ASTM E191-64(2011)
(Specification)Standard Specification for Apparatus For Microdetermination of Carbon and Hydrogen in Organic and Organo-Metallic Compounds
Standard Specification for Apparatus For Microdetermination of Carbon and Hydrogen in Organic and Organo-Metallic Compounds
ABSTRACT
This specification covers the design requirements of each component and basic equipment comprising the apparatus used for the microdetermination of carbon and hydrogen in organic and organometallic compounds along the lines of the conventional method of Pregl, but with modifications more in line with modern practice. Due to the diversity of this apparatus by which correct results can be obtained, this specification is intended to indicate what is acceptable rather than what is mandatory. The components covered here are the oxygen supply, pressure, regulator, drying and purifying tube, flowmeter, combustion unit, absorption tubes, guard tube, Mariotte bottle, and weighing accessories.
SCOPE
1.1 This specification covers apparatus and basic equipment for the determination of carbon and hydrogen in organic and organometallic compounds along the lines of the conventional method of Pregl, but with modifications more in line with modern practice. Owing to the diversity of apparatus by which correct results can be obtained, this specification is intended to indicate what is acceptable rather than what is mandatory.
Note 1—Specifications for several items subsequently listed were developed by the Committee for the Standardization of Microchemical Apparatus, Division of Analytical Chemistry, American Chemical Society.
1.2 The values stated in inch-pound units are to be regarded as the standard. The metric equivalents of inch-pound units may be approximate.
General Information
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Designation:E191 −64 (Reapproved 2011)
Standard Specification for
Apparatus For Microdetermination of Carbon and
Hydrogen in Organic and Organo-Metallic Compounds
This standard is issued under the fixed designation E191; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
This standard has been approved for use by agencies of the U.S. Department of Defense.
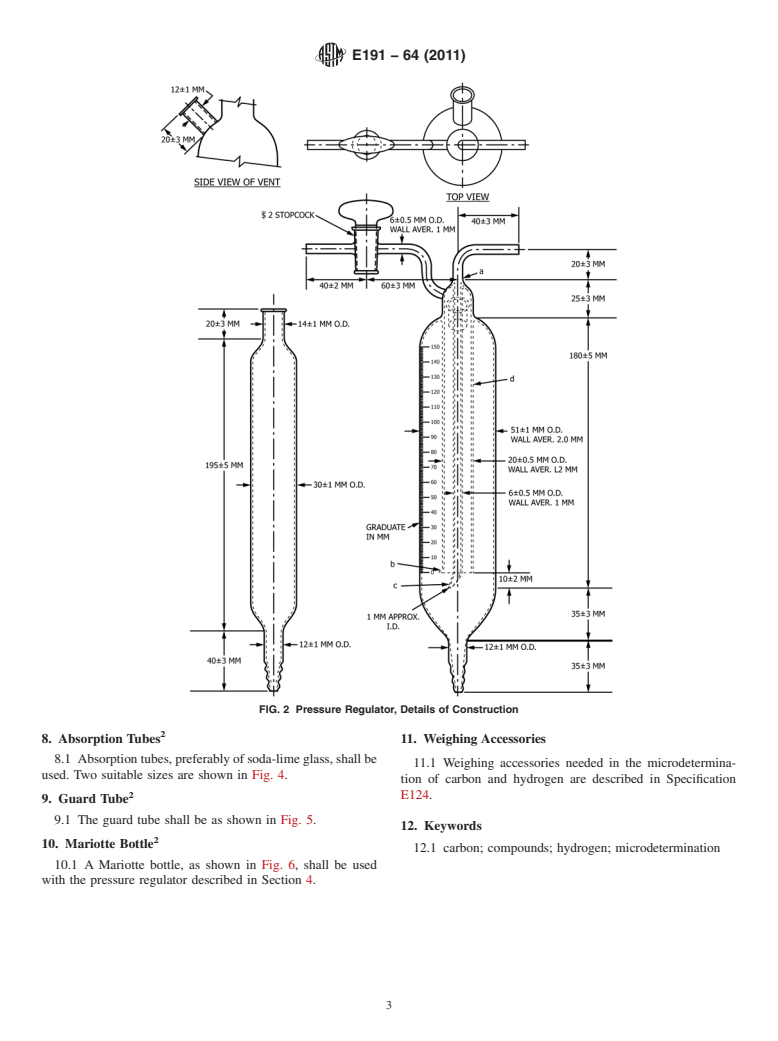
1. Scope 4. Pressure Regulator
1.1 This specification covers apparatus and basic equipment 4.1 The pressure regulator, shown in Fig. 1 and Fig. 2,
for the determination of carbon and hydrogen in organic and consisting of a bell and inlet tube submerged in a suitable
organometallic compounds along the lines of the conventional confining liquid, shall be used to supply air or oxygen, or both,
method of Pregl, but with modifications more in line with at constant pressure to the combustion system. Substitution of
modern practice. Owing to the diversity of apparatus by which a fine gas-control valve and flowmeter for the pressure regu-
correct results can be obtained, this specification is intended to lator is optional.
indicate what is acceptable rather than what is mandatory.
5. Drying and Purifying Tube
NOTE 1—Specifications for several items subsequently listed were
developed by the Committee for the Standardization of Microchemical
5.1 The conventional bubble-container U-tube shown in
Apparatus, Division of Analytical Chemistry, American Chemical Soci-
Fig. 3 shall be used for drying and purifying the entering air or
ety.
oxygen, or both.
1.2 The values stated in inch-pound units are to be regarded
as the standard. The metric equivalents of inch-pound units
6. Flowmeter
may be approximate.
6.1 The rate of gas flow shall be determined by the bubble
counter of the bubble-counter U-tube, or by a more accurate
2. Referenced Documents
flow-meter, such as the floating ball-in-column.
2.1 ASTM Standards:
E124 Specification for Weighing and Drying Apparatus for
7. Combustion Unit
Microchemical Analysis
7.1 The combustion unit shall consist of a long furnace, a
E148 Specification for Apparatus for Microdetermination of
sample furnace, a constant-temperature heating mortar, a
Nitrogen by the Dumas Method (Withdrawn 1987)
combustion tube, and a combustion-tube closure.
3. Oxygen Supply 7.1.1 Long Furnace:
7.1.1.1 The long furnace shall have a maximum over-all
3.1 Any cylinder or other suitable source of oxygen free of
length of 8 in. (203 mm) with the wall thickness at the ends not
hydrogen and organic impurities may be used. Oxygen pre-
to exceed ⁄4 in. (6 mm). The furnace shall accommodate
pared from liquid air is satisfactory.
combustion tubes up to 13 mm in outside diameter. Electric
heating elements shall be easily replaceable. The furnace shall
This specification is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee E41 on
be mounted firmly on a substantial support.
Laboratory Apparatus and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee E41.01 on
7.1.1.2 Thefurnaceshallbecapableofcontinuousoperation
Apparatus.
Current edition approved Oct. 1, 2011. Published November 2011. Originally
attemperaturesupto900°Casmeasuredinsidethecombustion
approved in 1962. Discontinued in 1988 and reinstated in 1989. Last previous
tube at the middle of the furnace. The temperature drop from
edition approved in 2005 as E191 – 64 (2005). DOI: 10.1520/E0191-64R11.
the center to points 1 in. (25 mm) and 1 ⁄4 in. (45 mm) from
Committee for the Standardization of Microchemical Apparatus. Division of
Analytical Chemistry,American Chemistry Society, 1949 Report on Recommended either end shall not exceed 15 and 7 %, respectively, based
Specifications for Microchemical Apparatus, Carbon-Hydrogen, Dumas Nitrogen,
Sulfur, and Halogen, Analytical Chemistry Vol 21, p. 1555 (1949).
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM Furter, M. F., and Steyermark, A., “Pressure Regulator for Use in Microdeter-
Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on mination of Carbon and Hydrogen,” Analytical Chemistry, Vol 20, 1948, p. 257.
the ASTM website. Kuck, J. A., and Altieri, P. L., “Spherical Ground-Glass Joints vs. Rubber
The last approved version of this historical standard is referenced on Tubing Connectors on the C and HAbsorptionTrain,” MikrochimicaActa,1956,p.
www.astm.org. 1556.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
E191−64 (2011)
FIG. 1 Pressure Regulator, Glass Parts
upon the temperature in the middle of the furnace. Means or more than one speed of movement over this distance, the
1 5
shall be provided for varying the temperature.
rates of travel shall be within the limits of ⁄8 to ⁄8 in. (3 to 16
7.1.1.3 The furnace shall be equipped with some device for
mm)/min. An automatic control shall be provided to stop the
indicating the temperature at the middle of the furnace.
travel of the sample furnace when it reaches the long furnace.
7.1.2 Sample Furnace, Traveling Ty
...







Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.