ASTM E2548-11
(Guide)Standard Guide for Sampling Seized Drugs for Qualitative and Quantitative Analysis
Standard Guide for Sampling Seized Drugs for Qualitative and Quantitative Analysis
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
This guide provides information for the sampling of seized-drug submissions.
The principal purpose of sampling in the context of this guide is to answer relevant questions about a population by examination of a portion of the population. For example: What is the net weight of the population? What portion of the units of a population can be said to contain a given drug at a given level of confidence?
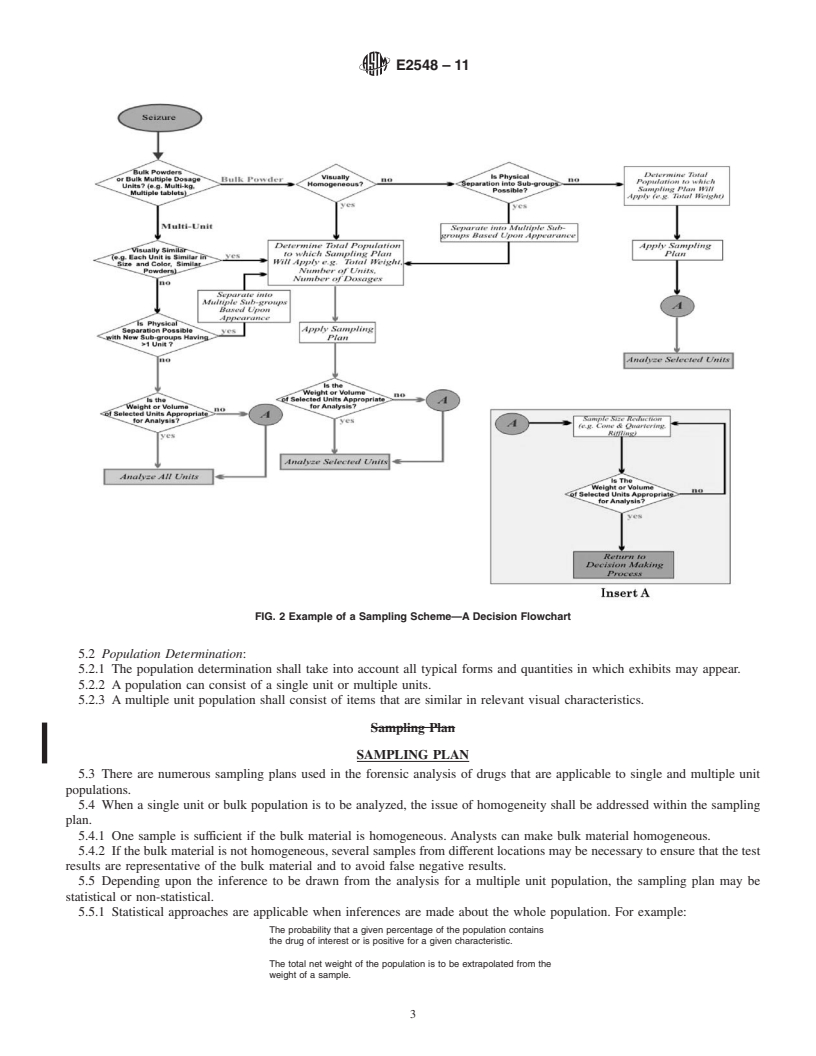
By developing a sampling strategy and implementing appropriate sampling schemes, as illustrated in Fig. 1, a laboratory will minimize the total number of required analytical determinations, while ensuring that all relevant legal and scientific requirements are met.
FIG. 1 Relationship of Various Levels Required in Sampling
SCOPE
1.1 This guide covers minimum considerations for sampling of seized drugs for qualitative and quantitative analysis.
General Information
Relations
Buy Standard
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Designation:E2548–11
Standard Guide for
Sampling Seized Drugs for Qualitative and Quantitative
1
Analysis
This standard is issued under the fixed designation E2548; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope
What is the net weight of the population?
1.1 Thisguidecoversminimumconsiderationsforsampling
What portion of the units of a population can be said to contain a
of seized drugs for qualitative and quantitative analysis.
given drug at a given level of confidence?
3.3 By developing a sampling strategy and implementing
2. Referenced Documents
appropriate sampling schemes, as illustrated in Fig. 1,a
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
laboratory will minimize the total number of required analyti-
E105 Practice for Probability Sampling of Materials
cal determinations, while ensuring that all relevant legal and
E122 Practice for Calculating Sample Size to Estimate,
scientific requirements are met.
With Specified Precision, the Average for a Characteristic
of a Lot or Process
4. Sampling Strategy
E141 Practice for Acceptance of Evidence Based on the
4.1 Asampling strategy is highly dependent on the purpose
Results of Probability Sampling
of the investigation, the original question, and the ultimate use
E1732 Terminology Relating to Forensic Science
of the results. Laws and legal practices form the foundation of
E2329 Practice for Identification of Seized Drugs
most strategies and shall be taken into account when designing
E2334 Practice for Setting an Upper Confidence Bound For
a sampling scheme. Therefore, specific sampling strategies are
a Fraction or Number of Non-Conforming items, or a Rate
not defined in this guide.
of Occurrence for Non-conformities, UsingAttribute Data,
4.2 The laboratory has the responsibility to develop its own
When There is a Zero Response in the Sample
strategies consistent with these recommendations. It is recom-
3
2.2 ISO Standards:
mended that the following key points be addressed:
ISO 3534-1 Statistics – Vocabulary and Symbols – Part 1:
4.2.1 Sampling may be statistical or non-statistical.
Probability and General Statistical Terms
NOTE 1—For the purpose of this guide, the use of the term statistical is
ISO 3534-2 Statistics – Vocabulary and Symbols – Part 2:
meant to include the notion of an approach that is probability-based.
Statistical Quality Control
4.2.1.1 In many cases, a non-statistical approach may suf-
3. Significance and Use
fice. The sampling plan shall provide an adequate basis for
3.1 This guide provides information for the sampling of
answering questions of applicable law. For example,
seized-drug submissions.
Is there a drug present in the population?
3.2 The principal purpose of sampling in the context of this
Are statutory enhancement levels satisfied by the analysis of a
guide is to answer relevant questions about a population by
specified number of units?
examination of a portion of the population. For example:
4.2.1.2 If an inference about the whole population is to be
drawn from a sample, then the plan shall be statistically based
and limits of the inference shall be documented.
1
4.2.2 Statistically selected units shall be analyzed to meet
This guide is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee E30 on Forensic
Sciences and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee E30.01 on Criminalistics.
PracticeE2329ifstatisticalinferencesaretobemadeaboutthe
Current edition approved Sept. 1, 2011. Published October 2011. Originally
whole population.
approved in 2007. Last previous version approved in 2007 as E2548– 07. DOI:
10.1520/E2548-11.
5. Sampling Scheme
2
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
5.1 The sampling scheme is an overall approach that in-
Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on
cludespopulationdetermination,selectionofthesamplingplan
the ASTM website.
3
andprocedureand,whenappropriate,samplereductionpriorto
Available from International Organization for Standardization (ISO), 1 rue de
Varembé, Case postale 56, CH-1211, Geneva 20, Switzerland, http://www.iso.ch. analysis (Fig. 2).
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959, United States.
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
E2548–11
FIG. 1 Relationship of Various Levels Required in Sampling
FIG. 2 Example of a Sampling Scheme—A Decision Flowchart
5.2 Population Determination: 5.2.2 A population can consist of a single unit or multiple
5.2.1 The population determination shall take
...
This document is not an ASTM standard and is intended only to provide the user of an ASTM standard an indication of what changes have been made to the previous version. Because
it may not be technically possible to adequately depict all changes accurately, ASTM recommends that users consult prior editions as appropriate. In all cases only the current version
of the standard as published by ASTM is to be considered the official document.
Designation:E2548–07 Designation:E2548–11
Standard Guide for
Sampling Seized Drugs for Qualitative and Quantitative
1
Analysis
This standard is issued under the fixed designation E2548; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope
1.1 This guide covers minimum considerations for sampling of seized drugs for qualitative and quantitative analysis.
2. Referenced Documents
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
E105 Practice for Probability Sampling of Materials
E122 Practice for Calculating Sample Size to Estimate, With Specified Precision, the Average for a Characteristic of a Lot or
Process
E141 Practice for Acceptance of Evidence Based on the Results of Probability Sampling
E1732 Terminology Relating to Forensic Science
E2329 Practice for Identification of Seized Drugs
E2334 Practice for Setting an Upper Confidence Bound For a Fraction or Number of Non-Conforming items, or a Rate of
Occurrence for Non-conformities, Using Attribute Data, When There is a Zero Response in the Sample
3
2.2 ISO Standards:
ISO 3534-1 Statistics – Vocabulary and symbolsSymbols – Part 1: Probability and general statistical terms General Statistical
Terms
ISO 3534-2 Statistics – Vocabulary and symbolsSymbols – Part 2: Statistical quality controlQuality Control
3. Significance and Use
3.1 This guide provides information for the sampling of seized-drug submissions.
3.2 The principal purpose of sampling in the context of this guide is to answer relevant questions about a population by
examination of a portion of the population. For example:
What is the net weight of the population?
What portion of the units of a population can be said to contain a
given drug at a given level of confidence?
3.3 By developing a sampling strategy and implementing appropriate sampling schemes, as illustrated in Fig. 1, a laboratory
will minimize the total number of required analytical determinations, while ensuring that all relevant legal and scientific
requirements are met.
4. Sampling Strategy
4.1 A sampling strategy is highly dependent on the purpose of the investigation, the original question, and the ultimate use of
the results. Laws and legal practices form the foundation of most strategies and shall be taken into account when designing a
sampling scheme. Therefore, specific sampling strategies are not defined in this guide.
4.2 The laboratory has the responsibility to develop its own strategies consistent with these recommendations. It is
recommended that the following key points be addressed:
4.2.1 Sampling may be statistical or non-statistical.
1
This guide is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee E30 on Forensic Sciences and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee E30.01 on Criminalistics.
Current edition approved March 1, 2007. Published April 2007. DOI: 10.1520/E2548-07.
Current edition approved Sept. 1, 2011. Published October 2011. Originally approved in 2007. Last previous version approved in 2007 as E2548– 07. DOI:
10.1520/E2548-11.
2
For referencedASTM standards, visit theASTM website, www.astm.org, or contactASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. ForAnnualBookofASTMStandards
volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on the ASTM website.
3
Available from International Organization for Standardization (ISO), 1 rue de Varembé, Case postale 56, CH-1211, Geneva 20, Switzerland, http://www.iso.ch.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959, United States.
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
E2548–11
FIG. 1 Relationship of Various Levels Required in Sampling
NOTE 1—For the purpose of this guide, the use of the term statistical is meant to include the notion of an approach that is probability-based.
4.2.1.1 In many cases, a non-statistical approach may suffice. The sampling plan shall provide an adequate basis for answering
questions of applicable law. For example,
Is there a drug present in the population?
Are statutory enhancement levels satisfied by the analysis of a
specified number of units?
4.2.1.2 If an inference about the whole population is to be drawn from a sample, then the plan shall be statistically based and
limits of the inference shall be documented.
4.2.2 StatisticallyselectedunitsshallbeanalyzedtomeetPracticeE2329ifstatisticalinferencesaretobema
...









Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.