ASTM G208-12
(Practice)Standard Practice for Evaluating and Qualifying Oilfield and Refinery Corrosion Inhibitors Using Jet Impingement Apparatus
Standard Practice for Evaluating and Qualifying Oilfield and Refinery Corrosion Inhibitors Using Jet Impingement Apparatus
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
5.1 Selection of corrosion inhibitor for oilfield and refinery applications involves qualification of corrosion inhibitors in the laboratory (see Guide G170). Field conditions should be simulated in the laboratory in a fast and cost-effective manner.
5.2 Oilfield and refinery corrosion inhibitors should provide protection over a range of flow conditions from stagnant to that found during typical production conditions. The inhibitors are not equally effective over all flow conditions, so it is important to determine the flow conditions in which they are effective.
5.3 Severity of hydrodynamic conditions depends on the type of laboratory methodology. Typically, rotating cylinder electrode is effective up to 20 Pa of wall shear stress, rotating cage (RC) is effective between 20 and 200 Pa of wall shear stress, and jet impingement (JI) is effective at wall shear stress above 200 Pa (1)3 of wall shear stress.
5.4 The JI test system is relatively inexpensive and uses simple flat specimens.
5.5 In this practice, a general procedure is presented to obtain reproducible results using JI simulating the effects of different types of coupon materials; inhibitor concentrations; oil, gas, and brine compositions; temperature; pressure; and flow. Erosive effects predominate when the flow rate is very high (typically above 500 Pa) or when sand or solid particles are present; however, this practice does not cover the erosive effects.
SCOPE
1.1 This practice covers a generally accepted procedure to use the jet impingement (JI) apparatus for evaluating corrosion inhibitors for oilfield and refinery applications in defined flow conditions.
1.2 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as standard. No other units of measurement are included in this standard.
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
General Information
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Designation:G208 −12
Standard Practice for
Evaluating and Qualifying Oilfield and Refinery Corrosion
1
Inhibitors Using Jet Impingement Apparatus
This standard is issued under the fixed designation G208; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope G31 Guide for Laboratory Immersion Corrosion Testing of
Metals
1.1 This practice covers a generally accepted procedure to
G46 Guide for Examination and Evaluation of Pitting Cor-
use the jet impingement (JI) apparatus for evaluating corrosion
rosion
inhibitors for oilfield and refinery applications in defined flow
G59 Test Method for Conducting Potentiodynamic Polariza-
conditions.
tion Resistance Measurements
1.2 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as
G96 Guide for Online Monitoring of Corrosion in Plant
standard. No other units of measurement are included in this
Equipment (Electrical and Electrochemical Methods)
standard.
G102 Practice for Calculation of Corrosion Rates and Re-
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the lated Information from Electrochemical Measurements
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
G106 Practice for Verification of Algorithm and Equipment
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro- for Electrochemical Impedance Measurements
priate safety and health practices and determine the applica-
G111 Guide for Corrosion Tests in High Temperature or
bility of regulatory limitations prior to use. High Pressure Environment, or Both
G170 Guide for Evaluating and Qualifying Oilfield and
2. Referenced Documents
Refinery Corrosion Inhibitors in the Laboratory
2
2.1 ASTM Standards: G184 Practice for Evaluating and Qualifying Oil Field and
Refinery Corrosion Inhibitors Using Rotating Cage
D1141 Practice for the Preparation of Substitute Ocean
Water G185 Practice for Evaluating and Qualifying Oil Field and
RefineryCorrosionInhibitorsUsingtheRotatingCylinder
D1193 Specification for Reagent Water
Electrode
D4410 Terminology for Fluvial Sediment
G193 Terminology and Acronyms Relating to Corrosion
G1 Practice for Preparing, Cleaning, and Evaluating Corro-
sion Test Specimens
3. Terminology
G5 Reference Test Method for Making Potentiodynamic
3.1 Theterminologyusedhereinshallbeinaccordancewith
Anodic Polarization Measurements
Terminology D4410, Guide G170, and Terminology G193.
G16 Guide for Applying Statistics to Analysis of Corrosion
Data
4. Summary of Practice
4.1 Thispracticeprovidesamethodforevaluatingcorrosion
1
This practice is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee G01 on Corrosion
inhibitor efficiency in jet impingement (JI) apparatus. The
of Metals and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee G01.05 on Laboratory
method uses a well-defined impinging jet set up and mass loss
Corrosion Tests.
or electrochemical techniques to measure corrosion rates.
Current edition approved May 1, 2012. Published December 2012. DOI:
10.1520/G0208–12.
Measurements are made using three different experimental
2
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
designs and at several flow rates to evaluate the inhibitor
contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
performance under increasingly severe hydrodynamic condi-
Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on
the ASTM website. tions.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
G208−12
5. Significance and Use flow. Erosive effects predominate when the flow rate is very
high (typically above 500 Pa) or when sand or solid particles
5.1 Selection of corrosion inhibitor for oilfield and refinery
are present; however, this practice does not cover the erosive
applicationsinvolvesqualificationofcorrosioninhibitorsinthe
effects.
laboratory (see Guide G170). Field conditions should be
simulated in the laboratory in a fast and cost-effective manner.
6. Apparatus
5.2 Oilfield and refinery corrosion inhibitors should provide
6.1 The actual hydrodynamic conditions in the tests must be
protectionoverarangeofflowconditionsfromstagnanttothat
known to enable comparison of results with those obtained in
found during typical production conditions. The inhibitors are
other tests or predictions of inhibitor performance in practical
not equally effective over all flow conditions, so it is important
operating systems. Hydrodynamic parameters in jet impinge-
to determine the flow conditions in which they are effective.
ment are described in Annex A1. These h
...







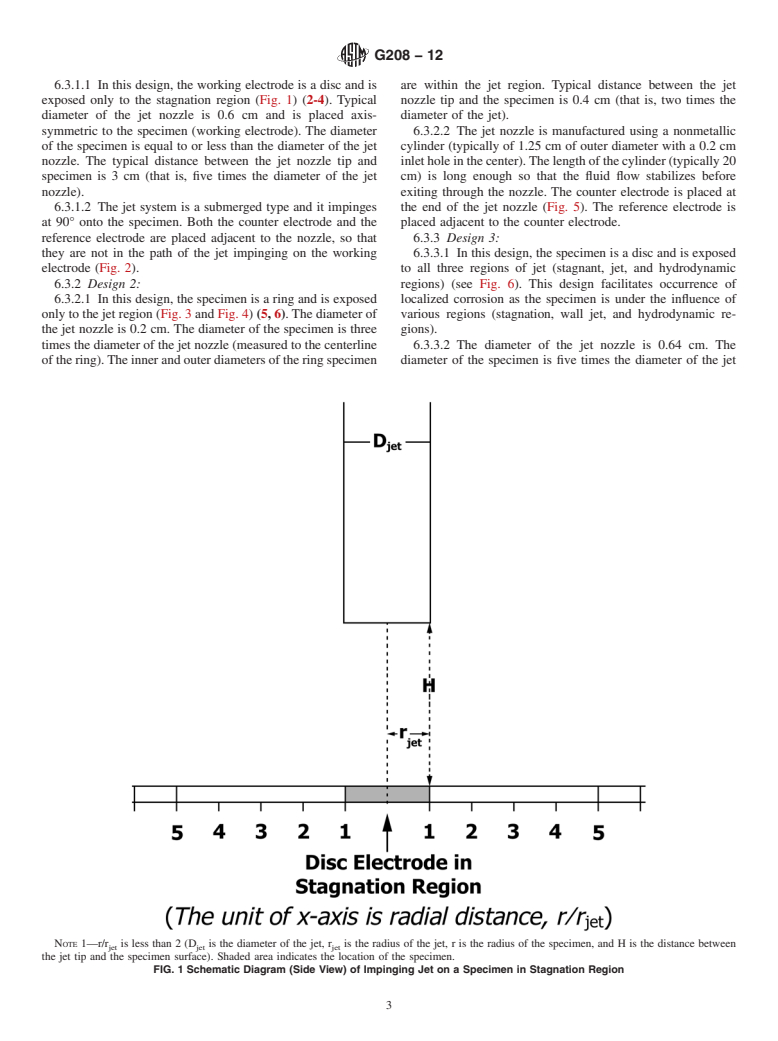
Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.