ISO 3016:1974
(Main)Petroleum oils — Determination of pour point
Petroleum oils — Determination of pour point
Huiles de pétrole — Détermination du point d'écoulement
General Information
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
INTERNATIONAL STANDARD 3016
INTERNATIONAL ORGANIZATION FOR STANDARDIZATION .MEX&YHAPOJ&HAR OPïA"3ALwI no CïAiiAApI1IuIuM .ORGANISATION INTERNATIONALE DE NORMALISATION
O
Petroleum oils - Determination of pour point
Huiles de pétrole - Détermination du point d'écoulement
First edition - 1974-05-01
I
w UDC 665.7.035.6 Ref. No. IS0 3016-1974 (E)
izt
!?
Descriptors : petroleum products, oils, tests, low temperature tests, measurement, solidification points, test equipment.
E
O
m
Price based on 3 pages
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
FOREWORD
IS0 (the International Organization for Standardization) is a worldwide federation
of national standards institutes (IS0 Member Bodies). The work of developing
International Standards is carried out through IS0 Technical Committees. Every
Member Body interested in a subject for which a Technical Committee has been set
up has the right to be represented on that Committee. International organizations,
governmental and non-governmental, in liaison with ISO, also take part in the work.
Draft International Standards adopted by the Technical Committees are circulated
as International
to the Member Bodies for approval before their acceptance
Standards by the IS0 Council.
IS0 3016 was drawn up by Technical Committee
International Standard
ISO/TC 28, Petroleum products, and circulated to the Member Bodies in March
1973.
It has been approved by the Member Bodies of the following countries :
Australia
India South Africa, Rep. of
Austria Iran Spain
Belgium Israel Sweden
Brazil Mexico Thailand
Bulgaria Netherlands Turkey
Chile New Zealand United Kingdom
Czechoslovakia Norway U.S.A.
Egypt, Arab Rep. of Poland U.S.S.R.
Germany Portugal
Hungary Romania
The Member Bodies of the following countries expressed disapproval of the
document on technical grounds :
Canada
France
O International Organization for Standardization, 1974 O
Printed in Switzerland
---------------------- Page: 2 ----------------------
INTERNATIONAL STANDARD IS0 3016-1974 (E)
Petroleum oils - Determination of pour point
1 SCOPE AND FIELD OF APPLICATION 3 PRINCIPLE
This International Standard specifies a method for the After preliminary heating, the sample is cooled at a
determination of the pour point of any petroleum oil. A specified rate and examined at intervals of 3 OC for flow
procedure suitable for black oils, cylinder stock, and characteristics. The lowest temperature at which movement
non-distillate fuel oil is described in 5.9. of the oil is observed is recorded as the pour point.
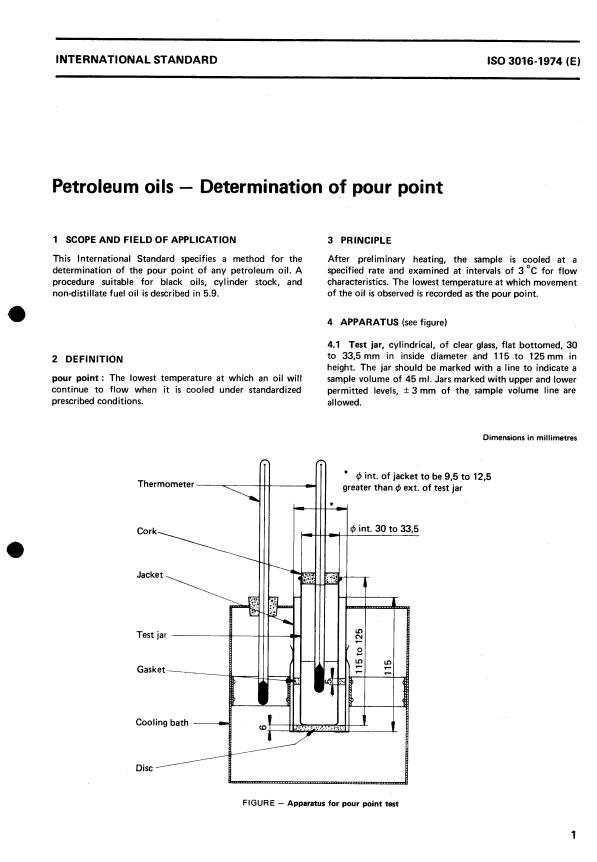
4 APPARATUS (see figure)
4.1 Test jar, cylindrical, of clear glass, flat bottomed, 30
to 33,5 mm in inside diameter and 115 to 125 mm in
2 DEFINITION
a line to indicate a
height. The jar should be marked with
pour point : The lowest temperature at which an oil will sample volume of 45 ml. Jars marked with upper and lower
continue to flow when it is cooled under standardized
permitted levels, rt 3 mm of the sample volume line are
prescribed conditions.
al I owed.
Dimensions in millimetres
*
$ int. of jacket to be 9,5 to 12.5
greater than @I ext. of test jar
6 int. 30 to 33.5
cork-
,-----
FIGURE - Apparatus for pour point test
1
---------------------- Page: 3 ----------------------
IS0 3016-1974 (E)
position, is essential. For the determination of pour points
4.2 Thermometers, partial immersion type conforming to
below 10 OC two or more baths are needed. The required
the following specifications :
bath temperatures may be maintained by refrigeration or
High cloud Low cloud
by suitable freezing mixtures.
Spacif ication
and pour
and pour
NOTE - The freezing mixtures commonly used are as follows :
-38 to + 50°C
-80 to + 20 "C
Range
For temperatures down to
76 mm
Immersion 108 mm
10 "C : ice and water
- 12 "C : crushed ice and sodium chloride crystals;
Graduation at each 1 "c 1 "C
- 26 "C : crushed ice and calcium chloride crystals;
Longer lines at each 5 "C 5°C
-57'C : solid carbon dioxide and acetone or petroleum
naphtha.' )
Figured at each 10°C 10°C
Scale error not to
0.5 "C 1 "c
exceed
down to - 33 "C
5 PROCEDURE
2O c
below - 33 C
5.1 Pour the clear oil into the test jar to the level mark or
Expansion chamber
to a level between the two etched lines according to type
permitting heating
(see note). When necessary heat the oil in a water bath until
to 100 Oc 60 "C
it is just sufficiently fluid to pour into the test jar.
Overall length 231 * 5 mm 232 f 5 mm
NOTE - When it is known that a sample has been heated to some
Stem diameter 7to8mm 7 to8 mm
temperature higher than 45 OC during the preceding 24 h or when
the thermal history of the sample is not known, keep the sample at
Bulb length 7.0 to 9.5 mm 8.0 to 9.5 mm
room temperature for 24 h before testing it.
5,5 to 7.0 mm 5,O to 6,5 mm
Bulb diameter
5.2 Close the test jar tightly by the cork carrying the high
Distance from bottom
-38°C:
of bulb to line at -57OC: cloud and pour thermometer (4.2), or in the case of pour
120 to 130 mm 120 to 130 mm
points above 39 OC, a thermometer as described in note 1.
Adjust the position of the cork and the thermometer so
Distance from bottom
that the cork fits tightly, the thermometer and the jar are
of bulb to line at 49°C: 20°C :
coaxial, and the thermometer bulb is immersed so that the
195 to 205 mm 182 to 196 mm
beginning of the capillary is 3 rnm below the surface of the
oil (see note 2).
4.3 Cork, to fit the test jar, bored centrally to take the
test thermometer.
NOTES
1 For tests above 39 OC it is permissible to use any thermometer
4.4 Jacket, watertight, cylindrical, of glass or metal,
that includes the range from 32 to 105OC. A total immersion
flat-bottomed, about 11 5 mm in depth, with inside
thermometer with graduations of 0,5 OC is suggested.
diameter 9,5 to 12,5 mm greater than the outside diameter
2 Since separation of the mercury or toluene thread of cloud and
of the test jar.
pour thermometers occasionally occurs, and since such separation
may otherwise escape immediate detection, it is suggested that the
ice points of the thermometers be checked immediately prior to the
4.5 Disc, of cork or felt, 6mm in thickness and of the
test. Any thermometer that shows an ice point differing from O "C
same diameter as the inside of the jacket.
by more than 1 "C should be further examined or recalibrated, or
both, before use.
4.6 Gasket, ring form, about 5 mm in thickness, to fit
snugly around the outside of the test jar and loosely insi
...

Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.