ASTM E1730-19
(Specification)Standard Specification for Rigid Foam for Use in Structural Sandwich Panel Cores
Standard Specification for Rigid Foam for Use in Structural Sandwich Panel Cores
ABSTRACT
This specification covers rigid closed-cell polyurethane and polyisocyanurate thermal insulation foams for application in sandwich structural panel cores used in shelter construction for exposure to specified ambient temperatures. The unfaced foam thermal insulation boards are classified into three types (Types 1, 2, 3, and 4) according to increasing nominal density. The morphology of the insulation shall consist of a multitude of individual cells of uniform size and dimension, essentially closed off from each other, homogeneous throughout, free of voids, accumulations of unexpanded material, foreign inclusions, or seams. Upon undergoing appropriate acceptance tests, sampled specimens should adhere accordingly to the limiting values set for the following physical and mechanical properties: density; thermal conductivity; compressive strength; shear strength; percent closed cell; linear and volumetric dimensional stability; flame resistance (extinguish time and burn distance); and impact resistance.
SCOPE
1.1 This specification covers rigid, closed cell, polyurethane and polyisocyanurate thermal insulation for sandwich panels used in shelter construction for exposure to ambient temperatures of −25 to 160 °F (−32 to 71 °C). Painted surfaces of shelters in actual field use reach temperatures of 200 °F (93 °C). The materials in this specification must be capable of withstanding processing, (laminating) temperatures of 230 °F (110 °C).
1.2 The values stated in inch-pound units are to be regarded as standard. The values given in parentheses are mathematical conversions to SI units that are provided for information only and are not considered standard.
1.3 The following precautionary caveat pertains only to the test method portion, Section 12, of this specification: This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety, health, and environmental practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
1.4 This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization established in the Decision on Principles for the Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
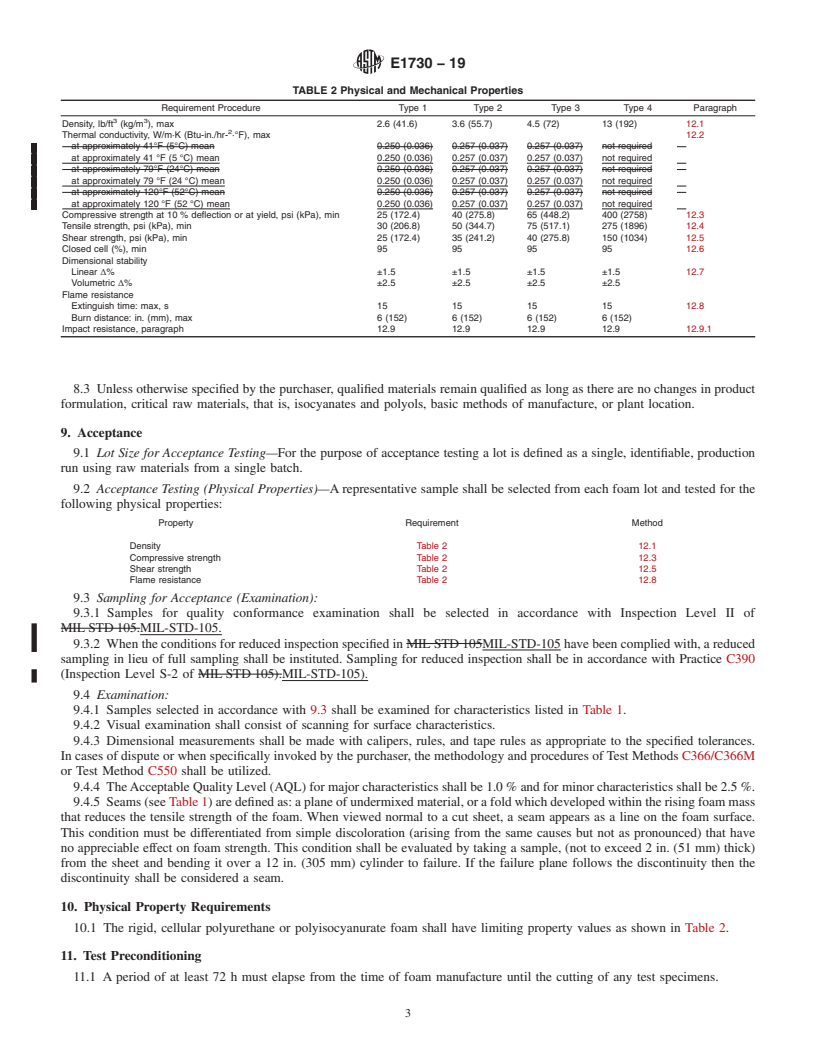
General Information
Relations
Buy Standard
Standards Content (Sample)
This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization established in the Decision on Principles for the
Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
Designation:E1730 −19
Standard Specification for
1
Rigid Foam for Use in Structural Sandwich Panel Cores
This standard is issued under the fixed designation E1730; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision.Anumber in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval.A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
This standard has been approved for use by agencies of the U.S. Department of Defense.
1. Scope C177Test Method for Steady-State Heat Flux Measure-
ments and Thermal Transmission Properties by Means of
1.1 Thisspecificationcoversrigid,closedcell,polyurethane
the Guarded-Hot-Plate Apparatus
and polyisocyanurate thermal insulation for sandwich panels
C273/C273MTestMethodforShearPropertiesofSandwich
used in shelter construction for exposure to ambient tempera-
Core Materials
tures of−25 to 160°F (−32 to 71°C). Painted surfaces of
C366/C366MTest Methods for Measurement of Thickness
shelters in actual field use reach temperatures of 200°F
of Sandwich Cores
(93°C). The materials in this specification must be capable of
C390Practice for Sampling and Acceptance of Thermal
withstanding processing, (laminating) temperatures of 230°F
Insulation Lots
(110°C).
C518Test Method for Steady-State Thermal Transmission
1.2 The values stated in inch-pound units are to be regarded
Properties by Means of the Heat Flow Meter Apparatus
as standard. The values given in parentheses are mathematical
C550Test Method for Measuring Trueness and Squareness
conversions to SI units that are provided for information only
of Rigid Block and Board Thermal Insulation
and are not considered standard.
D883Terminology Relating to Plastics
1.3 The following precautionary caveat pertains only to the
D1621Test Method for Compressive Properties of Rigid
test method portion, Section 12, of this specification: This Cellular Plastics
standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns,
D1622/D1622MTest Method forApparent Density of Rigid
if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user Cellular Plastics
of this standard to establish appropriate safety, health, and
D1623Test Method for Tensile and Tensile Adhesion Prop-
environmental practices and determine the applicability of erties of Rigid Cellular Plastics
regulatory limitations prior to use.
D2126Test Method for Response of Rigid Cellular Plastics
1.4 This international standard was developed in accor-
to Thermal and Humid Aging
dance with internationally recognized principles on standard- D2856TestMethodforOpen-CellContentofRigidCellular
3
ization established in the Decision on Principles for the
Plastics by the Air Pycnometer (Withdrawn 2006)
Development of International Standards, Guides and Recom- E631Terminology of Building Constructions
mendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical
E1749Terminology Relating to Rigid Wall Relocatable
Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee. Shelters
4
2.2 Code of Federal Regulations Aeronautics and Space:
2. Referenced Documents
14 CFR25.853(Federal Air Regulation 25.853) Compart-
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
ment Interior (Amend. 25-72)
C165TestMethodforMeasuringCompressivePropertiesof
5
2.3 Federal Standard:
Thermal Insulations
QQ-A-250/11 Aluminum Alloy 6061-T6 Plate and Sheet
C168Terminology Relating to Thermal Insulation
5
2.4 Military Standard:
MIL-STD-105Sampling Procedures and Tables for Inspec-
1
tion by Attributes
This specification is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee E06 on
Performance of Buildings and is under the direct responsibility of Subcommittee
E06.53 on Materials and Processes for Durable Rigidwall Relocatable Structures.
Current edition approved July 1, 2019. Published August 2019. Originally
3
approved in 1995. Last previous edition approved in 2015 as E1730–15. DOI: The last approved version of this historical standard is referenced on
10.1520/E1730–19. www.astm.org.
2 4
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or Available from U.S. Government Publishing Office, 732 N. Capitol St., NW,
contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM Washington, DC 20401-0001, http://www.gpo.gov.
5
Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on Available from DLA Document Services, Building 4/D, 700 Robbins Ave.,
the ASTM website. Philadelphia, PA 19111-5094, http://quicksearch.dla.mil.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
E1730−
...
This document is not an ASTM standard and is intended only to provide the user of an ASTM standard an indication of what changes have been made to the previous version. Because
it may not be technically possible to adequately depict all changes accurately, ASTM recommends that users consult prior editions as appropriate. In all cases only the current version
of the standard as published by ASTM is to be considered the official document.
Designation: E1730 − 15 E1730 − 19
Standard Specification for
1
Rigid Foam for Use in Structural Sandwich Panel Cores
This standard is issued under the fixed designation E1730; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
This standard has been approved for use by agencies of the U.S. Department of Defense.
1. Scope
1.1 This specification covers rigid, closed cell, polyurethane and polyisocyanurate thermal insulation for sandwich panels used
in shelter construction for exposure to ambient temperatures of −25°of −25 to 160°F (−32°160 °F (−32 to 71°C).71 °C). Painted
surfaces of shelters in actual field use reach temperatures of 200°F (93°C).200 °F (93 °C). The materials in this specification must
be capable of withstanding processing, (laminating) temperatures of 230°F (110°C).230 °F (110 °C).
1.2 The values stated in inch-pound units are to be regarded as standard. The values given in parentheses are mathematical
conversions to SI units that are provided for information only and are not considered standard.
1.3 The following precautionary caveat pertains only to the test method portion, Section 12, of this specification:This standard
does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this
standard to establish appropriate safety safety, health, and healthenvironmental practices and determine the applicability of
regulatory limitations prior to use.
1.4 This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization
established in the Decision on Principles for the Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued
by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
2. Referenced Documents
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
C165 Test Method for Measuring Compressive Properties of Thermal Insulations
C168 Terminology Relating to Thermal Insulation
C177 Test Method for Steady-State Heat Flux Measurements and Thermal Transmission Properties by Means of the
Guarded-Hot-Plate Apparatus
C273/C273M Test Method for Shear Properties of Sandwich Core Materials
C366/C366M Test Methods for Measurement of Thickness of Sandwich Cores
C390 Practice for Sampling and Acceptance of Thermal Insulation Lots
C518 Test Method for Steady-State Thermal Transmission Properties by Means of the Heat Flow Meter Apparatus
C550 Test Method for Measuring Trueness and Squareness of Rigid Block and Board Thermal Insulation
D883 Terminology Relating to Plastics
D1621 Test Method for Compressive Properties of Rigid Cellular Plastics
D1622/D1622M Test Method for Apparent Density of Rigid Cellular Plastics
D1623 Test Method for Tensile and Tensile Adhesion Properties of Rigid Cellular Plastics
D2126 Test Method for Response of Rigid Cellular Plastics to Thermal and Humid Aging
3
D2856 Test Method for Open-Cell Content of Rigid Cellular Plastics by the Air Pycnometer (Withdrawn 2006)
E631 Terminology of Building Constructions
E1749 Terminology Relating to Rigid Wall Relocatable Shelters
4
2.2 Code of Federal Regulations Aeronautics and Space:
14 CFR 25.853 CFR 25.853 (Federal Air Regulation 25.853) Compartment Interior (Amend. 25-72)
1
This specification is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee E06 on Performance of Buildings and is under the direct responsibility of Subcommittee E06.53 on
Materials and Processes for Durable Rigidwall Relocatable Structures.
Current edition approved May 1, 2015July 1, 2019. Published August 2015August 2019. Originally approved in 1995. Last previous edition approved in 20092015 as
E1730 – 09.E1730–15. DOI: 10.1520/E1730-15.10.1520/E1730–19.
2
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM Standards
volume information, refer to the standard’sstandard’s Document Summary page on the ASTM website.
3
The last approved version of this historical standard is referenced on www.astm.org.
4
Available from U.S. Government Publishing Office, 732 N. Capitol St., NW, Washington, DC 20401-0001, http://www.gpo.gov.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 -------------------
...










Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.