ASTM D2504-88(1998)
(Test Method)Standard Test Method for Noncondensable Gases in C2 and Lighter Hydrocarbon Products by Gas Chromatography
Standard Test Method for Noncondensable Gases in C<sub>2</sub> and Lighter Hydrocarbon Products by Gas Chromatography
SCOPE
1.1 This test method covers the determination of hydrogen, nitrogen, oxygen, and carbon monoxide in the parts per million volume (ppmv) range in C2 and lighter hydrocarbon products. This test method should be applicable to light hydrocarbons other than ethylene, but the test program did not include them.
1.2 The values stated in acceptable metric units are to be regarded as the standard. The values in parentheses are for information only.
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety problems, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use. For some specific hazard statements, see Notes 3, 4, and 5.
General Information
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the lastest information
Designation:D2504–88 (Reapproved 1998) AnAmerican National Standard
AMERICAN SOCIETY FOR TESTINGAND MATERIALS
100 Barr Harbor Dr., West Conshohocken, PA19428
Reprinted from theAnnual Book ofASTM Standards. CopyrightASTM
Standard Test Method for
Noncondensable Gases in C and Lighter Hydrocarbon
Products by Gas Chromatography
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D2504; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision.Anumber in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval.A
superscript epsilon (e) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope tions below 100 ppmv. Argon, if present in the sample,
interferes with oxygen determination.
1.1 This test method covers the determination of hydrogen,
nitrogen,oxygen,andcarbonmonoxideinthepartspermillion
4. Significance and Use
volume (ppmv) range in C and lighter hydrocarbon products.
4.1 Thepresenceoftraceamountsofhydrogen,oxygen,and
This test method should be applicable to light hydrocarbons
carbon monoxide can have deleterious effects in certain pro-
other than ethylene, but the test program did not include them.
cesses using hydrocarbon products as feed stock. This test
1.2 The values stated in acceptable metric units are to be
method is suitable for setting specifications, for use as an
regarded as the standard. The values in parentheses are for
internal quality control tool and for use in development or
information only.
research work.
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
5. Apparatus
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
5.1 Chromatograph—Any chromatographic instrument
priate safety and health practices and determine the applica-
havingeitherathermalconductivityorionizationdetectorwith
bility of regulatory limitations prior to use. For some specific
an overall sensitivity sufficient to detect 2 ppmv or less of the
hazard statements, see Note 3, Note 4, and Note 5.
compounds listed in the scope, with a peak height of at least 2
2. Referenced Documents mm without loss of resolution.
5.2 Detectors—Thermal Conductivity—If a methanation re-
2.1 ASTM Standards:
actor is used, a flame ionization detector is also required. To
D2505 TestMethodforEthylene,OtherHydrocarbons,and
determine carbon monoxide with a flame ionization detector, a
Carbon Dioxide In High-Purity Ethylene by Gas Chroma-
methanation reactor must be inserted between the column and
tography
3 the detector and hydrogen added as a reduction gas. Details on
E260 Practice for Packed Column Gas Chromatography
the preparation and use of the reactor are given in Appendix
F307 PracticeforSamplingPressurizedGasforGasAnaly-
4 X1.
sis
5.3 Constant-Volume Gas Sampling Valve.
2.2 Other Standard:
5.4 Column—Any column or set of columns that is capable
Compressed Gas Association Booklets G-4 and G-4.1 on
of resolving the components listed in the scope can be used.
the use of oxygen.
Copper, stainless steel, or aluminum tubing may be used. The
3. Summary of Test Method columns chosen must afford a resolution such that the depth of
the valleys ahead of the trace peak is no less than 50% of the
3.1 The sample is separated in a gas-solid chromatographic
trace peak height.
system using molecular sieves as the solid adsorbent. The
5.5 Recorder—A recorder with a full-scale response of 2 s
concentration of the gases to be determined is calculated from
or less and a maximum rate of noise of 60.3% of full scale.
the recorded peak heights or peak areas.Argon can be used as
5.6 Oven—The oven used for activating molecular sieves
a carrier gas for the determination of hydrogen in concentra-
mustbemaintainedat260to288°C(500to550°F)andshould
bedesignedsothatthegasesmaybedisplacedcontinuouslyby
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D-2 on
a stream of inert gas.The oven may be a thermostated piece of
Petroleum Products and Lubricantsand is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee
1-in. pipe about 0.3m (1 ft.) in length. Electrical heating tapes
D02.D0.02on C Test Methods.
or other means may be used for heating provided the heat is
Current edition approved Oct. 31, 1988. Published December 1988. Originally
published as D2504–66 T. Last previous edition D2504–83e .
distributed uniformly.
Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 05.01.
Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 14.02. NOTE 1—The use of copper tubing is not recommended with samples
Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 15.03.
containing acetylene as this could lead to the formation of potentially
Available from Compressed Gas Association, 1253 Jefferson Davis Highway,
explosive copper acetylide.
Arlington, VA, 22202.
--`,,,``,`,``,,`,,,,`,,`,,``,``-`-`,,`,,`,`,,`---
D2504
NOTE 7—Carrier gas rates of 36 to 60 mL/min and temperatures of 50
6. Reagents and Materials
to 60°C have been used successfully.
6.1 Molecular Sieves, 5A, 13A, or 13X—Any mesh sizes
9.2 Prepare at least three synthetic standard samples con-
canbeusedsolongassensitivityandresolutionaremaintained
taining the compounds to be determined over the range of
(seeNote2).Ifa40to60-meshsievesizeisdesired,butisnot
concentration desired in the products to be analyzed, using the
available, it may be prepared as described in 8.1.
pure gases or the certified blend. For the preparation of the
6.2 Coconut Charcoal, 30 to 60-mesh sieve size (optional).
second, third, and following calibration samples it is always
NOTE 2—Columns that have been found to give the desired separation
preferable not to dilute the first sample.
include a 1-m by 3.175-mm outside diameter column of 100 to 120 mesh
5Amolecular sieve, a 3-m by 6.35-mm outside diameter column of 40 to
NOTE 8—Synthetic standard samples should be prepared as described
60-mesh5Asieve,anda7.7-mby6.35-mmoutsidediametercolumnwith
in Test Method D2505.
13A or 13X sieve in the first 7.4 m and charcoal in the 0.3 m.
9.3 Inject a known volume of one of the standard samples,
6.3 Gases for Calibration—Pure or research grade hydro-
using a minimum of 1 mL for detecting 2 ppmv.
gen, oxygen, nitrogen, and carbon monoxide will be needed to
NOTE 9—Use of a reverse-flow arrangement will facilitate removal of
preparesyntheticstandardsamplesasdescribedinTestMethod
heavier gases and decrease the elapsed time of analysis.
D2505. (Warning—See Note 4 and Note 5.) Certified cali-
9.4 Record all of the desired peaks on each of the synthetic
bration blends are commercially available from numerous
blends prepared.
sources and can be used as the synthetic standard samples.
9.5 Prepare a chart for each compound, plotting the peak
NOTE 3—Warning:Flammable gases. Hazardous pressure. See An-
height of the compound or peak area of the compound against
nexes A1.1-A1.5.
the concentration of the compounds in ppmv. The peak area
NOTE 4—Warning:Flammable. Poison. Harmful if inhaled. Danger-
can be determined by any method that meets the precision
ous when exposed to flame. See Annex A1.5.
requirements of Section 12. Methods found to be acceptable
NOTE 5—Warning:Hazardous pressure. See Annex A1.2.
include planimetering, integration (electronic or mechanical or
6.4 Carrier Gases—Argon or helium.
computer processing), and triangulation.
NOTE 6—Practice E260 contains information that will be helpful to
10. Procedure
those using this test method.
10.1 Connect the sample cylinder containing a gaseous
7. Sampling
sampletothegassamplevalvewithametaltubeandallowthe
7.1 Samples shall be supplied to the laboratory in high-
sample to flow from the sample tube for about ⁄2min. at a rate
pressure sample cylinders, obtained using the procedures
of 70 to 100 mL/min.
described in Practice F307 or similar methods.
10.2 Inject into the instrument the same volume of sample
as used for calibration, (pressure of sample and calibration gas
8. Preparation ofApparatus
mustbethesameinthesampleloop)andrecordthepeakareas
8.1 Chromatographic Column Packing—Crush in a porce-
or peak heights desired.
lain mortar and sieve to 40 to 60-mesh size about 200 g of
11. Calculation
molecular sieves 5A in order to have enough for several
columns. All work of preparing molecular sieves and packing 11.1 From the peak height or area of the compound in the
columns with this material shall be done rapidly, preferably sample, determine the moles per million of the compound
under a blanket of dry nitrogen in order to minimize moisture using the charts prepared in calibration.Atypical characteriza-
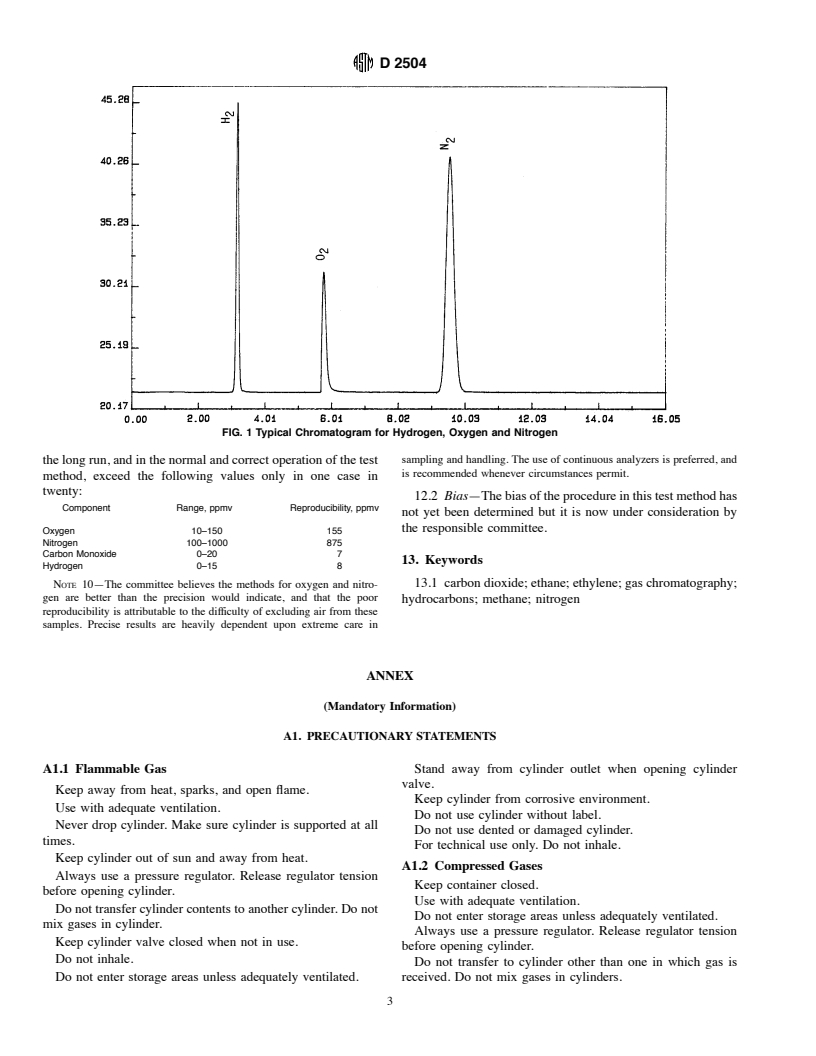
absorption. Heat the screened molecular sieves in an oven at tion showing hydrogen, oxygen, and nitrogen in ethylene is
2746 14°C (5256 25°F) for 24 h purging with dry nitrogen presented in Fig. 1.
at a rate of about 5 mL/min during this time.The nitrogen rate
12. Precision and Bias
is not critical and can be measured by any convenient means
12.1 The precision of this test method as determined by
suchasanorificemeter,rotameter,manometer,etc.Donotuse
statistical examination of interlaboratory results is as follows:
a wet test meter.
12.1.1 Repeatability—The difference between successive
8.2 ChromatographicColumn—Purgethemetaltubingwith
test results, obtained by the same operator with the same
dry nitrogen. Insert a small amount of glass wool in the end.
apparatus under constant operating conditions on identical test
Fill rapidly with the screened and activated molecular sieves,
material would, in the long run, and in the normal and correct
adding the latt
...







Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.