ASTM A564/A564M-04(2009)
(Specification)Standard Specification for Hot-Rolled and Cold-Finished Age-Hardening Stainless Steel Bars and Shapes
Standard Specification for Hot-Rolled and Cold-Finished Age-Hardening Stainless Steel Bars and Shapes
ABSTRACT
This specification covers bars and shapes of age-hardening stainless steels. Hot-finished or cold-finished rounds, squares, hexagons, bar shapes, angles, tees, and channels are included. These shapes may be produced by hot rolling, extruding, or forging. Type 631 and 632 stainless steels contain a large amount of ferrite in the microstructure and can have low ductility in forgings and large diameter bars. Material of types other than XM-16, XM-25, and Type 630 shall be furnished in the solution-annealed condition, or in the equalized and oven-tempered condition. Types 630, XM-16, and XM-25 may be furnished in the solution-annealed or age-hardened condition. Type UNS S46910 shall be furnished in solution annealed, cold-worked or aged-hardened condition. Shapes may be subjected to either Class A or Class C preparation for removal of visible surface imperfections. The material shall be subjected to tension, impact, and hardness tests.
SCOPE
1.1 This specification covers bars and shapes of age-hardening stainless steels. Hot-finished or cold-finished rounds, squares, hexagons, bar shapes, angles, tees, and channels are included; these shapes may be produced by hot rolling, extruding, or forging. Billets or bars for reforging may be purchased to this specification.
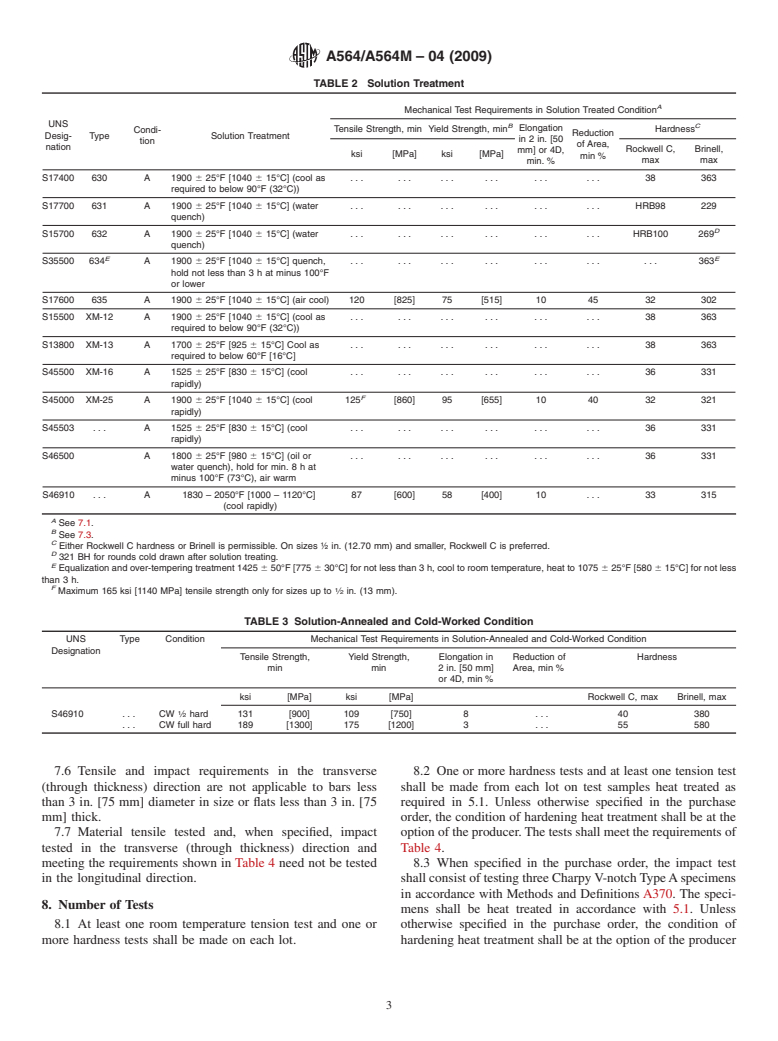
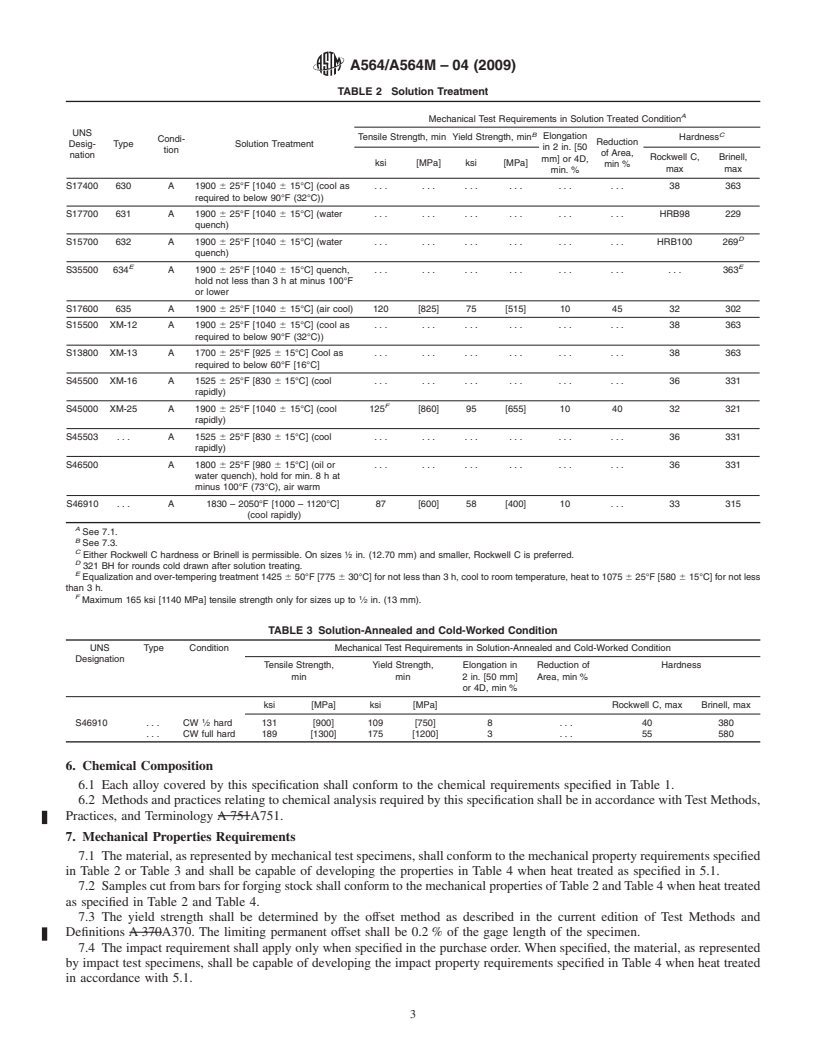
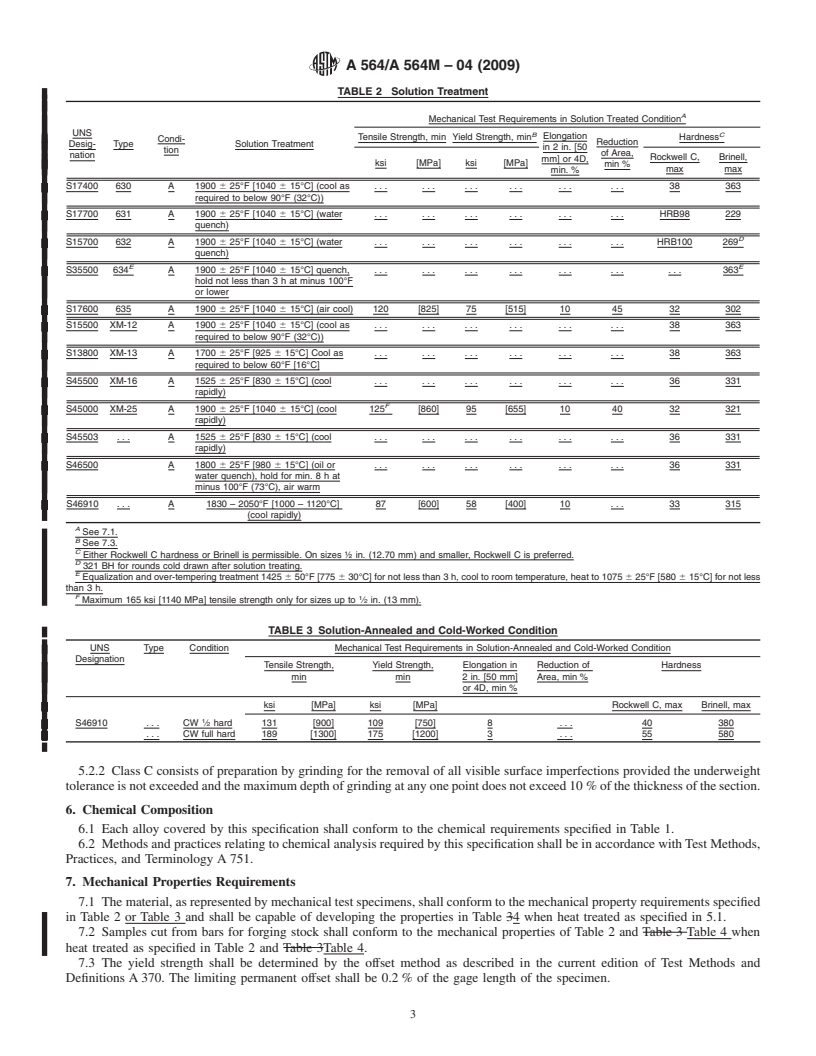
1.2 These steels are generally used for parts requiring corrosion resistance and high strength at room temperature, or at temperatures up to 600°F [315°C]; 700°F [370°C] for Type 632; 840°F [450°C] for Type UNS S46910. They are suitable for machining in the solution-annealed condition after which they may be age-hardened to the mechanical properties specified in Section 7 without danger of cracking or distortion. Type XM-25 is machinable in the as-received fully heat treated condition. Type UNS S46910 is suitable for machining in the solution-annealed, cold-worked, and aged-hardened condition.
1.3 Types 631 and 632 contain a large amount of ferrite in the microstructure and can have low ductility in forgings and larger diameter bars. Applications should be limited to small diameter bar.
1.4 The values stated in either inch-pound units or SI (metric) units are to be regarded separately as standards; within the text and tables, the SI units are shown in [brackets]. The values stated in each system are not exact equivalents; therefore, each system must be used independent of the other. Combining values from the two systems may result in nonconformance with the specification.
1.5 Unless the order specifies an “M'' designation, the material shall be furnished to inch-pound units.
Note 1—For forgings, see Specification A 705/A 705M.
Note 2—For billets and bars for forging see Specification A 314.
General Information
Relations
Buy Standard
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Designation: A564/A564M – 04 (Reapproved 2009)
Standard Specification for
Hot-Rolled and Cold-Finished Age-Hardening Stainless Steel
1
Bars and Shapes
This standard is issued under the fixed designationA564/A564M; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year
of original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval.
A superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
This standard has been approved for use by agencies of the Department of Defense.
1. Scope 2. Referenced Documents
2 3
1.1 This specification covers bars and shapes of age- 2.1 ASTM Standards:
hardeningstainlesssteels.Hot-finishedorcold-finishedrounds, A314 Specification for Stainless Steel Billets and Bars for
squares, hexagons, bar shapes, angles, tees, and channels are Forging
included; these shapes may be produced by hot rolling, A370 Test Methods and Definitions for Mechanical Testing
extruding, or forging. Billets or bars for reforging may be of Steel Products
purchased to this specification. A484/A484M Specification for General Requirements for
1.2 These steels are generally used for parts requiring Stainless Steel Bars, Billets, and Forgings
corrosion resistance and high strength at room temperature, or A705/A705M Specification for Age-Hardening Stainless
at temperatures up to 600°F [315°C]; 700°F [370°C] for Type Steel Forgings
632; 840°F [450°C] for Type UNS S46910. They are suitable A751 Test Methods, Practices, andTerminology for Chemi-
for machining in the solution-annealed condition after which cal Analysis of Steel Products
they may be age-hardened to the mechanical properties speci- E527 Practice for Numbering Metals and Alloys in the
fied in Section 7 without danger of cracking or distortion.Type Unified Numbering System (UNS)
XM-25 is machinable in the as-received fully heat treated 2.2 Other Documents:
condition. Type UNS S46910 is suitable for machining in the SAE J1086 Recommended Practice for Numbering Metals
4
solution-annealed, cold-worked, and aged-hardened condition. and Alloys (UNS)
1.3 Types 631 and 632 contain a large amount of ferrite in
3. Ordering Information
the microstructure and can have low ductility in forgings and
3.1 It is the responsibility of the purchaser to specify all
larger diameter bars. Applications should be limited to small
diameter bar. requirements that are necessary for material ordered under this
specification. Such requirements may include but are not
1.4 The values stated in either inch-pound units or SI
(metric)unitsaretoberegardedseparatelyasstandards;within limited to the following:
3.1.1 Quantity (weight or number of pieces),
the text and tables, the SI units are shown in [brackets]. The
values stated in each system are not exact equivalents; there- 3.1.2 Type or UNS designation (Table 1),
3.1.3 Specific melt type when required,
fore, each system must be used independent of the other.
Combining values from the two systems may result in noncon- 3.1.4 Heat treated condition (5.1),
3.1.5 Transverse properties when required (7.6),
formance with the specification.
1.5 Unless the order specifies an “M’’ designation, the 3.1.6 Finish (Specification A484/A484M),
3.1.7 Surface preparation of shapes (5.2.1),
material shall be furnished to inch-pound units.
3.1.8 Size, or applicable dimension including diameter,
NOTE 1—For forgings, see Specification A705/A705M.
thickness, width, length, etc.,
NOTE 2—For billets and bars for forging see Specification A314.
3.1.9 Preparation for delivery (SpecificationA484/A484M),
3.1.10 Special requirements (refer to 7.4 and 8.3),
1
8This specification is under the jurisdiction ofASTM CommitteeA01 on Steel,
Stainless Steel and Related Alloys and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee
3
A01.17 on Flat-Rolled and Wrought Stainless Steel. For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
Current edition approved May 1, 2009. Published May 2009. Originally contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
approved in 1966. Last previous edition approved in 2004 as A564/A564M – 04. Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on
DOI: 10.1520/A0564_A0564M-04R09. the ASTM website.
2 4
For ASME Boiler and Pressure Vessel Code applications, see related Specifi- Available from Society of Automotive Engineers (SAE), 400 Commonwealth
cation SA-564/SA-564M in Section II of that Code. Dr., Warrendale, PA 15096-0001, http://www.sae.org.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959, United States.
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
A564/A564M – 04 (2009)
A
TABLE 1 Chemical Requirements
Composition, %
UNS Phospho- Sul- Sili- Alumi- Moly
...
This document is not an ASTM standard and is intended only to provide the user of an ASTM standard an indication of what changes have been made to the previous version. Because
it may not be technically possible to adequately depict all changes accurately, ASTM recommends that users consult prior editions as appropriate. In all cases only the current version
of the standard as published by ASTM is to be considered the official document.
Designation:A 564/A 564M–04 Designation: A564/A564M – 04 (Reapproved 2009)
Standard Specification for
Hot-Rolled and Cold-Finished Age-Hardening Stainless Steel
1
Bars and Shapes
This standard is issued under the fixed designationA564/A564M; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year
of original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval.
A superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
This standard has been approved for use by agencies of the Department of Defense.
1. Scope *
2
1.1 This specification covers bars and shapes of age-hardening stainless steels. Hot-finished or cold-finished rounds, squares,
hexagons, bar shapes, angles, tees, and channels are included; these shapes may be produced by hot rolling, extruding, or forging.
Billets or bars for reforging may be purchased to this specification.
1.2These1.2 These steels are generally used for parts requiring corrosion resistance and high strength at room temperature, or
at temperatures up to 600°F [315°C]; 700°F [370°C] for Type 632; 840°F [450°C] for Type UNS S46910. They are suitable for
machining in the solution-annealed condition after which they may be age-hardened to the mechanical properties specified in
Section 7 without danger of cracking or distortion.Type XM-25 is machinable in the as-received fully heat treated condition.Type
UNS S46910 is suitable for machining in the solution-annealed, cold-worked, and aged-hardened condition.
1.3 Types 631 and 632 contain a large amount of ferrite in the microstructure and can have low ductility in forgings and larger
diameter bars. Applications should be limited to small diameter bar.
1.4 The values stated in either inch-pound units or SI (metric) units are to be regarded separately as standards; within the text
and tables, the SI units are shown in [brackets]. The values stated in each system are not exact equivalents; therefore, each system
must be used independent of the other. Combining values from the two systems may result in nonconformance with the
specification.
1.5 Unless the order specifies an “M’’ designation, the material shall be furnished to inch-pound units.
NOTE1—For forgings, see Specification A 705A 705/A 705M/A 705M. 1—For forgings, see Specification A705/A705M.
NOTE 2—For billets and bars for forging see Specification A 314A314.
2. Referenced Documents
3
2.1 ASTM Standards:
A314 Specification for Stainless Steel Billets and Bars for Forging
A370 Test Methods and Definitions for Mechanical Testing of Steel Products
A484/A484M Specification for General Requirements for Stainless Steel Bars, Billets, and Forgings
A705/A705M Specification for Age-Hardening, Stainless Steel Forgings
A751 Test Methods, Practices, and Terminology for Chemical Analysis of Steel Products
E527 Practice for Numbering Metals and Alloys (UNS) Practice for Numbering Metals and Alloys in the Unified Numbering
System (UNS)
2.2 Other Documents:
4
SAE J1086 Recommended Practice for Numbering Metals and Alloys (UNS)
3. Ordering Information
3.1 It is the responsibility of the purchaser to specify all requirements that are necessary for material ordered under this
specification. Such requirements may include but are not limited to the following:
1
8This specification is under the jurisdiction ofASTM CommitteeA01 on Steel, Stainless Steel,Steel and RelatedAlloys and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee
A01.17 on Flat Stainless Steel Products.
Current edition approved March 1, 2004. Published March 2004. Originally approved in 1966. Last previous edition approved in 2002 as A 564/A 564M–02a.on
Flat-Rolled and Wrought Stainless Steel.
Current edition approved May 1, 2009. Published May 2009. Originally approved in 1966. Last previous edition approved in 2004 as A564/A564M – 04. DOI:
10.1520/A0564_A0564M-04R09.
2
For ASME Boiler and Pressure Vessel Code applications, see related Specification SA-564/SA-564M in Section II of that Code.
3
For referencedASTM standards, visit theASTM website, www.astm.org, or contactASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book ofASTM Standards
volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on the ASTM website.
4
Available from Society of Automotive Engineers (SAE), 400 Commonwealth Dr., Warrendale, PA 15096-0001, http://www.sae.org.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959, United States.
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----
...
This document is not an ASTM standard and is intended only to provide the user of an ASTM standard an indication of what changes have been made to the previous version. Because
it may not be technically possible to adequately depict all changes accurately, ASTM recommends that users consult prior editions as appropriate. In all cases only the current version
of the standard as published by ASTM is to be considered the official document.
Designation:A 564/A 564M–02a Designation: A 564/A 564M – 04 (Reapproved 2009)
Standard Specification for
Hot-Rolled and Cold-Finished Age-Hardening Stainless Steel
1
Bars and Shapes
This standard is issued under the fixed designationA 564/A 564M; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year
of original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval.
A superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
This standard has been approved for use by agencies of the Department of Defense.
1. Scope *
2
1.1 This specification covers bars and shapes of age-hardening stainless steels. Hot-finished or cold-finished rounds, squares,
hexagons, bar shapes, angles, tees, and channels are included; these shapes may be produced by hot rolling, extruding, or forging.
Billets or bars for reforging may be purchased to this specification.
1.2 These steels are generally used for parts requiring corrosion resistance and high strength at room temperature, or at
temperatures up to 600°F [315°C]; 700°F [370°C] for Type 632; 840°F [450°C] for Type UNS S46910. They are suitable for
machining in the solution-annealed condition after which they may be age-hardened to the mechanical properties specified in
Section 7 without danger of cracking or distortion.Type XM-25 is machinable in the as-received fully heat treated condition.Type
UNS S46910 is suitable for machining in the solution-annealed, cold-worked, and aged-hardened condition.
1.3 Types 631 and 632 contain a large amount of ferrite in the microstructure and can have low ductility in forgings and larger
diameter bars. Applications should be limited to small diameter bar.
1.4 The values stated in either inch-pound units or SI (metric) units are to be regarded separately as standards; within the text
and tables, the SI units are shown in [brackets]. The values stated in each system are not exact equivalents; therefore, each system
must be used independent of the other. Combining values from the two systems may result in nonconformance with the
specification.
1.5 Unless the order specifies an “M’’ designation, the material shall be furnished to inch-pound units.
NOTE1—For forgings, see Specification A705/A705M. 1—For forgings, see Specification A 705/A 705M.
NOTE 2—For billets and bars for forging see Specification A 314.
2. Referenced Documents
3
2.1 ASTM Standards:
A 314 Specification for Stainless Steel Billets and Bars for Forging
A 370 Test Methods and Definitions for Mechanical Testing of Steel Products
A 484/A 484M Specification for General Requirements for Stainless Steel Bars, Billets, and Forgings
A 705/A 705M Specification for Age-Hardening, Stainless Steel Forgings
A 751 Test Methods, Practices, and Terminology for Chemical Analysis of Steel Products
E 527 Practice for Numbering Metals and Alloys (UNS) Practice for Numbering Metals and Alloys in the Unified Numbering
System (UNS)
2.2 Other Documents:
4
SAE J1086 Recommended Practice for Numbering Metals and Alloys (UNS)
3. Ordering Information
3.1 It is the responsibility of the purchaser to specify all requirements that are necessary for material ordered under this
specification. Such requirements may include but are not limited to the following:
1
8This specification is under the jurisdiction ofASTM CommitteeA01 on Steel, Stainless Steel,Steel and RelatedAlloys and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee
A01.17 on Flat Stainless Steel Products.
Current edition approved Sept. 10, 2002. Published November 2002. Originally published as A564–66. Last previous edition A564/A564M–02. on Flat-Rolled and
Wrought Stainless Steel.
Current edition approved May 1, 2009. Published May 2009. Originally approved in 1966. Last previous edition approved in 2004 as A 564/A 564M – 04.
2
For ASME Boiler and Pressure Vessel Code applications, see related Specification SA-564/SA-564M in Section II of that Code.
3
For referencedASTM standards, visit theASTM website, www.astm.org, or contactASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book ofASTM Standards
, Vol 01.03.volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on the ASTM website.
4
Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 01.01.
4
Available from Society of Automotive Engineers (SAE), 400 Commonwealth Dr., Warrendale, PA 15096-0001, http://www.sae.org.
*ASummary of Changes section appears at the end of this standard.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 1
...









Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.