ASTM F290-94(2010)
(Specification)Standard Specification for Round Wire for Winding Electron Tube Grid Laterals
Standard Specification for Round Wire for Winding Electron Tube Grid Laterals
ABSTRACT
This specification covers round wires made from UNS N02211, UNS N10001, or N03300 nickel alloy or molybdenum, with diameters within a specified range, for winding electron tube grid laterals. The wires are classified into five classes based on tensile properties. All wires should conform to the required values of tensile strength, yield strength, working range, and elongation properties. The surface of each bare wire should be bright and free from cracks, slivers, fissures, lubricants, or other detrimental defects, while all platings should be free from bubbles, flakes, blisters, porosity, and plating salts. Wires should be spooled in one continuous length and in such a manner that it can be unwound under reasonable tension without binding or becoming distorted.
SCOPE
1.1 This specification covers round wire up to 0.006 in. (0.15 mm) in diameter for use as electron tube grid lateral winding wire.
1.2 Five classes of wire are covered based on their tensile properties (see 5.2 and 5.3).
1.3 The values stated in inch-pound units are to be regarded as standard. The values given in parentheses are mathematical conversions to SI units that are provided for information only and are not considered standard.
1.4 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
General Information
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Designation:F290 −94(Reapproved 2010)
Standard Specification for
Round Wire for Winding Electron Tube Grid Laterals
ThisstandardisissuedunderthefixeddesignationF290;thenumberimmediatelyfollowingthedesignationindicatestheyearoforiginal
adoptionor,inthecaseofrevision,theyearoflastrevision.Anumberinparenthesesindicatestheyearoflastreapproval.Asuperscript
epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope F289Specification for Molybdenum Wire and Rod for
Electronic Applications
1.1 This specification covers round wire up to 0.006 in.
(0.15 mm) in diameter for use as electron tube grid lateral
3. Terminology
winding wire.
3.1 Description of Terms:
1.2 Five classes of wire are covered based on their tensile
3.1.1 The following description of terms shall apply to the
properties (see 5.2 and 5.3).
requirements specified in Table 1:
1.3 The values stated in inch-pound units are to be regarded
3.1.1.1 breakingstrength—Thestressatwhichthespecimen
as standard. The values given in parentheses are mathematical
breaks.
conversions to SI units that are provided for information only
3.1.1.2 elongation—The maximum percent of stretch in a
and are not considered standard.
specimen of 10-in. (250-mm) gage length.
1.4 This standard does not purport to address all of the 3.1.1.3 tensile strength—The ultimate strength of the mate-
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the rialexpressedeitherasgramspermilligramper200mmlength
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro- of wire or pounds per square inch.
priate safety and health practices and determine the applica- 3.1.1.4 ultimate strength—The maximum stress developed
bility of regulatory limitations prior to use. in a specimen.
3.1.1.5 work load—The difference between the yield load
2. Referenced Documents
and the ultimate load.
3.1.1.6 yield strength—The stress developed at 1 percent
2.1 ASTM Standards:
elongation when testing a specimen of 10-in. (250-mm) gage
E39Methods for Chemical Analysis of Nickel (Withdrawn
length.
1995)
E107Test Methods for Chemical Analysis of Electronic
4. Chemical Composition
Nickel (Withdrawn 2003)
E129Test Method for Spectrographic Analysis of Thermi- 4.1 The wire shall conform to the requirements as to
onicNickelAlloysbythePowderTechniques(Withdrawn
chemical composition as prescribed in Table 2.
1999)
F16Test Methods for Measuring Diameter or Thickness of
5. Tensile Properties
Wire and Ribbon for Electronic Devices and Lamps
5.1 The wire shall conform to the requirements as to tensile
F205Test Method for Measuring Diameter of Fine Wire by
strength, yield strength, working range, and elongation prop-
Weighing
erties as prescribed in Table 1 for the class of wire designated.
F288Specification for Tungsten Wire for Electron Devices
5.2 The class designations for the nickel-titanium-
and Lamps
magnesium alloy UNS N03300; the nickel-manganese alloy
UNSN02211;molybdenumwire,andthenickel-molybdenum-
ironalloyUNSN10001;arebasedontheirtensilepropertiesas
This specification is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee F01 on
follows:
Electronicsand is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee F01.03 on Metallic
Materials.
5.2.1 Class I—The wire shall conform to elongation prop-
Current edition approved Oct. 1, 2010. Published November 2010. Originally
erties as specified in ranges in Table 1.
approved in 1954 as B290–54T; redesignated F290 in 1955. Last previous edition
5.2.2 Class II—The wire shall conform to the following
approved in 2005 as F290–94 (2005). DOI: 10.1520/F0290-94R10.
tensile properties:
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
5.2.2.1 Yield strength with a spread of approximately6
Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on
15%, as shown in grams-force, minimum and maximum, in
the ASTM website.
Table 2,
The last approved version of this historical standard is referenced on
www.astm.org. 5.2.2.2 Working range, as specified in Table 1, and
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
F290−94 (2010)
TABLE 1 Tensile Properties for Nickel-Titanium-Magnesium Alloy (UNS N03300), Nickel-Manganese Alloy (UNS N02211),
Molybdenum Wire, and Nickel-Molybdenum-Iron Alloy (UNS N10001) Wire
CLASS I
NOTE 1—Wire supplied as Class I shall conform to the following elongation values as specified by range:
Material Range Wire Diameter, Elongation,
in. (mm) %
Nickel-titanium-magnesium alloy (UNS N03300)
and nickel-manganese alloy (UNS N02211) 1 All 8 to 16
2 All 14 to 22
3 0.003 (0.08) and under 20 and over
4 Above 0.003 (0.08) 22 and over
Molybdenum 1 All 8 to 16
2 All 14 to 22
Nickel-molybdenum-iron alloy (UNS N10001) 1 0.001 (0.025) 8 to 18
2 0.0015 (0.038) 18 to 32
3 0.002 (0.050) and above 25 and over
CLASS II
NOTE 1—Wire supplied as Class II shall conform to the following requirements as to yield strength (± 15 percent), working range, and elongation:
Wire Diameter Yield Strength
Working Elongation,
Material Approximate Center Load
Load, min, gf min, %
in. (mm)
Stress psi (Mpa) min, gf max, gf
Nickel-titanium-magnesium 0.0015 (0.038) 74 000 (510) 51 67 17 8
alloy (UNS N03300)
0.0016 (0.041) 74 000 (510) 56 76 17 8
0.0017 (0.043) 70 500 (486) 62 84 17 8
0.0018 (0.046) 70 500 (486) 69 93 20 8
0.0019 (0.048) 70 500 (486) 76 104 20 10
0.0020 (0.051) 70 000 (483) 85 115 35 10
0.0025 (0.064) 68 500 (472) 130 175 60 10
0.0027 (0.069) 64 500 (445) 145 190 75 10
0.0030 (0.076) 63 500 (438) 175 235 90 15
0.0033 (0.084) 63 000 (434) 210 280 115 15
0.0035 (0.089) 63 000 (434) 235 315 135 20
0.0040 (0.102) 61 500 (424) 300 400 190 20
0.0045 (0.114) 60 000 (414) 370 500 250 20
0.0050 (0.127) 60 000 (414) 450 610 330 20
0.0055 (0.140) 60 000 (414) 550 745 400 20
0.0060 (0.152) 60 000 (414) 655 885 475 20
Nickel-manganese al- 0.0020 (0.051) 59 600 (411) 70 100 30 14
loy (UNS N02211)
0.0025 (0.064) 58 400 (403) 110 150 50 14
0.0027 (0.067) 56 800 (392) 125 170 60 14
0.0030 (0.076) 56 600 (390) 150 210 80 18
0.0033 (0.084) 50 400 (347) 175 245 105 18
0.0035 (0.089) 50 400 (347) 200 270 120 18
0.004 (0.102) 51 000 (352) 250 340 170 22
0.0045 (0.114) 47 000 (324) 295 395 230 22
0.005 (0.127) 46 000 (317) 350 470 305 22
0.006 (0.152) 43 000 (296) 465 635 490 22
Molybdenum 0.0008 (0.020) 120 000 (827) 24 34 1 8
0.0010 (0.025) 120 000 (827) 35 50 4 8
0.0012 (0.030) 118 500 (817) 50 70 6 8
0.0013 (0.033) 118 500 (817) 60 80 8 8
0.00133 (0.034) 118 500 (817) 65 85 8 8
0.00150 (0.038) 113 500 (782) 77 105 10 12
0.0017 (0.043) 113 500 (782) 95 135 15 12
0.0020 (0.051) 105 000 (724) 127 173 25 12
0.0025 (0.064) 101 000 (696) 191 259 40 15
0.0030 (0.076) 96 000 (662) 262 354 65 17
0.0033 (0.084) 96 000 (662) 317 429 80 17
0.0035 (0.089) 96 000 (662) 356 482 90 17
0.0040 (0.102) 96 000 (662) 466 630 115 17
0.0045 (0.114) 96 000 (662) 589 797 145 17
0.0050 (0.127) 96 000 (662) 728 984 180 17
0.0055 (0.140) 96 000 (662) 880 1190 220 17
0.0060 (0.152) 96 000 (662) 1047 1417 260 17
Nickel-molybdenum-iron 0.0016 (0.041) 92 000 (634) 70 95 40 10
alloy (UNS N10001)
0.0020 (0.051) 85 000 (586) 102 138 65 10
0.0025 (0.064) 85 000 (586) 160 215 110 10
0.0030 (0.076) 80 000 (552) 219 297 165 15
0.0033 (0.084) 80 000 (552) 272 368 205 15
0.0035 (0.089) 80 000 (552) 287 389 240 15
F290−94 (2010)
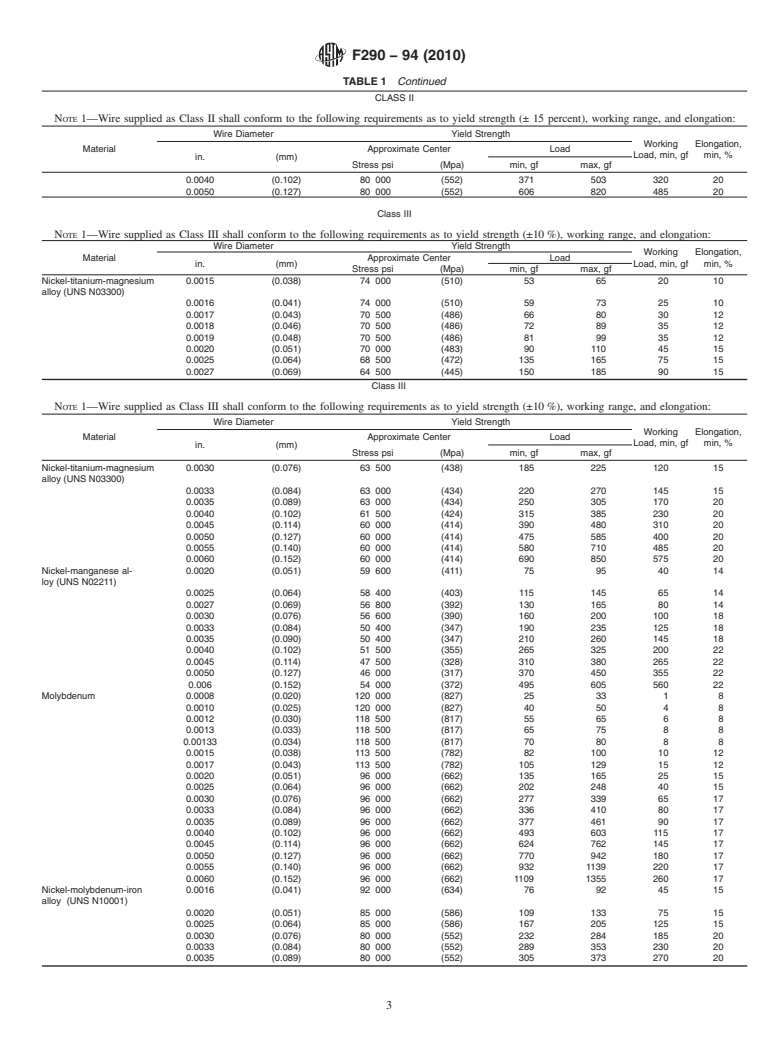
TABLE1 Continued
CLASS II
NOTE 1—Wire supplied as Class II shall conform to the following requirements as to yield strength (± 15 percent), working range, and elongation:
Wire Diameter Yield Strength
Working Elongation,
Material Approximate Center Load
Load, min, gf min, %
in. (mm)
Stress psi (Mpa) min, gf max, gf
0.0040 (0.102) 80 000 (552) 371 503 320 20
0.0050 (0.127) 80 000 (552) 606 820 485 20
Class III
NOTE 1—Wire supplied as Class III shall conform to the following requirements as to yield strength (±10%), working range, and elongation:
Wire Diameter Yield Strength
Working Elongation,
Material Approximate Center Load
in. (mm) Load, min, gf min, %
Stress psi (Mpa) min, gf max, gf
Nickel-titanium-magnesium 0.0015 (0.038) 74 000 (510) 53 65 20 10
alloy (UNS N03300)
0.0016 (0.041) 74 000 (510) 59 73 25 10
0.0017 (0.043) 70 500 (486) 66 80 30 12
0.0018 (0.046) 70 500 (486) 72 89 35 12
0.0019 (0.048) 70 500 (486) 81 99 35 12
0.0020 (0.051) 70 000 (483) 90 110 45 15
0.0025 (0.064) 68 500 (472) 135 165 75 15
0.0027 (0.069) 64 500 (445) 150 185 90 15
Class III
NOTE 1—Wire supplied as Class III shall conform to the following requirements as to yield strength (±10%), working range, and elongation:
Wire Diameter Yield Strength
Working Elongation,
Material Approximate Center Load
Load, min, gf min, %
in. (mm)
Stress psi (Mpa) min, gf max, gf
Nickel-titanium-magnesium 0.0030 (0.076) 63 500 (438) 185 225 120 15
alloy (UNS N03300)
0.0033 (0.084) 63 000 (434) 220 270 145 15
0.0035 (0.089) 63 000 (434) 250 305 170 20
0.0040 (0.102) 61 500 (424) 315 385 230 20
0.0045 (0.114) 60 000 (414) 390 480 310 20
0.0050 (0.127) 60 000 (414) 475 585 400 20
0.0055 (0.140) 60 000 (414) 580 710 485 20
0.0060 (0.152) 60 000 (414) 690 850 575 20
Nickel-manganese al- 0.0020 (0.051) 59 600 (411) 75 95 40 14
loy (UNS N02211)
0.0025 (0.064) 58 400 (403) 115 145 65 14
0.0027 (0.069) 56 800 (392) 130 165 80 14
0.0030 (0.076) 56 600 (390) 160 200 100 18
0.0033 (0.084) 50 400 (347) 190 235 125 18
0.0035 (0.090) 50 400 (347) 210 260 145 18
0.0040 (0.102) 51 500 (355) 265 325 200 22
0.0045 (0.114) 47 500 (328) 310 380 265 22
0.0050 (0.127) 46 000 (317) 370 450 355 22
0.006 (0.152) 54 000 (372) 495 605 560 22
Molybdenum 0.0008 (0.020) 120 000 (827) 25 33 1 8
0.0010 (0.025) 120 000 (827) 40 50 4 8
0.0012 (0.030) 118 500 (817) 55 65 6 8
0.0013 (0.033) 118 500 (817) 65 75 8 8
0.00133 (0.034) 118 500 (817) 70 80 8 8
0.0015 (0.038) 113 500 (782) 82 100 10 12
0.0017 (0.043) 113 500 (782) 105 129 15 12
0.0020 (0.051) 96 000 (662) 135 165 25 15
0.0025 (0.064) 96 000 (662) 202 248 40 15
0.0030 (0.076) 96 000 (662) 277 339 65 17
0.0033 (0.084) 96 000 (662) 336 410 80 17
0.0035 (0.089) 96 000 (662) 377 461 90 17
0.0040 (0.102) 96 000 (662) 493 603 115 17
0.0045 (0.114) 96 000 (662) 624 762 145 17
0.0050 (0.127) 96 000 (662) 770 942 180 17
0.0055 (0.140) 96 000 (662) 932 1139 220 17
0.0060 (0.
...







Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.