ASTM D1478-07
(Test Method)Standard Test Method for Low-Temperature Torque of Ball Bearing Grease
Standard Test Method for Low-Temperature Torque of Ball Bearing Grease
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
This test method was developed using greases having very low torque characteristics at −54°C (−65°F). Specifications for greases of this type commonly require testing at this temperature. Specifications for greases of other types can require testing at temperatures from −75 to −20°C (−100 to 0°F).
This test method has proved helpful in the selection of greases for low-powered mechanisms, such as instrument bearings used in aerospace applications. The suitability of this test method for other applications requiring different greases, speeds, and temperatures should be determined on an individual basis.
Test Method D 4693 may be better suited for applications using larger bearings or greater loads. However, greases having such characteristics that permit torque evaluations by either this test method or Test Method D 4693 will not give the same values in the two test methods (even when converted to the same torque units) because the apparatus and test bearings are different.
FIG. 1 Torque Test Apparatus Assembly
FIG. 2 Drive (Top View)
SCOPE
1.1 This test method covers the determination of the extent to which a grease retards the rotation of a slow-speed ball bearing by measuring starting and running torques at low temperatures (below -20°C (0°F)).
1.1.1 Torque measurements are limited by the capacity of the torque-measuring equipment. Note 1 - When initially developed, the original dynamometer scale limited the torque capacity to approximately 30 000 gcm; the original dynamometer scale is obsolete, however. The suggested replacement scale has not been evaluated; it could extend the limit to approximately 75 000 gcm.
1.2 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as the standard. The values given in parentheses are for information only. The exception is torque values that are given in cgs-metric units, which are universally used in grease specification.
This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use. For specific hazard and warning statements, see 6.1.1, 7.2, 7.4, 8.7, and 8.11.
General Information
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Designation:D1478–07
Standard Test Method for
1
Low-Temperature Torque of Ball Bearing Grease
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D1478; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision.Anumber in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval.A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
This standard has been approved for use by agencies of the Department of Defense.
1. Scope Grease-Lubricated Wheel Bearings
2.2 ANSI/AFBMA Standard:
1.1 This test method covers the determination of the extent
Standard20-1987 Radial Bearings of Ball, Cylindrical,
to which a grease retards the rotation of a slow-speed ball
Roller, and Spherical-Roller Type—Metric Designs (AF-
bearing by measuring starting and running torques at low
3
BMA Code 20BCO2JO)
temperatures (below−20°C (0°F)).
2.3 ASTM Adjuncts:
1.1.1 Torque measurements are limited by the capacity of
4
Standard ball bearings (set of 5 ball bearings)
the torque-measuring equipment.
NOTE 1—When initially developed, the original dynamometer scale 3. Terminology
limited the torque capacity to approximately 30000 g·cm; the original
3.1 Definitions of Terms Specific to This Standard:
dynamometerscaleisobsolete,however.Thesuggestedreplacementscale
3.1.1 low-temperature torque, n—the torque in g·cm re-
has not been evaluated; it could extend the limit to approximately 75000
quired to restrain the outer ring of a No. 6204 size open ball
g·cm.
bearing lubricated with the test grease while the inner ring is
1.2 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as
rotated at 1 6 0.05 r/min at the test temperature.
standard. The values given in parentheses are for information
3.1.2 running torque, n—the 15-s average value of the
only. The exception is torque values that are given in cgs-
torque after rotation for a specified period of time (60 min).
metric units, which are universally used in grease specifica-
3.1.3 starting torque, n—the maximum torque measured at
tions.
the start of rotation.
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
4. Summary of Test Method
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
4.1 ANo. 6204 open ball bearing is packed completely full
priate safety and health practices and determine the applica-
of the test grease and cleaned off flush with the sides. The
bility of regulatory limitations prior to use. For specific hazard
bearing remains stationary while ambient temperature is low-
and warning statements, see 6.1.1, 7.2, 7.4, 8.7, and 8.11.
ered to the test temperature and held there for 2 h. At the end
of this time, the inner ring of the ball bearing is rotated at 1 6
2. Referenced Documents
0.05 r/min while the restraining force on the outer ring is
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
measured.
D4693 Test Method for Low-Temperature Torque of
4.2 Torque is determined by multiplying the restraining
forcebytheradiusofthebearinghousing.Bothstartingtorque
1 and torque after 60 min of rotation (running torque) are
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D02 on
determined.
Petroleum Products and Lubricants and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee
D02.G0.05 on Functional Tests - Temperature.
Current edition approved July 15, 2007. Published August 2007. Originally
approved in 1957. Last previous edition approved in 2002 as D1478–02. DOI:
3
10.1520/D1478-07. Available from AFBMA (Anti-Friction Bearing Manufacturers’ Association),
2
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or 1101 Connecticut Avenue, N.W., Suite 700, Washington, DC 20036–4303.
4
contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM The ball bearing has been standardized by Subcommittee D02.G0. Available
Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on from ASTM International Headquarters. Order Adjunct No. ADJD3336. Original
the ASTM website. adjunct produced in 1984.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959, United States.
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
D1478–07
measuredatapointonthesurfaceofthetestshaftbetweenthe
test bearing and wall of the box shall be not more than 0.5°C
(1°F) above the test temperature.)
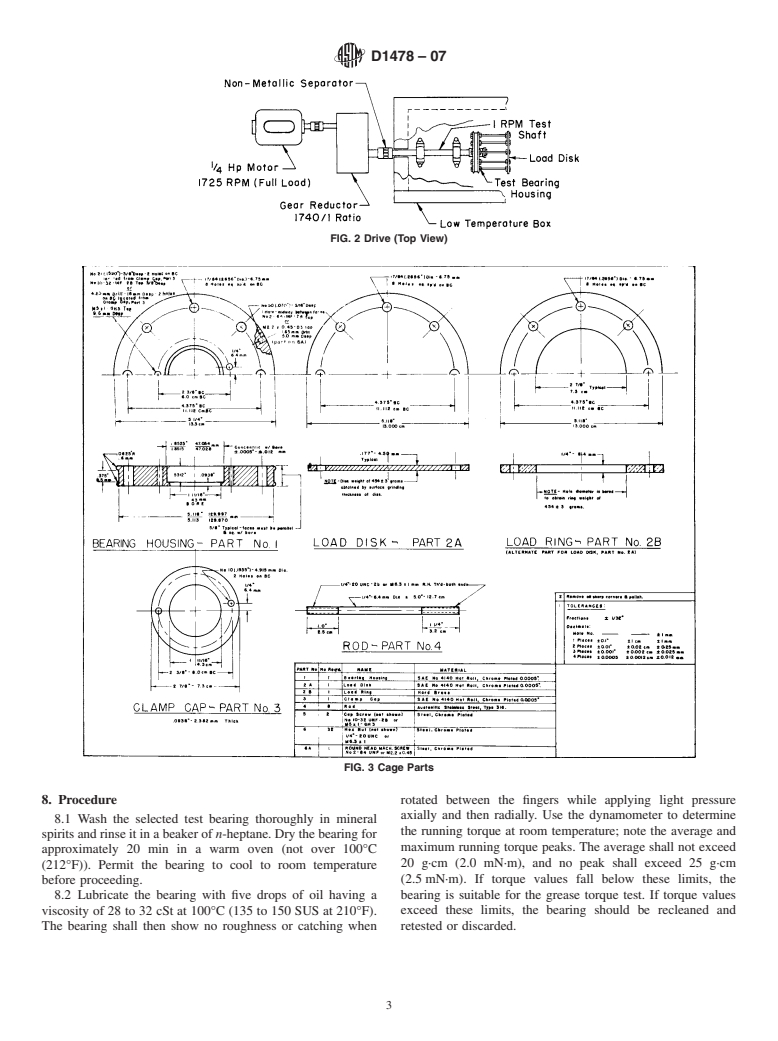
6.1.2 Drive Assembly, as shown in Fig. 2, including drive
motor, gear reductor, and test shaft.The test shaft shall receive
the test bearing against a shoulder having a diameter smaller
than the inner race shoulder of the bearing. Use a spacer
1
washerofthesamediameterandatleast1.6mm( ⁄16in.)thick,
alongwithatestbearinglocknut,toclamptheinnerringofthe
test bearing to the 1 r/min shaft.
6.1.3 Housing (Cag
...







Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.