ASTM D7641-21
(Guide)Standard Guide for Textile Fibers
Standard Guide for Textile Fibers
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
4.1 This guide is intended for use as a reference to improve the understanding of the relationship between commercial name, fiber identification and geographical regions of fiber origins that make up the composition of textile products.
4.2 This guide is intended to be used as a source of information only.
4.2.1 Detailed analysis, to verify specific data related to the composition of a particular fiber, may be necessary.
SCOPE
1.1 This guide lists fibers used to manufacture textile products.
1.2 Specific groups of fibers are identified using tables of standard classification.
1.2.1 Animal fibers are identified by commercial name, biological name, end use, and geographic source.
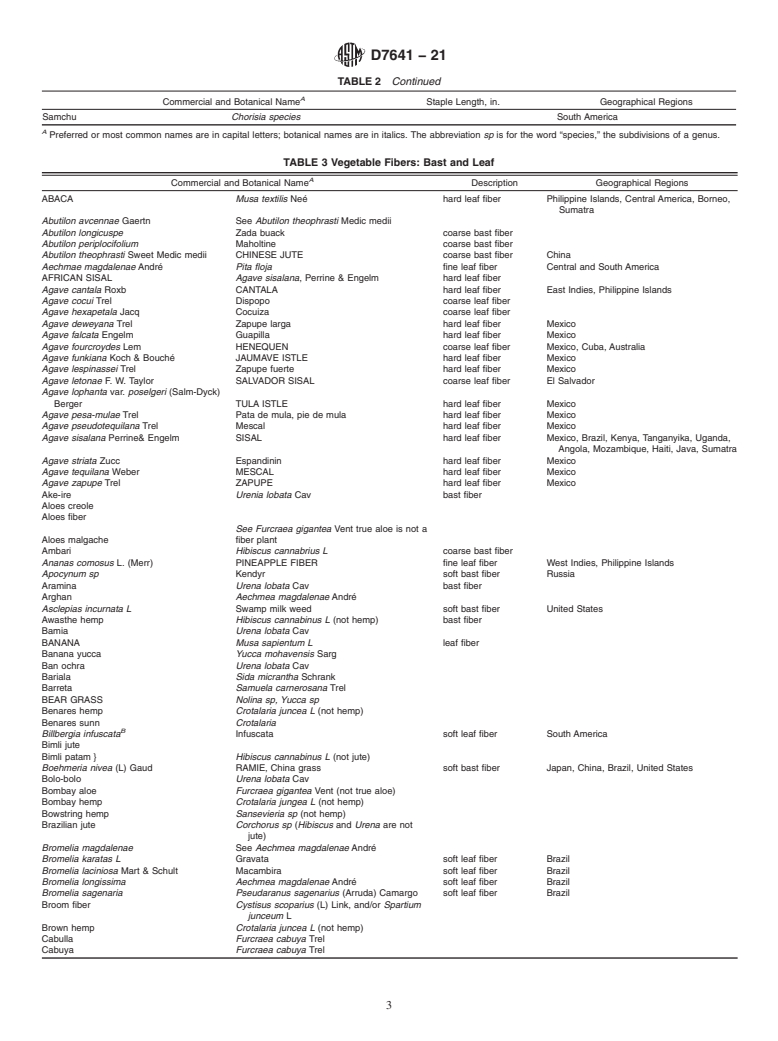
1.2.2 Vegetable fibers are identified by commercial name, botanical name, staple length or description, and geographic source.
1.2.3 Mineral fibers are identified by commercial name, mineralogical name, chemical description, and geographic source.
1.2.4 Manufactured fibers are identified by commercial name, generic name, and major component.
1.3 Major fiber types used for textile purposes are further classified.
1.3.1 Manufactured fibers are identified as having either an organic base or inorganic base.
1.3.2 Natural fibers are identified as having a cellulosic, protein, or mineral base.
1.4 A glossary of generic names and definitions for manufactured fibers is included as additional information.
1.5 This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization established in the Decision on Principles for the Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
General Information
Standards Content (Sample)
This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization established in the Decision on Principles for the
Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
Designation: D7641 − 21
Standard Guide for
1
Textile Fibers
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D7641; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope 2. Referenced Documents
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
1.1 This guide lists fibers used to manufacture textile
D123 Terminology Relating to Textiles
products.
2.2 ISO Standards:
1.2 Specific groups of fibers are identified using tables of
ISO 2076:1999 (E) Textiles–Man-made Fibers–Generic
standard classification.
Names
2.3 Other Documents:
1.2.1 Animal fibers are identified by commercial name,
Code of Federal Regulations, Title 16, Section 303.7
biological name, end use, and geographic source.
1.2.2 Vegetable fibers are identified by commercial name,
3. Terminology
botanical name, staple length or description, and geographic
3.1 Definitions:
source.
3.1.1 plastic, n—as related to textiles, a polymer which can
1.2.3 Mineral fibers are identified by commercial name,
be combined with curatives, plasticizers, and fillers that can be
mineralogical name, chemical description, and geographic
molded under heat and pressure.
source.
3.1.1.1 Discussion—General – One of a large group of
1.2.4 Manufactured fibers are identified by commercial
organic compounds synthesized from cellular hydrocarbons,
name, generic name, and major component.
protein, and resins. The compounds are capable of being cast,
extruded, or molded into various shapes.
1.3 Major fiber types used for textile purposes are further
Specific–DerivationfromGreek“plastikos”whichmeans
classified.
“fit for molding”.
1.3.1 Manufactured fibers are identified as having either an
3.2 For definitions of textile terms used in the guide see
organic base or inorganic base.
Terminology D123.
1.3.2 Natural fibers are identified as having a cellulosic,
4. Significance and Use
protein, or mineral base.
4.1 This guide is intended for use as a reference to improve
1.4 A glossary of generic names and definitions for manu-
the understanding of the relationship between commercial
factured fibers is included as additional information.
name, fiber identification and geographical regions of fiber
1.5 This international standard was developed in accor-
origins that make up the composition of textile products.
dance with internationally recognized principles on standard-
4.2 This guide is intended to be used as a source of
ization established in the Decision on Principles for the
information only.
Development of International Standards, Guides and Recom-
4.2.1 Detailed analysis, to verify specific data related to the
mendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical
composition of a particular fiber, may be necessary.
Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
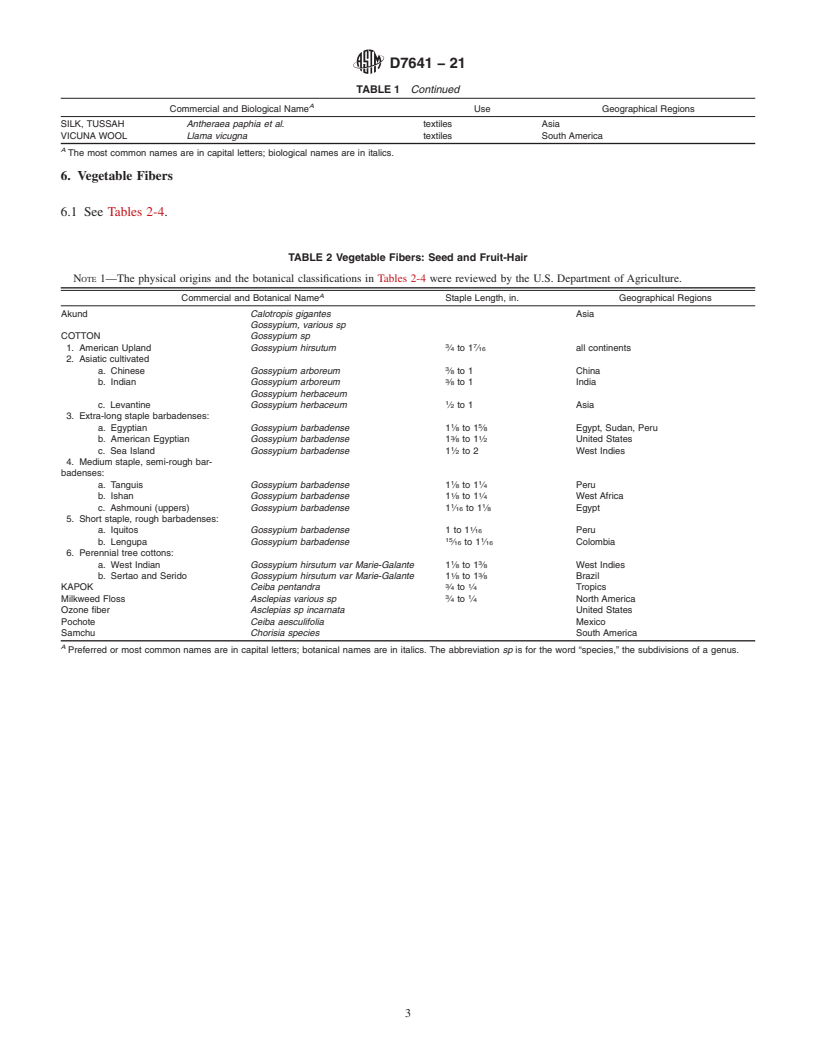
5. Animal (Protein Base) Fibers
5.1 See Table 1.
1
This guide is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D13 on Textiles and
2
is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee D13.92 on Terminology. For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
Current edition approved Oct. 1, 2021. Published October 2021. Originally contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
ɛ1
approved in 2010. Last previous edition approved in 2014 as D7641–10 (2014) . Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on
DOI: 10.1520/D7641-21. the ASTM website.
TABLE 1 Animal (Protein-Base) Fibers
A
Commercial and Biological Name Use Geographical Regions
ALPACA WOOL Llama glama textiles South America, North America
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
D7641 − 21
TABLE 1 Continued
A
Commercial and Biological Name Use Geographical Regions
American ring tail Bassariscusbacus astutus soft brushes North America
Angora See Rabbit, Angora, Mohair
Badger Meles meles soft brushes Asia, Europe
Camelus dromedarius textiles, soft Asia
h
Camelus bactrianus textiles, coarse Asia
CAMEL HAIR
“Camel hair” See Squirrel soft brushes Asia, North America
CASHMERE HAIR Caprahircus sp (Goat) textiles Asia
Cattle hair Bos taurus upholstery Asia, Europe
“Civet,” “Black Sable” See Spotted Skunk
“Fitch” Mephitis mephitis et al (Skunk) soft brushes North America
Fox Vulpes fulva stuffing North America, Europe
Genet Genetta soft brushes Africa, Asia, Europe
Goat hair Capra sp soft brushes Asia
Hog bristle Sus scrofa paint brushes Asia, North America
Horse hair, body Eq
...
This document is not an ASTM standard and is intended only to provide the user of an ASTM standard an indication of what changes have been made to the previous version. Because
it may not be technically possible to adequately depict all changes accurately, ASTM recommends that users consult prior editions as appropriate. In all cases only the current version
of the standard as published by ASTM is to be considered the official document.
´1
Designation: D7641 − 10 (Reapproved 2014) D7641 − 21
Standard Guide for
1
Textile Fibers
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D7641; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1
ε NOTE—Editorial changes were made to Annex A1 in August 2014.
1. Scope
1.1 This guide lists fibers used to manufacture textile products.
1.2 Specific groups of fibers are identified using tables of standard classification.
1.2.1 Animal fibers are identified by commercial name, biological name, end use, and geographic source.
1.2.2 Vegetable fibers are identified by commercial name, botanical name, staple length or description, and geographic source.
1.2.3 Mineral fibers are identified by commercial name, mineralogical name, chemical description, and geographic source.
1.2.4 Manufactured fibers are identified by commercial name, generic name, and major component.
1.3 Major fiber types used for textile purposes are further classified.
1.3.1 Manufactured fibers are identified as having either an organic base or inorganic base.
1.3.2 Natural fibers are identified as having a cellulosic, protein, or mineral base.
1.4 A glossary of generic names and definitions for manufactured fibers is included as additional information.
1.5 This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization
established in the Decision on Principles for the Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued
by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
2. Referenced Documents
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
D123 Terminology Relating to Textiles
2.2 ISO Standards:
ISO 2076:1999 (E) Textiles–Man-made Fibers–Generic Names
1
This guide is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D13 on Textiles and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee D13.92 on Terminology.
Current edition approved July 1, 2014Oct. 1, 2021. Published August 2015October 2021. Originally approved in 2010. Last previous edition approved in 2014 as
ɛ1
D7641–10 (2014) . DOI: 10.1520/D7641-10R14E01.10.1520/D7641-21.
2
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM Standards
volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on the ASTM website.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
D7641 − 21
2.3 Other Documents:
Code of Federal Regulations, Title 16, Section 303.7
3. Terminology
3.1 Definitions:
3.1.1 plastic, n—as related to textiles, a polymer which can be combined with curatives, plasticizers, and fillers that can be molded
under heat and pressure.
3.1.1.1 Discussion—
General – One of a large group of organic compounds synthesized from cellular hydrocarbons, protein, and resins. The compounds
are capable of being cast, extruded, or molded into various shapes.
Specific – Derivation from Greek “plastikos” which means “fit for molding”.
3.2 For definitions of textile terms used in the guide see Terminology D123.
4. Significance and Use
4.1 This guide is intended for use as a reference to improve the understanding of the relationship between commercial name, fiber
identification and geographical regions of fiber origins that make up the composition of textile products.
4.2 This guide is intended to be used as a source of information only.
4.2.1 Detailed analysis, to verify specific data related to the composition of a particular fiber, may be necessary.
5. Animal (Protein Base) Fibers
5.1 See Table 1.
TABLE 1 Animal (Protein-Base) Fibers
A
Commercial and Biological Name Use Geographical Regions
ALPACA WOOL Llama glama textiles South America, North America
American ring tail Bassariscusbacus astutus soft brushes North America
Angora See Rabbit, Angora, Mohair
Badger Meles meles soft brushes Asia, Europe
Camelus dromedarius textiles, soft Asia
h
Camelus bactrianus textiles, coarse Asia
CAMEL HAIR
“Camel hair” See Squirrel soft brushes Asia, North America
CASHMERE HAIR Caprahircus sp (Goat) textiles Asia
Cattle hair Bos taurus upholstery Asia, Europe
“Civet,” “Black Sable” See Spotted Skunk
“Fitch” Mephitis mephitis et al (Skunk) soft brushes North America
Fox Vulpes fulva stu
...









Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.