ASTM A278/A278M-01(2015)
(Specification)Standard Specification for Gray Iron Castings for Pressure-Containing Parts for Temperatures Up to 650°F (350°C)
Standard Specification for Gray Iron Castings for Pressure-Containing Parts for Temperatures Up to 650°F (350°C)
ABSTRACT
This specification covers gray iron for castings suitable for pressure-containing parts at elevated temperatures. Castings shall be stress-relieved by placing them in a suitable furnace and heating them uniformly to the temperatures and for the times specified. Castings to be used at a particular temperature range shall undergo heat treatment and cooling. Chemical analysis shall be performed on each class of castings and shall meet the maximum requirement for carbon, phosphorus and sulfur. Iron used in supplying castings shall conform to the required tensile strength. Separately cast test bars having the required dimensions shall be poured from the same lot as the castings represented. The test bars shall be cast in dried siliceous sand molds maintained at approximately room temperature. Tension test shall be performed on each lot and materials shall conform to the tensile requirements specified.
SCOPE
1.1 This specification2 covers gray iron for castings suitable for pressure-containing parts for use at temperatures up to 650°F (350°C).
1.2 Classes of Iron:
1.2.1 Castings of all classes are suitable for use up to 450°F (230°C). For temperatures above 450°F and up to 650°F, only Class 40, 45, 50, 55, and 60 castings are suitable.
1.2.2 Castings of all classes are suitable for use up to 230°C. For temperatures above 230°C and up to 350°C, only Class 275, 300, 325, 350, 380, and 415 castings are suitable.
1.3 The values stated in either SI units or inch-pound units are to be regarded separately as standard. The values stated in each system may not be exact equivalents; therefore, each system shall be used independently of the other. Combining values from the two systems may result in non-conformance with the standard.
General Information
Relations
Buy Standard
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Designation:A278/A278M −01 (Reapproved 2015)
Standard Specification for
Gray Iron Castings for Pressure-Containing Parts for
Temperatures Up to 650°F (350°C)
This standard is issued under the fixed designationA278/A278M; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year
of original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval.
A superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
This standard has been approved for use by agencies of the U.S. Department of Defense.
1. Scope 4.1.1 Castings ordered to this specification are classified
2 based upon the minimum tensile strength of the iron in ksi, in
1.1 This specification covers gray iron for castings suitable
English units. Class 25 has a minimum specified tensile
for pressure-containing parts for use at temperatures up to
strength of 25 ksi.
650°F (350°C).
4.1.2 Castings ordered to this specification are classified
1.2 Classes of Iron:
based upon the minimum tensile strength of the iron in MPa, in
1.2.1 Castings of all classes are suitable for use up to 450°F
Metric units. Class 150 has a minimum specified tensile
(230°C). For temperatures above 450°F and up to 650°F, only
strength of 150 MPa.
Class 40, 45, 50, 55, and 60 castings are suitable.
1.2.2 Castingsofallclassesaresuitableforuseupto230°C.
5. Ordering Information
For temperatures above 230°C and up to 350°C, only Class
5.1 Orders for material in this specification should include
275, 300, 325, 350, 380, and 415 castings are suitable.
the following information:
1.3 The values stated in either SI units or inch-pound units
5.1.1 ASTM designation and year date,
are to be regarded separately as standard. The values stated in
5.1.2 Class of iron required and service temperature,
each system may not be exact equivalents; therefore, each
5.1.3 Quantity,
system shall be used independently of the other. Combining
5.1.4 Heat Treatment:
values from the two systems may result in non-conformance
5.1.4.1 Whether or not heat treatment is required for Class
with the standard.
40, 45, 50, 55, and 60 castings to be used at temperatures at
450°F or less (see 6.2),
2. Referenced Documents
5.1.4.2 Whether or not heat treatment is required for Class
2.1 ASTM Standards: 275, 300, 325, 350, 380, and 415 castings to be used at
A644 Terminology Relating to Iron Castings temperatures at 230°C or less (see 6.2),
E8 Test Methods for Tension Testing of Metallic Materials 5.1.5 The size of separately cast test bar to be poured (see
Section 9 and Table 1),
3. Terminology
5.1.6 The size of test specimen to be machined from test
barsCorS,and
3.1 Definitions of many terms common to gray iron castings
5.1.7 Special requirements.
may be found in Terminology A644.
6. Materials and Manufacture
4. Classification
6.1 Castings intended for use above 450°F (230°C) shall be
4.1 Classification by tensile strength.
stress-relieved by placing them in a suitable furnace at a
temperature not exceeding 400°F (200°C) and heating them
This specification is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee A04 on Iron
uniformly to the temperatures and for the times specified in
CastingsandisthedirectresponsibilityofSubcommitteeA04.01onGreyandWhite
Table 2. The heating and cooling rates shall be uniform and
Iron Castings.
shall not be more than 400°F/h (250°C/h) for castings of 1-in.
Current edition approved Nov. 1, 2015. Published November 2015. Originally
approved in 1944. Last previous edition approved in 2011 as A278/
(25-mm) maximum section. For heavier sections the maximum
A278M – 01 (2011). DOI: 10.1520/A0278_A0278M-01R15.
heating and cooling rates in degrees Fahrenheit per hour shall
For ASME Boiler and Pressure Vessel Code applications see related Specifi-
be 400 divided by the maximum section thickness.
cation SA-278 in Section II of that Code.
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
6.2 Heat Treatment and Cooling Rate:
contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
6.2.1 CastingsofClassNos.45,50,55,and60,whichareto
Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on
the ASTM website. be used at temperatures below 450°F, may be heat treated in
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
A278/A278M−01 (2015)
TABLE 1 Diameters and Lengths of Cast Test Bars TABLE 3 Tensile Requirements
Test As-Cast Diameter, in. (mm) Length, in. (mm) Class Tensile Strength,
Bar min, ksi
Minimum Maximum Minimum Maximum
(Bottom) (Top) (Specified) (Recommended) No. 20 20
No. 25 25
A 0.88 (23) 0.85 (22) 0.96 (25) 5.0 (125) 6.0 (1.50)
No. 30 30
B 1.20 (33) 1.14 (32) 1.32 (36) 7.0 (150) 9.0 (230)
No. 35 35
C 2.00 (54) 1.90 (53) 2.10 (58) 6.0 (175) 10.0 (255)
A No. 40 40
S
No. 45 45
A
All dimensions of Test Bar S shall be agreed upon by the manufacturer and the
No. 50 50
purchaser.
No. 55 55
No. 60 60
TABLE 2 Stress Relieving Requirements
A TABLE 4 Tensile Requirements (SI)
Class Metal Temperature, °F Holding Time, h
(°C)
Class Tensile Strength,
40, 45, 50, 55, 60 1050 to 1200 2 12
min, MPa
B B
(275, 300, 325, 350, (565 to 650) (2 min) (12 max)
No. 150 150
380, 415)
No. 175 175
A
In no case shall the holding time be less than 1 h/in. of maximum metal section, No. 200 200
or in excess of 12 h max, dependent upon which governs.
No. 225 225
B
In no case shall the holding time be less than1hfor every 25-mm metal section,
No. 250 250
or in excess of 12 h max, depending upon which governs.
No. 275 275
No. 300 300
No. 325 325
No. 350 350
accordance with 6.1 or they shall be cooled in the mold to
No. 380 380
500°F at an average rate of not more than 100°F/h for castings
No. 415 415
up to 1 in. in section. For heavier sections the maximum
cooling rate in degrees Fahrenheit per hour shall be 100
represented. The size of the test bar to be poured shall be
divided by the maximum section thickness.
selected by the purchaser using Table 5. In the event no choice
6.2.2 Castings of Class Nos. 275, 300, 325, 350, 380, and
is made, the selection will be made by the manufacturer.
415,whicharetobeusedattemperaturesbelow230°C,maybe
heat treated in accordance with 6.1 or they shall be cooled in
9.2 Separately cast test bars shall be heat treated in the same
the mold to 250°C at an average rate of not more than 50°C/h
furnace together with the castings represented.
for castings up to 25-mm in section. For heavier sections the
9.3 At the option of the manufacturer, test coupons may be
maximum cooling rate in degrees Celsius per hour shall be
removed from the casting at a location agreed upon between
1250 divided by the maximum section thickness.
the manufacturer and purchaser.
7. Chemical Composition
9.4 Castings weighing in excess of 2000 lb may be repre-
sented either by separately cast test bars (9.1) or by integrally
7.1 Carbon Equivalent:
cast test bars having a cooling rate closely approximating that
7.1.1 Class 40, 45, 50, 55, and 60 castings intended for
of the controlling section of the casting.
service above 450°F (230°C) shall have a maximum carbon
equivalent of 3.8 % as calculated from the equation CE = %C
9.5 For castings weighing in excess of 10 000 lb or having
+ 0.3 (%Si + %P). The maximum phosphorus and sulfur
a controlling section greater than 2 in., test bars may be
contents shall be 0.25 % and 0.12 %, respectively.
removed from the casting or integral projections having a cross
7.1.2 Class 275, 300, 325, 350, 380, and 415 castings
section no less than the controlling section. The minimum
intended for service above 230°C shall have a maximum
tensile strength requirement for tension tests performed on
carbon equivalent of 3.8 % as calculated from the equation CE
eit
...
This document is not an ASTM standard and is intended only to provide the user of an ASTM standard an indication of what changes have been made to the previous version. Because
it may not be technically possible to adequately depict all changes accurately, ASTM recommends that users consult prior editions as appropriate. In all cases only the current version
of the standard as published by ASTM is to be considered the official document.
Designation: A278/A278M − 01 (Reapproved 2011) A278/A278M − 01 (Reapproved 2015)
Standard Specification for
Gray Iron Castings for Pressure-Containing Parts for
Temperatures Up to 650°F (350°C)
This standard is issued under the fixed designation A278/A278M; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year
of original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval.
A superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
This standard has been approved for use by agencies of the U.S. Department of Defense.
1. Scope
1.1 This specification covers gray iron for castings suitable for pressure-containing parts for use at temperatures up to 650°F
(350°C).
1.2 Classes of Iron:
1.2.1 Castings of all classes are suitable for use up to 450°F (230°C). For temperatures above 450°F and up to 650°F, only Class
40, 45, 50, 55, and 60 castings are suitable.
1.2.2 Castings of all classes are suitable for use up to 230°C. For temperatures above 230°C and up to 350°C, only Class 275,
300, 325, 350, 380, and 415 castings are suitable.
1.3 The values stated in either SI units or inch-pound units are to be regarded separately as standard. The values stated in each
system may not be exact equivalents; therefore, each system shall be used independently of the other. Combining values from the
two systems may result in non-conformance with the standard.
2. Referenced Documents
2.1 ASTM Standards:
A644 Terminology Relating to Iron Castings
E8 Test Methods for Tension Testing of Metallic Materials
3. Terminology
3.1 Definitions of many terms common to gray iron castings may be found in Terminology A644.
4. Classification
4.1 Classification by tensile strength.
4.1.1 Castings ordered to this specification are classified based upon the minimum tensile strength of the iron in ksi, in English
units. Class 25 has a minimum specified tensile strength of 25 ksi.
4.1.2 Castings ordered to this specification are classified based upon the minimum tensile strength of the iron in MPa, in Metric
units. Class 150 has a minimum specified tensile strength of 150 MPa.
5. Ordering Information
5.1 Orders for material in this specification should include the following information:
5.1.1 ASTM designation and year date,
5.1.2 Class of iron required and service temperature,
5.1.3 Quantity,
5.1.4 Heat Treatment:
This specification is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee A04 on Iron Castings and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee A04.01 on Grey and White Iron
Castings.
Current edition approved March 1, 2011Nov. 1, 2015. Published September 2011November 2015. Originally approved in 1944. Last previous edition approved in 20062011
as A278/A278M – 01 (2011).(2006). DOI: 10.1520/A0278_A0278M-01R11. 10.1520/A0278_A0278M-01R15.
For ASME Boiler and Pressure Vessel Code applications see related Specification SA-278 in Section II of that Code.
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM Standards
volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on the ASTM website.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
A278/A278M − 01 (2015)
5.1.4.1 Whether or not heat treatment is required for Class 40, 45, 50, 55, and 60 castings to be used at temperatures at 450°F
or less (see 6.2),
5.1.4.2 Whether or not heat treatment is required for Class 275, 300, 325, 350, 380, and 415 castings to be used at temperatures
at 230°C or less (see 6.2),
5.1.5 The size of separately cast test bar to be poured (see Section 9 and Table 1),
5.1.6 The size of test specimen to be machined from test bars C or S, and
5.1.7 Special requirements.
6. Materials and Manufacture
6.1 Castings intended for use above 450°F (230°C) shall be stress-relieved by placing them in a suitable furnace at a temperature
not exceeding 400°F (200°C) and heating them uniformly to the temperatures and for the times specified in Table 2. The heating
and cooling rates shall be uniform and shall not be more than 400°F/h (250°C/h) for castings of 1-in. (25-mm) maximum section.
For heavier sections the maximum heating and cooling rates in degrees Fahrenheit per hour shall be 400 divided by the maximum
section thickness.
6.2 Heat Treatment and Cooling Rate:
6.2.1 Castings of Class Nos. 45, 50, 55, and 60, which are to be used at temperatures below 450°F, may be heat treated in
accordance with 6.1 or they shall be cooled in the mold to 500°F at an average rate of not more than 100°F/h for castings up to
1 in. in section. For heavier sections the maximum cooling rate in degrees Fahrenheit per hour shall be 100 divided by the
maximum section thickness.
6.2.2 Castings of Class Nos. 275, 300, 325, 350, 380, and 415, which are to be used at temperatures below 230°C, may be heat
treated in accordance with 6.1 or they shall be cooled in the mold to 250°C at an average rate of not more than 50°C/h for castings
up to 25-mm in section. For heavier sections the maximum cooling rate in degrees Celsius per hour shall be 1250 divided by the
maximum section thickness.
7. Chemical Composition
7.1 Carbon Equivalent:
7.1.1 Class 40, 45, 50, 55, and 60 castings intended for service above 450°F (230°C) shall have a maximum carbon equivalent
of 3.8 % as calculated from the equation CE = %C + 0.3 (%Si + %P). The maximum phosphorus and sulfur contents shall be
0.25 % and 0.12 %, respectively.
7.1.2 Class 275, 300, 325, 350, 380, and 415 castings intended for service above 230°C shall have a maximum carbon
equivalent of 3.8 % as calculated from the equation CE = %C + 0.3 (%Si + %P). The maximum phosphorus and sulfur contents
shall be 0.25 % and 0.12 %, respectively.
7.2 The chemical analysis for total carbon shall be made on either chilled cast pencil-type specimens or thin wafers
approximately ⁄32 in. thick cut from test coupons. Drillings shall not be used because of attendant loss of graphite.
8. Tensile Requirements
8.1 Iron used in supplying castings to this specification shall conform to the tensile requirements prescribed in Table 3 and Table
4.
9. Test Bars
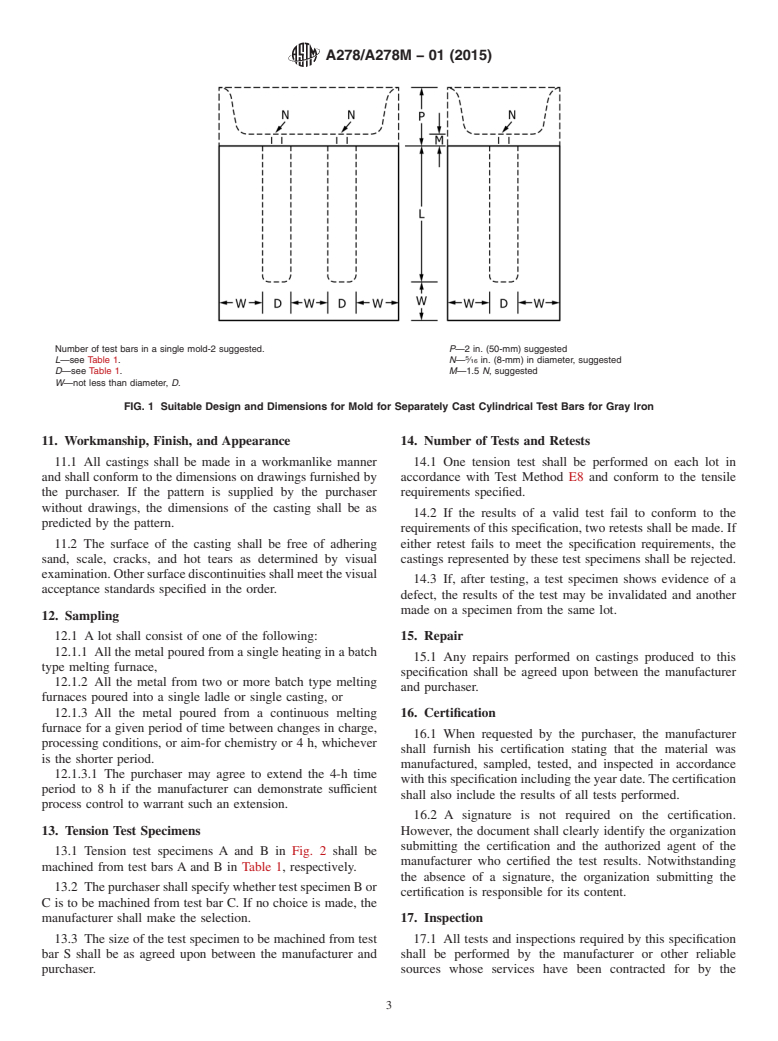
9.1 Separately cast test bars having the dimensions shown in Table 1 shall be poured from the same lot as the castings
represented. The size of the test bar to be poured shall be selected by the purchaser using Table 5. In the event no choice is made,
the selection will be made by the manufacturer.
9.2 Separately cast test bars shall be heat treated in the same furnace together with the castings represented.
9.3 At the option of the manufacturer, test coupons may be removed from the casting at a location agreed upon between the
manufacturer and purchaser.
TABLE 1 Diameters and Lengths of Cast Test Bars
Test As-Cast Diameter, in. (mm) Length, in. (mm)
Bar
Minimum Maximum Minimum Maximum
(Bottom) (Top) (Specified) (Recommended)
A 0.88 (23) 0.85 (22) 0.96 (25) 5.0 (125) 6.0 (1.50)
B 1.20 (33) 1.14 (32) 1.32 (36) 7.0 (150) 9.0 (230)
C 2.00 (54) 1.90 (53) 2.10 (58) 6.0 (175) 10.0 (255)
A
S
A
All dimensions of Test Bar S shall be agreed upon by the manufacturer and the
purchaser.
A278/A278M − 01 (2015)
TABLE 2 Stress Relieving Requirements
A
Class Metal Temperature, °F Holding Time, h
(°C)
40, 45, 50, 55, 60 1050 to 1200 2 12
B B
(275, 300, 325, 350, (565 to 650) (2 min) (12 max)
380, 415)
A
In no case shall the holding time be less than 1 h/in. of maximum metal section,
or in excess of 12 h max, dependent upon which governs.
B
In no case shall the holding time be less than 1 h for every 25-mm metal section,
or in excess of 12 h max, depending upon which governs.
TABLE 3 Tensile Requirements
Class Tensile Strength,
min
...









Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.