ASTM E1803-14(2022)
(Test Method)Standard Test Methods for Determining Strength Capacities of Structural Insulated Panels
Standard Test Methods for Determining Strength Capacities of Structural Insulated Panels
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
5.1 SIPs are used as roof, wall, and floor components in building structures. The structural performance properties need to be determined for design purposes.
SCOPE
1.1 These test methods cover procedures for determining strength properties under specified loads for rigid-faced structural insulated panels. These test methods are appropriate for structural insulated panels with rigid facings having a minimum thickness of 0.16 in. (4 mm) and an insulating core with a minimum thickness of 1.5 in. (38 mm). These specified loads include:
1.1.1 Transverse loads,
1.1.2 Axial loads,
1.1.3 Shear loads,
1.1.4 Diaphragm loads,
1.1.5 Uplift loads,
1.1.6 Long Term loads
1.1.7 Impact loads, and
1.1.8 Concentrated loads.
1.2 Structural insulated panels are intended to resist structural loads in permanent building structures.
1.3 These test methods are not intended for quality control purposes and do not evaluate the individual components of the structural insulated panels.
1.4 These test methods are not intended to measure dimensional stability.
1.5 The text of this standard references notes and footnotes, excluding tables and figures, which provide explanatory information. These notes and footnotes shall not be considered requirements of the standard.
1.6 The values stated in inch-pound units are to be regarded as standard. The values given in parentheses are mathematical conversions to SI units that are provided for information only and are not considered standard.
1.7 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety, health, and environmental practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
1.8 This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization established in the Decision on Principles for the Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
General Information
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization established in the Decision on Principles for the
Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
Designation: E1803 −14 (Reapproved 2022)
Standard Test Methods for
Determining Strength Capacities of Structural Insulated
Panels
This standard is issued under the fixed designation E1803; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
priate safety, health, and environmental practices and deter-
1.1 These test methods cover procedures for determining
mine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
strength properties under specified loads for rigid-faced struc-
tural insulated panels. These test methods are appropriate for 1.8 This international standard was developed in accor-
structural insulated panels with rigid facings having a mini- dance with internationally recognized principles on standard-
mum thickness of 0.16 in. (4 mm) and an insulating core with
ization established in the Decision on Principles for the
a minimum thickness of 1.5 in. (38 mm). These specified loads
Development of International Standards, Guides and Recom-
include:
mendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical
1.1.1 Transverse loads,
Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
1.1.2 Axial loads,
1.1.3 Shear loads,
2. Referenced Documents
1.1.4 Diaphragm loads,
2.1 ASTM Standards:
1.1.5 Uplift loads,
D1037 Test Methods for Evaluating Properties of Wood-
1.1.6 Long Term loads
Base Fiber and Particle Panel Materials
1.1.7 Impact loads, and
1.1.8 Concentrated loads. E72 Test Methods of Conducting Strength Tests of Panels
for Building Construction
1.2 Structural insulated panels are intended to resist struc-
E455 Test Method for Static Load Testing of Framed Floor
tural loads in permanent building structures.
or Roof Diaphragm Constructions for Buildings
1.3 These test methods are not intended for quality control
E575 Practice for Reporting Data from Structural Tests of
purposes and do not evaluate the individual components of the
Building Constructions, Elements, Connections, and As-
structural insulated panels.
semblies
1.4 These test methods are not intended to measure dimen-
E631 Terminology of Building Constructions
sional stability.
E695 Test Method of Measuring Relative Resistance of
1.5 The text of this standard references notes and footnotes, Wall, Floor, and Roof Construction to Impact Loading
excluding tables and figures, which provide explanatory infor-
mation. These notes and footnotes shall not be considered
3. Terminology
requirements of the standard.
3.1 Definitions—For definitions of general terms related to
1.6 The values stated in inch-pound units are to be regarded
building construction used in this test method, refer to Termi-
as standard. The values given in parentheses are mathematical
nology E631.
conversions to SI units that are provided for information only
3.2 Definitions of Terms Specific to This Standard:
and are not considered standard.
3.2.1 structural insulated panel (SIP), n—a prefabricated
1.7 This standard does not purport to address all of the
assembly consisting of an insulating core laminated between
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
tworigidfacingssuitabletoresiststructuralloadsinpermanent
building structures.
These test methods are under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee E06 on
Performance of Buildings and are the direct responsibility of Subcommittee E06.11
on Horizontal and Vertical Structures/Structural Performance of Completed Struc-
tures. For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
Current edition approved May 1, 2022. Published May 2022. Originally contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
approved in 1996. Last previous edition approved in 2014 as E1803 – 14. DOI: Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on
10.1520/E1803-14R22. the ASTM website.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
E1803 − 14 (2022)
4. Summary of Test Methods
4.1 SIPs are tested using various structural loading methods
to determine their strength properties for use as elements in
permanent structures.
5. Significance and Use
5.1 SIPs are used as roof, wall, and floor components in
building structures.The structural performance properties need
to be determined for design purposes.
TEST METHODS
6. Transverse Loads for Walls, Roofs, and Floors
6.1 SIPs shall be tested in accordance with Test Methods
E72, Section 11, with the following modifications:
6.2 Support conditions shall closely represent actual con-
struction and the bearing area shall be the minimum area
required by the manufacturer.
6.3 Incremental loads shall be applied.
6.3.1 The deflection shall be recorded at initial load and
after each increase in load increment.
6.4 After 0.75, 1.50, and 2.0 times the anticipated design FIG. 1 Transverse Deflection and Axial Displacement
loadisachieved,decreasetheloadtotheinitialloadandrecord
the set. Continue incremental loads and record the deflections
9. Diaphragm Loads for Floors or Roofs
at each load until further loading risks damage to the deflection
9.1 SIPs shall be tested in accordance with Test Method
measuring devices.
E455 with the following modifications:
6.5 Increase the load continuously until the maximum load
9.2 Cantilever Diaphragm and Simple Beam Diaphragm:
is determined.
NOTE1—Thetestassemblywillbeatleast8 ftby16ft(2.4 mby4.8 m)
7. Axial Loads for Walls
if the smallest element is 4 ft by 8 ft (1.2 m by 2.4 m).
7.1 SIPs shall be tested in accordance with Test Methods
9.2.1 Add to 6.1 of Test Method E455: the diaphragm shall
E72, Section 9, with the following modifications:
contain not less than four individual elements.
9.2.2 Modify paragraph 9.2 of Test Method E455 to read at
7.2 Bearing conditions at the bottom of the SIP shall be
0.75, 1.5, and 2 times the anticipated design load remove the
according to manufacturers’ requirements.
load and measure the recovery after 5 min. Delete the 10 min
7.3 A minimum of one gage at midwidth is required to
requirement to reach full design load.
measure axial displacement and a minimum of one gage
NOTE 2—Because framing inside of SIPs is not accessible for inserting
located at midspan is required to measure transverse displace-
andtighteningnuts,washers,andbolts,smallaccessopeningsthroughone
ment. See Fig. 1.
or both faces may be required.These are acceptable provided qualification
tests conducted with the holes in place.
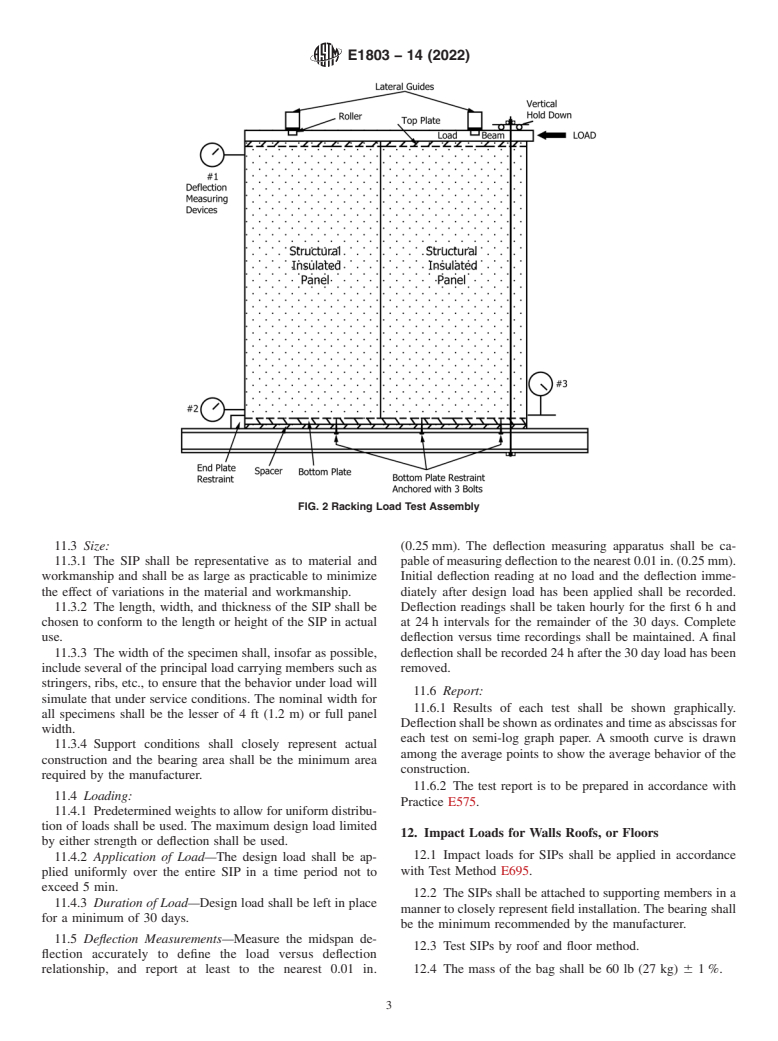
8. Shear Loads for Walls
8.1 SIPs shall be tested in accordance with Test Methods 10. Uplift Resistance for Roof Panels
E72, Section 14, with the following modifications:
10.1 The SIPs and the manufacturer’s recommended fasten-
8.2 The SIP manufacturer’s method for attaching the SIPs ing system shall be tested in accordance with Test Methods
D1037 for fastener head p
...







Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.