ASTM D5752-10
(Specification)Standard Specification for Supplemental Coolant Additives (SCAs) for Use in Precharging Coolants for Heavy-Duty Engines
Standard Specification for Supplemental Coolant Additives (SCAs) for Use in Precharging Coolants for Heavy-Duty Engines
ABSTRACT
This specification covers the general, physical, chemical, and performance requirements for supplemental coolant additives for use as precharging coolants in the cooling systems of heavy-duty engines. Test solutions shall be standard corrosive water, ethylene or propylene glycol in standard corrosive water, and NaCl dissolved in a solution of glycol in deionized water. These test solutions shall comply to the specific limits for the following requirements: corrosion in glassware mass loss; simulated service test mass loss; foaming; water pump cavitation erosion-corrosion rating; corrosion of cast aluminum alloys at heat-rejecting surfaces; ultrasonic cavitation resistance; supplemental coolant additive-glycol base coolant compatibility; hot surface scaling and deposits resistance; effect on nonmetals; storage stability; ash, chloride ion, and silicon contents; pH in distilled water; reserve alkalinity; and the effect on vehicle finish.
SCOPE
1.1 This specification covers the general, physical, chemical, and performance requirements for Supplemental Coolant Additives (SCAs) at a precharged level in the cooling systems of heavy-duty engines.
Note 1—After precharging, SCAs are customarily used periodically to service cooling systems at ¼ to 1/3 the precharged dosage to compensate for additives lost through dilution and depletion.
1.2 The SCA products meeting this specification are intended for use with water, with recommended dilutions of coolant concentrates, with prediluted engine coolants, or to upgrade the performance of light-duty engine coolants to meet the heav-duty requirements of Specification D6210. Engine coolant products shall be of the low-silicate type and, if ethylene glycol based, shall meet Specification D4985. Propylene glycol base low-silicate type coolant products may also be used, if these materials meet the chemical and performance requirements of Specification D4985.
1.3 The SCA concentrate, before dissolution, may be in either liquid, solid, or slurry form. The form is as agreed upon between the manufacturer and the user.
1.4 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as standard. The inch-pound units in parentheses are approximate equivalents provided for information only.
1.5 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
General Information
Relations
Buy Standard
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Designation:D5752 −10
Standard Specification for
Supplemental Coolant Additives (SCAs) for Use in
1,2
Precharging Coolants for Heavy-Duty Engines
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D5752; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision.Anumber in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval.A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope* 2. Referenced Documents
3
1.1 This specification covers the general, physical, 2.1 ASTM Standards:
chemical, and performance requirements for Supplemental D512Test Methods for Chloride Ion In Water
CoolantAdditives (SCAs) at a precharged level in the cooling D516Test Method for Sulfate Ion in Water
systems of heavy-duty engines. D1119Test Method for Percent Ash Content of Engine
Coolants
NOTE 1—After precharging, SCAs are customarily used periodically to
D1121Test Method for Reserve Alkalinity of Engine Cool-
1 1
service cooling systems at ⁄4 to ⁄3 the precharged dosage to compensate
ants and Antirusts
for additives lost through dilution and depletion.
D1126Test Method for Hardness in Water
1.2 The SCA products meeting this specification are in-
D1193Specification for Reagent Water
tended for use with water, with recommended dilutions of
D1287TestMethodforpHofEngineCoolantsandAntirusts
coolant concentrates, with prediluted engine coolants, or to
D1293Test Methods for pH of Water
upgrade the performance of light-duty engine coolants to meet
D1384Test Method for Corrosion Test for Engine Coolants
the heav-duty requirements of Specification D6210. Engine
in Glassware
coolant products shall be of the low-silicate type and, if
D1881Test Method for Foaming Tendencies of Engine
ethyleneglycolbased,shallmeetSpecificationD4985.Propyl-
Coolants in Glassware
ene glycol base low-silicate type coolant products may also be
D1882Test Method for Effect of Cooling System Chemical
used, if these materials meet the chemical and performance
Solutions on Organic Finishes for Automotive Vehicles
requirements of Specification D4985.
D2570TestMethodforSimulatedServiceCorrosionTesting
1.3 The SCA concentrate, before dissolution, may be in
of Engine Coolants
either liquid, solid, or slurry form. The form is as agreed upon
D2809Test Method for Cavitation Corrosion and Erosion-
between the manufacturer and the user.
Corrosion Characteristics of Aluminum Pumps With En-
gine Coolants
1.4 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as
standard.The inch-pound units in parentheses are approximate D3634Test Method for Trace Chloride Ion in Engine Cool-
ants
equivalents provided for information only.
D4327Test Method forAnions in Water by Suppressed Ion
1.5 This standard does not purport to address all of the
Chromatography
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
D4340Test Method for Corrosion of CastAluminumAlloys
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
in Engine Coolants Under Heat-Rejecting Conditions
priate safety and health practices and determine the applica-
D4985Specification for Low Silicate Ethylene Glycol Base
bility of regulatory limitations prior to use.
Engine Coolant for Heavy Duty Engines Requiring a
Pre-Charge of Supplemental Coolant Additive (SCA)
1
ThisspecificationisunderthejurisdictionofASTMCommitteeD15onEngine
D5827Test Method for Analysis of Engine Coolant for
Coolants and Related Fluids and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee
Chloride and Other Anions by Ion Chromatography
D15.07 on Specifications.
Current edition approved April 1, 2010. Published May 2010. Originally
3
approved in 1995. Last previous edition approved in 2005 as D5752-05. DOI: For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
10.1520/D5752-10. contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
2
Supporting data have been filed atASTM International Headquarters and may Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on
be obtained by requesting Research Report: RR:D15-1024. the ASTM website.
*A Summary of Changes section appears at the end of this standard
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
D5752−10
D5828Test Method for Compatibility of Supplemental SCAs be used only in conjunction with coolant products
Coolant Additives (SCAs) and Engine Coolant Concen- meeting Specification D4985.
trates
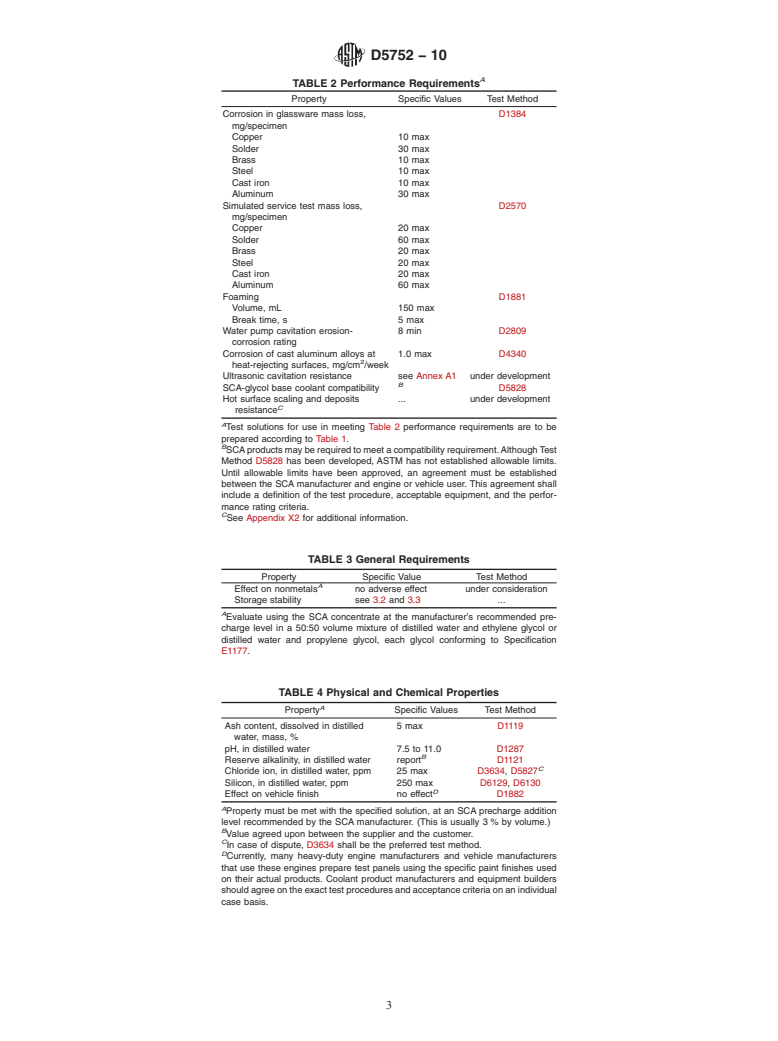
4. Preparation of Test Solutions
D6129Test Method for Silicon in Engine Coolant Concen-
4.1 The preparation of test solutions for this specification is
trates by Atomic Absorption Spectroscopy
listed in Table 1. The glycol used, either ethylene gly
...
This document is not anASTM standard and is intended only to provide the user of anASTM standard an indication of what changes have been made to the previous version. Because
it may not be technically possible to adequately depict all changes accurately, ASTM recommends that users consult prior editions as appropriate. In all cases only the current version
of the standard as published by ASTM is to be considered the official document.
Designation:D5752–05 Designation: D5752 – 10
Standard Specification for
Supplemental Coolant Additives (SCAs) for Use in
,
1 2
Precharging Coolants for Heavy-Duty Engines
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D5752; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision.Anumber in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval.A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope*
1.1 This specification covers the general, physical, chemical, and performance requirements for Supplemental Coolant
Additives (SCAs) at a precharged level in the cooling systems of heavy-duty engines.
1 1
NOTE 1—After precharging, SCAs are customarily used periodically to service cooling systems at ⁄4 to ⁄3 the precharged dosage to compensate for
additives lost through dilution and depletion.
1.2 The SCA products meeting this specification are intended for use with water, with recommended dilutions of coolant
concentrates, with prediluted engine coolants, or to upgrade the performance of light-duty engine coolants to meet the heav-duty
requirements of Specification D6210. Engine coolant products shall be of the low-silicate type and, if ethylene glycol based, shall
meet Specification D4985. Propylene glycol base low-silicate type coolant products may also be used, if these materials meet the
chemical and performance requirements of Specification D4985.
1.3 TheSCAconcentrate,beforedissolution,maybeineitherliquid,solid,orslurryform.Theformisasagreeduponbetween
the manufacturer and the user.
1.4 ThevaluesstatedinSIunitsaretoberegardedasstandard.Theinch-poundunitsinparenthesesareapproximateequivalents
provided for information only.
1.5 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility
of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory
limitations prior to use.
2. Referenced Documents
3
2.1 ASTM Standards:
D512 Test Methods for Chloride Ion In Water
D516 Test Method for Sulfate Ion in Water
D1119 Test Method for Percent Ash Content of Engine Coolants
D1121 Test Method for Reserve Alkalinity of Engine Coolants and Antirusts
D1126 Test Method for Hardness in Water
D1193 Specification for Reagent Water
D1287 Test Method for pH of Engine Coolants and Antirusts
D1293 Test Methods for pH of Water
D1384 Test Method for Corrosion Test for Engine Coolants in Glassware
D1881 Test Method for Foaming Tendencies of Engine Coolants in Glassware
D1882 Test Method for Effect of Cooling System Chemical Solutions on Organic Finishes forAutomotiveVehiclesD1888Test
Meth-
ods
for
Par-
ticu-
late
and
1
This specification is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D15 on Engine Coolants and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee D15.07 on Specifications.
Current edition approved Oct.April 1, 2005.2010. Published November 2005.May 2010. Originally approved in 1995. Last previous edition approved in 20042005 as
D5752-04a.D5752-05. DOI: 10.1520/D5752-105.
2
A research report is available from ASTM headquarters. Request: D15-1024.
3
ForreferencedASTMstandards,visittheASTMwebsite,www.astm.org,orcontactASTMCustomerServiceatservice@astm.org.ForAnnualBookofASTMStandards
volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on the ASTM website.
*ASummary of Changes section appears at the end of this standard.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959, United States.
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
D5752 – 10
Dis-
solved
Mat-
ter in
Water
D2570 Test Method for Simulated Service Corrosion Testing of Engine Coolants
D2809 TestMethodforCavitationCorrosionandErosion-CorrosionCharacteristicsofAluminumPumpsWithEngineCoolants
D3634 Test Method for Trace Chloride Ion in Engine Coolants
D4327 Test Method for Anions in Water by Chemically Suppressed Ion Chromatography
D4340 Test Method for Corrosion of Cast Aluminum Alloys in Engine Coolants Under Heat-Rejecting Conditions
D4985 Specification for Low Silicate Ethylene Glycol Base Engine Coolant for Heavy Duty Engines Requiring a Pre-Charge
of Supplemental Coolant Additive (SCA)
D5827 Test Method for Analysis of Engine Coolant for Chloride and Other Anions by Ion Chromatography
D5828 Test Method for Compatibility of Supplemental Coolant Additives (SCAs) and Engine Coolant Concentrates
D6129 Test Me
...








Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.