ASTM D3120-06e1
(Test Method)Standard Test Method for Trace Quantities of Sulfur in Light Liquid Petroleum Hydrocarbons by Oxidative Microcoulometry
Standard Test Method for Trace Quantities of Sulfur in Light Liquid Petroleum Hydrocarbons by Oxidative Microcoulometry
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
This test method is used to determine the concentration of sulfur in light liquid hydrocarbons, gasoline, and diesels and their additives, where such concentrations of sulfur can be detrimental to their production, performance, and use. The measurement of sulfur in the production and final product of gasoline and diesel is required for both regulatory purposes and to ensure maximum life expectancy of catalytic converters used in the automotive industry.
SCOPE
1.1 This test method covers the determination of sulfur concentration in the range from 3.0 to 1000 mg/kg in light liquid hydrocarbons boiling in the range from 26 to 274°C (80 to 525°F).
1.2 Other materials falling within the distillation range specified in 1.1, but having sulfur concentrations above 1000 mg/kg, may be tested using appropriate dilutions to bring them within the specified limit. In addition, sample types that may be outside the specified distillation range, such as diesels and biodiesels, may be analyzed by this test method.
1.3 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as the standard. The values given in parentheses are provided for information only. The preferred units are milligrams per kilogram (mg/kg).
1.4 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use. For specific hazard statements, see Sections 7-9.
General Information
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
An American National Standard
e1
Designation:D3120–06
Standard Test Method for
Trace Quantities of Sulfur in Light Liquid Petroleum
1
Hydrocarbons by Oxidative Microcoulometry
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D3120; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision.Anumber in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval.A
superscript epsilon (e) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
This standard has been approved for use by agencies of the Department of Defense.
1
e NOTE—Eq X2.2 was corrected editorially in April 2007.
1. Scope* D4057 Practice for Manual Sampling of Petroleum and
Petroleum Products
1.1 This test method covers the determination of sulfur
D4177 Practice for Automatic Sampling of Petroleum and
concentration in the range from 3.0 to 1000 mg/kg in light
Petroleum Products
liquid hydrocarbons boiling in the range from 26 to 274°C (80
D6299 Practice forApplying Statistical QualityAssurance
to 525°F).
Techniques to Evaluate Analytical Measurement System
1.2 Other materials falling within the distillation range
Performance
specified in 1.1, but having sulfur concentrations above 1000
2.2 OSHA Regulations:
mg/kg,maybetestedusingappropriatedilutionstobringthem
OSHA Regulations 29 CFR, paragraphs 1910.1000 and
withinthespecifiedlimit.Inaddition,sampletypesthatmaybe
3
1910.1200
outside the specified distillation range, such as diesels and
biodiesels, may be analyzed by this test method.
3. Summary of Test Method
1.3 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as the
3.1 A liquid sample is introduced into a pyrolysis tube
standard. The values given in parentheses are provided for
maintained at a temperature between 900-1200°C, having a
information only. The preferred units are milligrams per
flowing stream of gas containing 50-80% oxygen and 20-50%
kilogram (mg/kg).
inertgas(forexample,argon,helium,etc.)Oxidativepyrolysis
1.4 This standard does not purport to address all of the
converts the sulfur to sulfur dioxide, which then flows into a
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
titration cell where it reacts with triiodide ion present in the
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
electrolyte. The triiodide ion consumed is coulometrically
priate safety and health practices and determine the applica-
replaced and the total current (I 3 t) required to replace it is a
bility of regulatory limitations prior to use. For specific hazard
measure of the sulfur present in the sample.
statements, see Sections 7-9.
3.2 The reaction occurring in the titration cell as sulfur
2. Referenced Documents dioxide enters is:
2
2 2 1
2.1 ASTM Standards:
I 1SO 1H O→SO 13I 12H (1)
3 2 2 3
D1193 Specification for Reagent Water
The triiodide ion consumed in the above reaction is gener-
D1298 TestMethodforDensity,RelativeDensity(Specific
ated coulometrically thus:
Gravity), or API Gravity of Crude Petroleum and Liquid
2 2 2
3I →I 12e (2)
Petroleum Products by Hydrometer Method
3
D4052 Test Method for Density and Relative Density of
3.3 These microequivalents of triiodide ion (iodine) are
Liquids by Digital Density Meter
equal to the number of microequivalents of titratable SO ion
2
entering the titration cell.
1
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D02 on
4. Significance and Use
PetroleumProductsandLubricantsandisthedirectresponsibilityofSubcommittee
D02.03 on Elemental Analysis.
4.1 This test method is used to determine the concentration
Current edition approved Dec. 1, 2006. Published January 2007. Originally
ofsulfurinlightliquidhydrocarbons,gasoline,anddieselsand
approved in 1972. Last previous edition approved in 2003 as D3120–03a.
2
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
3
Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on Available from U.S. Government Printing Office, Superintendent of Docu-
the ASTM website. ments, 732 N. Capitol St., NW, Mail Stop: SDE, Washington, DC 20401.
*A Summary of Changes section appears at the end of this standard.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959, United States.
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
e1
D3120–06
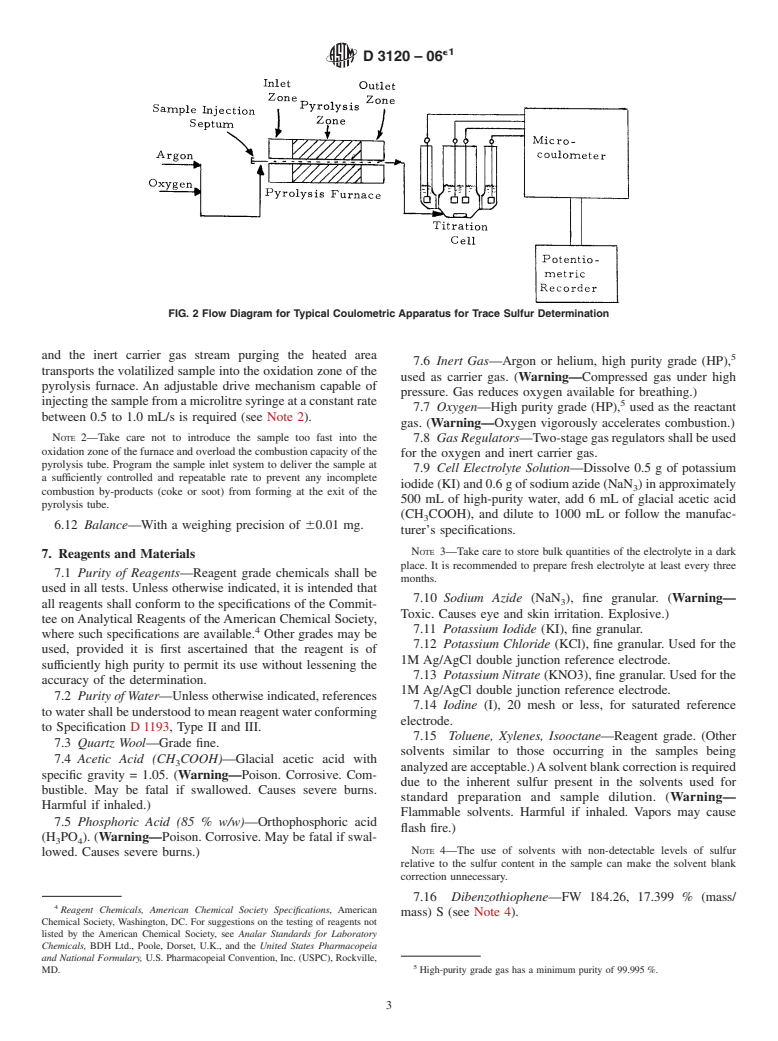
mixing, which can be accomplished with a magnetic stir bar,
stream of gas, or other suitable means. Other sensor and
reference electrodes may be used if they meet the performance
criteria of this test method.
NOTE 1—Take care not to use excessive stirring and possibly damage
theelectrodeswiththestirbar.Thecreationofaslightvortexisadequate.
6.6 Microcoulometer—The apparatus’ microcoulometer,
FIG.
...







Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.