ASTM E1175-87(2009)
(Test Method)Standard Test Method for Determining Solar or Photopic Reflectance, Transmittance, and Absorptance of Materials Using a Large Diameter Integrating Sphere
Standard Test Method for Determining Solar or Photopic Reflectance, Transmittance, and Absorptance of Materials Using a Large Diameter Integrating Sphere
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
To overcome the inadequacies of conventional spectrophotometric measurement techniques when nonhomogeneous materials are measured, a large integrating sphere may be used. , Since the beam employed in such spheres is large in comparison to the disparaties of the materials being tested, the nonisotropic nature of the specimen being measured is essentially averaged, or integrated out of the measurement, in a single experimental determination.
Solar and photopic optical properties may be measured either with monofunctional spheres individually tailored for the measurement of either transmittance or reflectance, or may be measured with a single multifunctional sphere that is employed to measure both transmittance and reflectance.
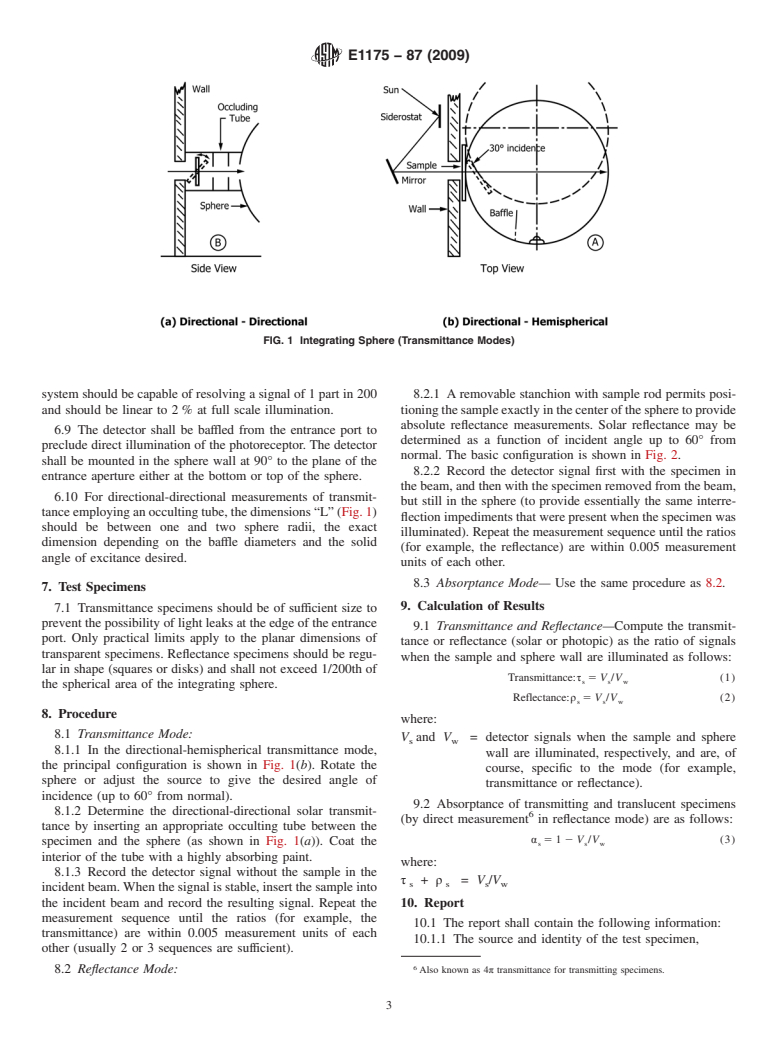
A multifunctional sphere is used for making total solar transmittance measurements in both a directional-hemispherical and a directional-directional mode. The solar absorptance can be evaluated in a single measurement as one minus the sum of the directional hemispherical reflectance and transmittance. When a sample at the center of the sphere is supported by its rim, the sum of the reflectance and transmittance can be measured as a function of the angle of incidence. The solar absorptance is then one minus the measured absorptance plus transmittance.
SCOPE
1.1 This test method covers the measurement of the absolute total solar or photopic reflectance, transmittance, or absorptance of materials and surfaces. Although there are several applicable test methods employed for determining the optical properties of materials, they are generally useful only for flat, homogeneous, isotropic specimens. Materials that are patterned, textured, corrugated, or are of unusual size cannot be measured accurately using conventional spectrophotometric techniques, or require numerous measurements to obtain a relevant optical value. The purpose of this test method is to provide a means for making accurate optical property measurements of spatially nonuniform materials.
1.2 This test method is applicable to large specimens of materials having both specular and diffuse optical properties. It is particularly suited to the measurement of the reflectance of opaque materials and the reflectance and transmittance of semitransparent materials including corrugated fiber-reinforced plastic, composite transparent and translucent samples, heavily textured surfaces, and nonhomogeneous materials such as woven wood, window blinds, draperies, etc.
1.3 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as the standard. The values given in parentheses are for information only.
1.4 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use. (For specific safety hazards, see Note 1.)
General Information
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Designation:E1175 −87(Reapproved 2009)
Standard Test Method for
Determining Solar or Photopic Reflectance, Transmittance,
and Absorptance of Materials Using a Large Diameter
Integrating Sphere
This standard is issued under the fixed designation E1175; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope 2. Referenced Documents
1.1 Thistestmethodcoversthemeasurementoftheabsolute 2.1 ASTM Standards:
total solar or photopic reflectance, transmittance, or absorp- E772 Terminology of Solar Energy Conversion
tance of materials and surfaces. Although there are several E892 Tables for Terrestrial Solar Spectral Irradiance at Air
applicable test methods employed for determining the optical Mass 1.5 for a 37° Tilted Surface
properties of materials, they are generally useful only for flat, E903 Test Method for Solar Absorptance, Reflectance, and
homogeneous, isotropic specimens. Materials that are Transmittance of Materials Using Integrating Spheres
patterned,textured,corrugated,orareofunusualsizecannotbe
3. Terminology
measured accurately using conventional spectrophotometric
techniques, or require numerous measurements to obtain a 3.1 Definitions:
3.1.1 absorptance, n—see Terminology E772.
relevant optical value. The purpose of this test method is to
provideameansformakingaccurateopticalpropertymeasure-
3.1.2 integrating sphere—optical device used to either col-
ments of spatially nonuniform materials.
lect flux reflected or transmitted from a sample into a hemi-
sphere or to provide isotropic irradiation of a sample from a
1.2 This test method is applicable to large specimens of
complete hemisphere.
materials having both specular and diffuse optical properties. It
3.1.2.1 Discussion—It consists of a cavity that is approxi-
is particularly suited to the measurement of the reflectance of
mately spherical in shape with apertures for admitting and
opaque materials and the reflectance and transmittance of
detecting flux and usually having additional apertures over
semitransparentmaterialsincludingcorrugatedfiber-reinforced
which sample and reference specimens are placed.
plastic, composite transparent and translucent samples, heavily
textured surfaces, and nonhomogeneous materials such as
3.1.3 photopic optical properties, n—absorptance,
woven wood, window blinds, draperies, etc.
reflectance, and transmittance of a sample evaluated as the
weighted average of the measured property, with the wave-
1.3 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as the
length by wavelength of the product of the spectral irradiance
standard. The values given in parentheses are for information
for the measurement and the Commission Internationale de
only.
l’Eclairage (CIE) photopic spectral response, as the weighting
1.4 This standard does not purport to address all of the
function.
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
3.1.4 photopic response, n—spectralresponseoftheaverage
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
human eye when fully adapted to daylight conditions.
priate safety and health practices and determine the applica-
bility of regulatory limitations prior to use. (For specific safety
3.1.5 reflectance, n—see Terminology E772.
hazards, see Note 1.)
3.1.6 transmittance, n—see Terminology E772.
1 2
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee E44 on Solar, For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
Geothermal and OtherAlternative Energy Sources and is the direct responsibility of contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
Subcommittee E44.05 on Solar Heating and Cooling Systems and Materials. Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on
Current edition approved April 1, 2009. Published June 2009. Originally the ASTM website.
approvedin1987.Lastpreviouseditionapprovedin2003asE1175–87(2003).DOI: Available from Commission Internationale de l’Eclairage (CIE), International
10.1520/E1175-87R09. Light Vocabulary, 3rd Ed., Bureau Central de la CIE, Paris, 1970.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
E1175−87 (2009)
4. Summary of Test Method 6. Apparatus
4.1 This test method describes a procedure and apparatus 6.1 An integrating sphere having a minimum radius of 1 m
for determining the area-averaged optical properties of com- and a maximum ratio of entrance aperture area to total sphere
plex or nonuniform materials and surfaces. This test method area of 1:200. The circular port defining the entrance aperture
employs a large diameter integrating sphere and a source shall have a diameter of not less than 230 mm (approximately
capable of illuminating a representative area of the test 9 in.), although a port diameter of 300 mm (approximately 12
specimen’s surface. in.) is preferred.
6.2 The sphere shall be mounted in such a manner as to
4.2 Transmittanceisdeterminedwiththespecimenmounted
4,5
externally at the sphere entrance port. Reflectance is deter- permit precision illumination of the sample at directions of
incidencefrom0°(normalincidence)to60°fromnormalinthe
mined by placing the specimen in the center of the integrating
sphere, in accordance with the diagram in Fig. A1.2 of Test transmittance mode, using natural sunlight as source. When
employing an artificial source for either simulated solar or
Method E903. For measurement of reflectance of partially
transmitting samples, the sample should be backed by a black photopic measurements, the off-angle mechanism may either
opaque absorber to eliminate the transmitted flux from the be made a part of the sphere (with a fixed position lamp) or a
measurement. part of the source assembly (with a fixed position sphere).
4.3 The source may be either natural sunlight or an artificial 6.3 For reflectance measurements, a center-positioned
sample mount that has two degrees of freedom is required: in
source that closely approximates anAir Mass 1.5 solar energy
distribution in accordance with Tables E892. and out of the sample beam, and rotation about the sample
beam to provide incident angles from 0° to 660°. The sample
4.4 Relevant optical properties are determined by the ratio
mount shall be designed so that the flux transmitted by the
of the total sphere flux transmitted or reflected by the specimen
sample is absorbed, for measurement of reflectance, or so that
to the total sphere flux, or both when no specimen is in place.
the sample is supported by its rim for simultaneous measure-
4.5 The use of a spectrally flat or spectrally sensitive
ment of reflectance plus transmittance.
detector determines whether a solar or a photopic optical
6.4 The interior of the integrating sphere shall be uniformly
characteristic is measured.
coated with a spectrally flat paint having a minimum hemi-
spherical reflectance of 0.85 in the spectral region of interest.
5. Significance and Use
For photopic measurements only, nearly any flat interior white
5.1 To overcome the inadequacies of conventional spectro-
paint will suffice. For solar and ultraviolet measurements, a
photometric measurement techniques when nonhomogeneous
good barium sulfate-pigmented sphere paint is required.
materials are measured, a large integrating sphere may be
4,5 6.5 Astable source illuminant having a spectral distribution
used. Since the beam employed in such spheres is large in
approximating that of a standard solar spectrum of Air Mass
comparison to the disparaties of the materials being tested, the
1.5 (Tables E892) shall be employed for simulated solar
nonisotropic nature of the specimen being measured is essen-
measurements. Other sources may be employed for photopic
tially averaged, or integrated out of the measurement, in a
measurements if the spectral energy distribution is essentially
single experimental determination.
flat in the 475 to 650-nm region.
5.2 Solar and photopic optical properties may be measured
6.6 For natural sunshine illumination, a solar siderostat (or
eitherwithmonofunctionalspheresindividuallytailoredforthe
heliostat) arrangement is required to provide uniform illumi-
measurement of either transmittance or reflectance, or may be
nation (unle
...







Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.