 1).
3.3 The results are expected to be useful in selection of
This procedure simulates the abrasive action of waterborne
materials, mixtures, and construction practices for use where
particles (silt, sand, gravel, and other solids).
such action is to be expected.
NOTE 1—Other procedures are available for measuring abrasion resis-
3.4 The test method is not intended to provide a quantitative
tance of concrete surfaces not under water. These include Test Methods
measurement of the length of service that may be expected
C 418, C 779, and C 944.
from a specific concrete.
1.2 The values stated in acceptable metric units are to be
regarded as the standard. 4. Apparatus
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the
4.1 Rotating Device—A drill press or similar device with a
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
chuck capable of holding and rotating the agitation paddle
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
under test conditions at a speed of 1200 6 100 rpm shall be
priate safety and health practices and determine the applica-
used.
bility of regulatory limitations prior to use.
4.2 Test Container—A steel pipe, 305 6 6-mm (12 6
⁄4-in.) inside diameter by 450 6 25-mm (18 6 1-in.) high,
2. Referenced Documents
fitted with a watertight steel base shall be used (see Fig. 1).
2.1 ASTM Standards:
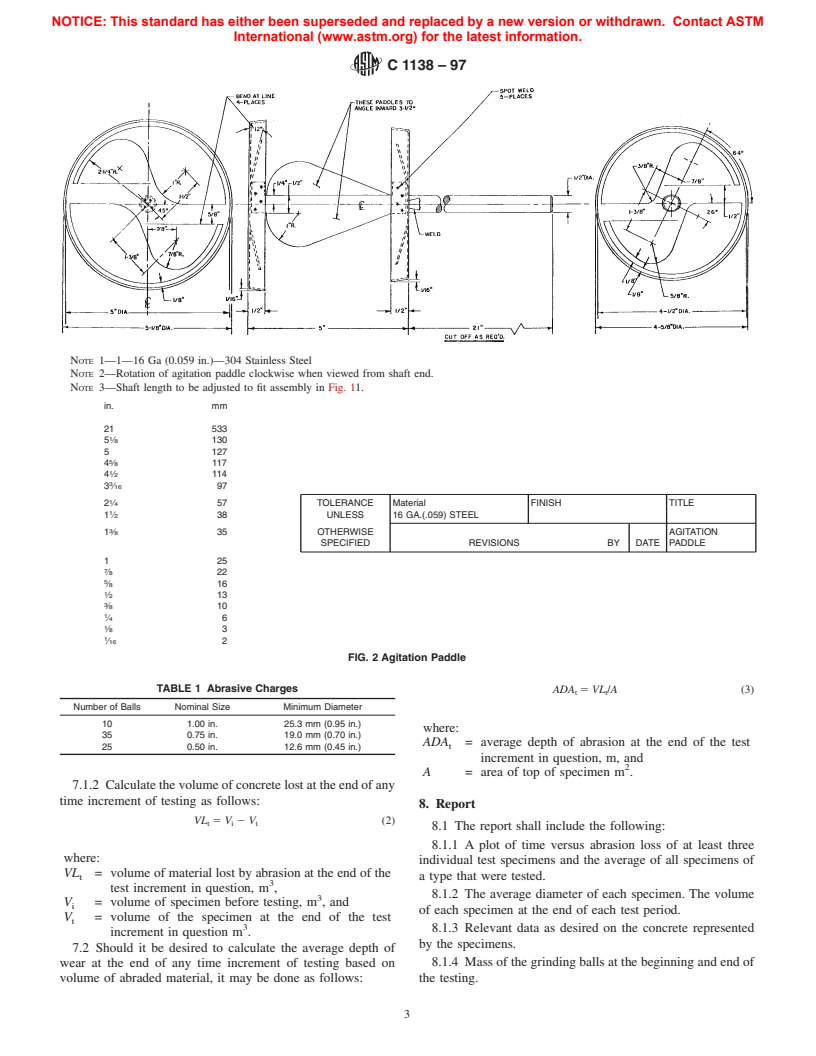
4.3 Agitation Paddle—The agitation paddle shall be as
C42 Test Method for Obtaining and Testing Drilled Cores
shown in Fig. 2.
and Sawed Beams of Concrete
4.4 Abrasive Charges—Seventy grade 1000 chrome steel
C 418 Test Method forAbrasion Resistance of Concrete by
grinding balls with nominal sizes as specified in Table 1 shall
Sandblasting
be used. The steel of which the balls are made shall have a
C 642 Test Method for Specific Gravity, Absorption, and
Rockwell C-scale hardness of 65 6 5 as determined by Test
Voids in Hardened Concrete
Methods E18. The balls shall have a smooth texture and no
C 670 Practice for Preparing Precision and Bias Statements
apparent mold seam (see Note 2).
for Test Methods for Construction Materials
NOTE 2—An abrasive charge meeting the requirements of Table 1 will
C 779 Test Method for Abrasion Resistance of Horizontal
have a mass of approximately 1530 to 1900 g (3.8 to 4.2 lb). When the
Concrete Surfaces
mass of the charge approaches the lower limit, replace the undersize or
C 944 Test Method for Abrasion Resistance of Concrete or
underweight balls not complying with Table 1.
Mortar Surfaces by the Rotating Cutter Method
4.5 Scales—A platform scale having a capacity of at least
E18 Test Methods for Rockwell Hardness and Rockwell
45 kg (100 lb) or more and accurate to within at least 5.0 g
Superficial Hardness of Metallic Materials
(0.01 lb) at any point within the range used in this test shall be
used. The scale shall be equipped with a suitable apparatus for
3. Significance and Use
suspending the sample in its container in water from the center
3.1 Thistestmethodisintendedtoqualitativelysimulatethe
of the weighing platform.
behavior of swirling water containing suspended and trans-
4.6 Weighing Basket—A wire basket or other suitable sup-
port shall be provided for weighing the specimen in water. The
This standard is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee C-9 on Concrete
andConcreteAggregatesandisthedirectresponsibilityofSubcommitteeC09.62on
Abrasion Testing.
Current edition approved Jan. 10, 1997. Published March 1997. Originally A suitable paddle is Model PS-21, manufactured by the Jiffy Mixer Company,
published as C 1138 – 89. Last previous edition C 1138 – 89. Inc., 1342-3H Bell Ave., Tustin, CA 92680-6467.
2 5
Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 04.02. AsuitablesourceofgrindingballsistheHoover-UniversalCompany,Route10,
Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 03.01. Box 558, Cumming, GA 30130.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959, United States.
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn. Contact ASTM
International (www.astm.org) for the latest information.
C1138–97
5.3 Soak the specimen in lime-saturated water or in the
water to which the concrete shall be subjected in service for a
minimum of 48 h prior to testing.
5.4 Determine the average diameter of the top surface of the
specimen to be tested to the nearest 2 mm ( ⁄16 in.) by
averagingtwodiametersmeasuredatrightanglestoeachother.
This average diameter shall be used in calculating the top
surface area.
5.5 Surface dry the specimen. Determine and record the
mass in air to the nearest 25.0 g (0.05 lb). Determine and
record the apparent mass of the specimen immersed in water to
the nearest 25.0 g (0.05 lb). The procedure of Test Method
C 642 shall be followed using water at 23 6 1.7°C (73.4 6
3°F) having a density of 997 6 2 kg/m . Remove all entrapped
air by shaking the specimen while it is immersed in the water
for weighing.
6. Procedure
6.1 Place the specimen in the test container with the surface
to be tested facing up and the seating blocks in place.
6.2 Position the specimen so that its surface is normal to the
drill shaft and the center of the specimen coincides with the
drill shaft.
6.3 Mounttheagitationpaddleinthedrillpress.Thebottom
1 1
oftheagitationpaddleshallbe38 65mm(1 ⁄2 6 ⁄4in.)above
the surface of the specimen.
6.4 Determine and record the mass of the abrasive charge to
the nearest 10 g (0.02 lb). Place it on the surface of the
specimen and add water of the same type as used in the
1 1
saturation period to 165 65mm(6 ⁄2 6 ⁄4 in.) above the
FIG. 1 Test Apparatus
surface of the specimen.
6.5 Start the paddle rotating and check that the paddle is
weighing basket shall be constructed to prevent entrapping air
rotating at the required speed with the paddle immersed.
when it and the specimen are submerged.
6.6 Remove the specimen from the test container at the end
4.7 Water Tank—A suitable watertight tank into which the
of every 12 h of operation. Flush off the abraded material and
basket and the specimen can be suspended below the scale
surface dry. Determine and record the mass of the specimen in
shall be
...







Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.