ASTM A565/A565M-10(2017)e1
(Specification)Standard Specification for Martensitic Stainless Steel Bars for High-Temperature Service
Standard Specification for Martensitic Stainless Steel Bars for High-Temperature Service
ABSTRACT
This guide covers standard specification for hot-finished and cold-finished martensitic chromium steel bars for high-temperature service. The mechanical properties shall be developed by suitable heat treatment, as indicated for each alloy. The steel shall conform to the required chemical composition for carbon, manganese, phosphorus, sulfur, silicon, chromium, nickel, molybdenum, vanadium, tungsten, nitrogen, aluminum, columbium, and copper. The microstructure shall not contain more than 5% delta-ferrite after full heat treatment. The material shall conform to the required mechanical properties such as tensile strength, yield strength, elongation, impact strength, and Brinell hardness. The material shall also undergo stress rupture testing using a combination test bar.
SCOPE
1.1 This specification covers hot-finished and cold-finished martensitic chromium steel bars for high-temperature service. The mechanical properties are developed by suitable heat treatment, as indicated for each alloy.
1.2 Where strength at temperature is a factor, these steels are generally limited to a maximum service temperature of 1200°F [650°C]. For oxidation (scaling) resistance and at low stresses, these steels are useful to 1450°F [790°C].
1.3 This specification is expressed in both inch-pound units and SI units; however, unless the purchase order or contract specifies the applicable M specification designation (SI units), the inch-pound units shall apply. The values stated in either inch-pound units or SI units are to be regarded separately as standard. Within the text, the SI units are shown in brackets. The values stated in each system may not be exact equivalents; therefore, each system shall be used independently of the other. Combining values from the two systems may result in nonconformance with the specification.
General Information
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization established in the Decision on Principles for the
Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
´1
Designation: A565/A565M −10 (Reapproved 2017)
Standard Specification for
Martensitic Stainless Steel Bars for High-Temperature
Service
This standard is issued under the fixed designationA565/A565M; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year
of original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision.Anumber in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval.
A superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
This standard has been approved for use by agencies of the U.S. Department of Defense.
ε NOTE—Revised Table 1 editorially to show commonly accepted element name Niobium (formerly Columbium) in
March 2017.
1. Scope A994Guide for Editorial Procedures and Form of Product
Specifications for Steel, Stainless Steel, and Related
1.1 This specification covers hot-finished and cold-finished
Alloys
martensitic chromium steel bars for high-temperature service.
E112Test Methods for Determining Average Grain Size
The mechanical properties are developed by suitable heat
E292Test Methods for ConductingTime-for-Rupture Notch
treatment, as indicated for each alloy.
Tension Tests of Materials
1.2 Where strength at temperature is a factor, these steels
E527Practice for Numbering Metals and Alloys in the
are generally limited to a maximum service temperature of
Unified Numbering System (UNS)
1200°F [650°C]. For oxidation (scaling) resistance and at low
E562Test Method for Determining Volume Fraction by
stresses, these steels are useful to 1450°F [790°C].
Systematic Manual Point Count
1.3 This specification is expressed in both inch-pound units
2.2 SAE Document:
and SI units; however, unless the purchase order or contract
SAE J1086Recommended Practice for Numbering Metals
specifies the applicable M specification designation (SI units),
and Alloys (UNS)
the inch-pound units shall apply. The values stated in either
inch-pound units or SI units are to be regarded separately as
3. Ordering Information
standard. Within the text, the SI units are shown in brackets.
3.1 It is the responsibility of the purchaser to specify all
Thevaluesstatedineachsystemmaynotbeexactequivalents;
requirements that are necessary for material ordered under this
therefore,eachsystemshallbeusedindependentlyoftheother.
specification. Such requirements may include, but are not
Combining values from the two systems may result in noncon-
limited to, the following:
formance with the specification.
3.1.1 Quantity (weight or number of pieces);
2. Referenced Documents
3.1.2 Name of material (martensitic stainless steel);
3.1.3 Form (bar, and so forth);
2.1 ASTM Standards:
3.1.4 Condition;
A370Test Methods and Definitions for Mechanical Testing
of Steel Products 3.1.5 Finish;
A484/A484MSpecification for General Requirements for 3.1.6 Size, or applicable dimension including diameter,
Stainless Steel Bars, Billets, and Forgings
thickness, width, length, and so forth;
A751Test Methods, Practices, and Terminology for Chemi-
3.1.7 Grade designation (Table 1); and
cal Analysis of Steel Products
3.1.8 ASTM designation number and date of issue.
4. General Requirements
This specification is under the jurisdiction ofASTM Committee A01 on Steel,
Stainless Steel and Related Alloysand is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee
4.1 Product furnished to this specification shall conform to
A01.17 on Flat-Rolled and Wrought Stainless Steel.
the requirements of Specification A484/A484M, including any
Current edition approved March 15, 2017. Published March 2017. Originally
supplementary requirements indicated in the purchase order.
approved in 1966. Last previous edition approved in 2010 as A565–10. DOI:
10.1520/A0565_A0565M-10R17E01.
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on Available from Society of Automotive Engineers (SAE), 400 Commonwealth
the ASTM website. Dr., Warrendale, PA 15096-0001, http://www.sae.org.
*A Summary of Changes section appears at the end of this standard
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
´1
A565/A565M − 10 (2017)
TABLE 1 Chemical Requirements
Grade UNS Carbon Man- Phos- Sulfur Silicon Chromium Nickel Molyb- Vana- Tungsten Nitrogen Alumi- Niobium Copper
Desig- ganese phorus denum dium num
A
nation
XM-32 S64152 0.08–0.15 0.50–0.90 0.025 0.025 0.35 max 11.00–12.50 2.00–3.00 1.50–2.00 0.25–0.40 . . . 0.01–0.05 . . . . . . . . .
max max
. . . S41041 0.13–0.18 0.40–0.60 0.030 0.030 0.50 max 11.50–13.00 0.50 max 0.20 max . . . . . . . . . 0.05 0.15 .
max max max –0.45
. . . S41425 0.05 max 0.50–1.00 0.02 max 0.005 0.50 max 12.00–15.00 4.00–7.00 1.50–2.00 . . . . . . 0.06–0.12 . . . . . . 0.30
max max
615 S41800 0.15–0.20 0.50 max 0.040 0.030 0.50 max 12.00–14.00 1.80–2.20 0.50 max . . . 2.50–3.50 . . . . . . . . . . . .
max max
616 S42200 0.20–0.25 0.50–1.00 0.025 0.025 0.50 max 11.00–12.50 0.50–1.00 0.90–1.25 0.20–0.30 0.90–1.25 . . . . . . . . . . . .
max max
619 S42300 0.27–0.32 0.95–1.35 0.025 0.025 0.50 max 11.00–12.00 0.50 max 2.50–3.00 0.20–0.30 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
max max
. . . S42226 0.15–0.20 0.50–0.80 0.020 0.010 0.20–0.60 10.0–11.5 0.30–0.60 0.80–1.10 0.15–0.25 0.25 0.04–0.08 0.05 0.35 .
–0.55
A
New designation established in accordance with Practice E527 and SAE J1086.
Failure to comply with the general requirements of Specifica- 5.2.2.3 Polished (rounds only).
tionA484/A484Mconstitutesnonconformancewiththisspeci-
fication. In case of conflict between the requirements of this
6. Chemical Requirements
specificationandSpecificationA484/A484M,thisspecification
6.1 Eachalloycoveredbythisspecificationshallconformto
shall prevail.
the chemical composition specified in Table 1.
5. Manufacture
6.2 Methods and practices relating to chemical analysis
5.1 Heat Treatment:
required by this specification shall be in accordance with Test
5.1.1 The product forms covered in this specification may
Methods, Practices, and Terminology A751.
be furnished in one of the following conditions:
5.1.1.1 Condition A—Annealed,
7. Metallurgical Requirements
5.1.1.2 Condition T—Heat treated (for machining),
7.1 The microstructure shall not contain more than 5%
5.1.1.3 Condition HT—Heat treated (for high-temperature
delta-ferrite after full heat treatment as described in Table 2.
service), or
Visual examination for the volume fraction of delta ferrite of
5.1.1.4 Condition H—Heat treated.
various representative areas of examination is acceptable.
5.2 Condition and Finish:
When the visual estimation method indicates the delta ferrite
5.2.1 Bars may be furnished in one of the following
contentisgreaterthantheallowedlimit,themanufacturermay
hot-finished conditions:
employTest Method E562 for determining the acceptability of
5.2.1.1 Hot rolled, or
the lot.
5.2.1.2 Rough turned (rounds only).
5.2.2 Bars may be furnished in one of the following
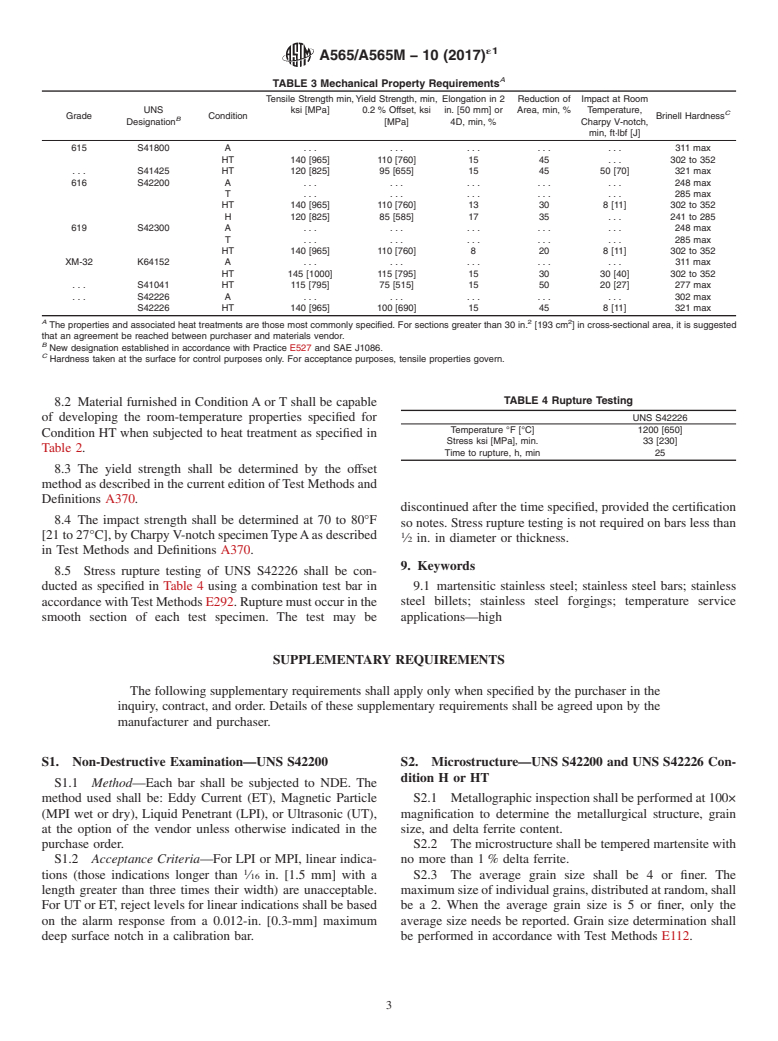
8. Mechanical Properties Requirements
cold-finished conditions:
5.2.2.1 Cold drawn, 8.1 The material shall conform to the mechanical properties
5.2.2.2 Centerless ground (rounds only), or listed in Table 3 for the ordered condition.
TA
...







Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.