ASTM A1000-05
(Specification)Standard Specification for Steel Wire, Carbon and Alloy Specialty Spring Quality
Standard Specification for Steel Wire, Carbon and Alloy Specialty Spring Quality
ABSTRACT
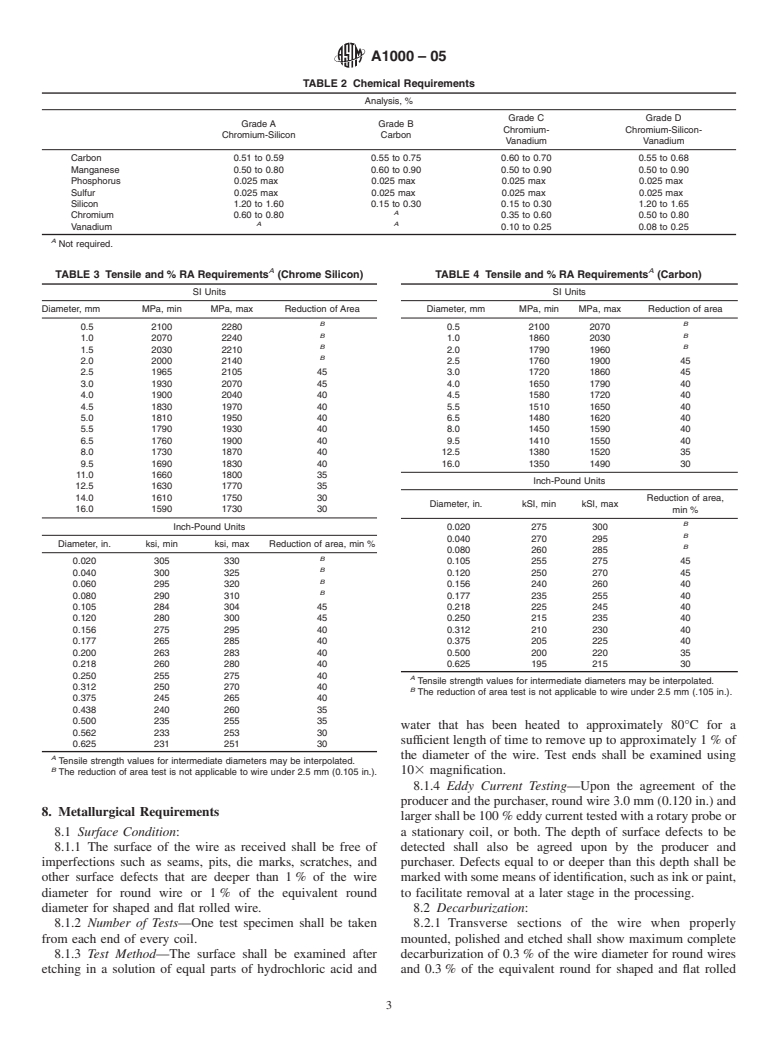
This specification covers round, shaped and flat rolled plain carbon and alloy steel spring wires, uniform in quality and temper, intended for the manufacture of mechanical springs that can withstand moderate fatigue stresses over some relatively low number of cycles. This wire shall be either in the annealed and cold-drawn or oil-tempered conditions. The steel may be made by any commercially accepted steel making process in either ingot cast or strand cast form. The percentage of the following elements: carbon, manganese, phosphorus, sulfur, silicon, chromium, and vanadium, shall conform to the chemical composition requirements and be determined by heat analysis. Tensile and wrap tests shall conform to the mechanical requirements such as tensile strength. Metallurgical requirements including eddy current testing for etched surface, decarburization, and inclusion content are detailed.
SCOPE
1.1 This specification covers a quality of round and shaped plain carbon and alloy steel spring wire, uniform in quality and temper, intended for the manufacture of mechanical springs that can withstand moderate fatigue stresses over some relatively low number of cycles. The quality level is between the commercial quality grades of wire such as Specifications A 401/A 401M, A 231/A 231M, and A 229/A 229M and the valve spring quality grades such Specifications as A 230/A 230M, A 232/A 232M, A 877/A 877M and A 878/A 878M. It is similar to the grade TD (referenced in EN 10270-2) intended for medium fatigue levels, such as required for clutch springs. This wire shall be either in the annealed and cold-drawn or oil-tempered condition as specified by purchaser.
1.2 The values stated in either SI units or inch-pound units are to be regarded separately as standard. Within the text, the inch-pound units are shown in parentheses. The values stated in each system are not exact equivalents; therefore, each system must be used independent of the other.
General Information
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Designation: A1000 – 05
Standard Specification for
1
Steel Wire, Carbon and Alloy Specialty Spring Quality
This standard is issued under the fixed designation A1000; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope* ods for Steel Products for Shipment
A751 Test Methods, Practices, andTerminology for Chemi-
1.1 This specification covers a quality of round and shaped
cal Analysis of Steel Products
plain carbon and alloy steel spring wire, uniform in quality and
A877/A877M Specification for Steel Wire, Chromium-
temper, intended for the manufacture of mechanical springs
Silicon Alloy Valve Spring Quality
that can withstand moderate fatigue stresses over some rela-
A878/A878M Specification for Steel Wire, Modified Chro-
tively low number of cycles. The quality level is between the
mium Vanadium Valve Spring Quality
commercial quality grades of wire such as Specifications
A941 Terminology Relating to Steel, Stainless Steel, Re-
A401/A401M,A231/A231M, andA229/A229M and the valve
lated Alloys, and Ferroalloys
spring quality grades such Specifications as A230/A230M,
E29 Practice for Using Significant Digits in Test Data to
A232/A232M,A877/A877M andA878/A878M. It is similar to
Determine Conformance with Specifications
the gradeTD (referenced in EN 10270-2) intended for medium
E45 Test Methods for Determining the Inclusion Content of
fatigue levels, such as required for clutch springs. This wire
Steel
shall be either in the annealed and cold-drawn or oil-tempered
2.2 Federal Standard:
condition as specified by purchaser.
3
Fed. Std. No. 123 Marking for Shipment (Civil Agencies)
1.2 The values stated in either SI units or inch-pound units
2.3 Military Standard:
are to be regarded separately as standard. Within the text, the
MIL-STD-163 Steel Mill Products, Preparation for Ship-
inch-pound units are shown in parentheses. The values stated
3
ment and Storage
in each system are not exact equivalents; therefore, each
2.4 AIAG Standard:
system must be used independent of the other.
AIAG B-5 02.00 Primary Metals Identification Tag Appli-
4
2. Referenced Documents
cation Standard
2
2.5 European Standard:
2.1 ASTM Standards:
EN 10270-2 Steel Wire for Mechanical Springs Part 2:
A229/A229M Specification for Steel Wire, Oil-Tempered
Oil-Hardened and Tempered Springsteel Wire of Unal-
for Mechanical Springs
5
loyed and Alloyed Steels
A230/A230M Specification for Steel Wire, Oil-Tempered
Carbon Valve Spring Quality
3. Terminology
A231/A231M Specification for Chromium-VanadiumAlloy
3.1 Definitions:
Steel Spring Wire
3.1.1 For definition of terms used in this specification, see
A232/A232M Specification for Chromium-VanadiumAlloy
Terminology A941.
Steel Valve Spring Quality Wire
3.2 Definitions of Terms Specific to This Standard:
A370 Test Methods and Definitions for Mechanical Testing
3.2.1 commercial quality wire—a grade of wire that is fairly
of Steel Products
common quality and intended for applications that are primar-
A401/A401M Specification for Steel Wire, Chromium-
ily static in nature, not involving significant fatigue loading.
Silicon Alloy
A700 PracticesforPackaging,Marking,andLoadingMeth-
4. Ordering Information
4.1 It shall be the responsibility of the purchaser to specify
1
This specification is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee A01 on Steel,
all requirements that are necessary for material under this
Stainless Steel and Related Alloys and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee
A01.03 on Steel Rod and Wire.
Current edition approved Jan. 1, 2005. Published January 2005. Originally
3
approved in 1999. Last previous edition approved in 1999 as A1000 – 99. DOI: Available from Standardization Documents Order Desk, DODSSP, Bldg. 4,
10.1520/A1000-05. Section D, 700 Robbins Ave., Philadelphia, PA 19111-5098
2 4
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or Available fromAutomotive IndustryAction Group (AIAG), 26200 Lahser Rd.,
contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM Suite 200, Southfield, MI 48034.
5
Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on Available from European Committee for Standardization, rue de Stassart
the ASTM website. 36,B-1050 Brussels
*A Summary of Changes section appears at the end of this standard.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959, United States.
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
A1000 – 05
specification. Such requirements may include, but are not 6.3 Product Analysis—An analysis may be made by the
limited to the follow
...







Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.