ASTM B977-11
(Specification)Standard Specification for Titanium and Titanium Ingots
Standard Specification for Titanium and Titanium Ingots
ABSTRACT
This specification covers titanium and titanium alloy ingots. The chemical requirements and permissible variations in product analysis are specified. This standard does not claim to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use.
SCOPE
1.1 This specification covers titanium and titanium alloy ingots as follows:
1.1.1 Grade 1—Unalloyed titanium,
1.1.2 Grade 2—Unalloyed titanium,
1.1.3 Grade 3—Unalloyed titanium,
1.1.4 Grade 4—Unalloyed titanium,
1.1.5 Grade 5—Titanium alloy (6 % aluminum, 4 % vanadium),
1.1.6 Grade 6—Titanium alloy (5 % aluminum, 2.5 % tin),
1.1.7 Grade 7—Unalloyed titanium plus 0.12 to 0.25 % palladium,
1.1.8 Grade 9—Titanium alloy (3 % aluminum, 2.5 % vanadium),
1.1.9 Grade 11—Unalloyed titanium plus 0.12 to 0.25 % palladium,
1.1.10 Grade 12—Titanium alloy (0.3 % molybdenum, 0.8 % nickel),
1.1.11 Grade 13—Titanium alloy (0.5 % nickel, 0.05 % ruthenium),
1.1.12 Grade 14—Titanium alloy (0.5 % nickel, 0.05 % ruthenium),
1.1.13 Grade 15—Titanium alloy (0.5 % nickel, 0.05 % ruthenium),
1.1.14 Grade 16—Unalloyed titanium plus 0.04 to 0.08 % palladium,
1.1.15 Grade 17—Unalloyed titanium plus 0.04 to 0.08 % palladium,
1.1.16 Grade 18—Titanium alloy (3 % aluminum, 2.5 % vanadium) plus 0.04 to 0.08 % palladium,
1.1.17 Grade 19—Titanium alloy (3 % aluminum, 8 % vanadium, 6 % chromium, 4 % zirconium, 4 % molybdenum),
1.1.18 Grade 20—Titanium alloy (3 % aluminum, 8 % vanadium, 6 % chromium, 4 % zirconium, 4 % molybdenum) plus 0.04 to 0.08 % palladium,
1.1.19 Grade 21—Titanium alloy (15 % molybdenum, 3 % aluminum, 2.7 % niobium, 0.25 % silicon),
1.1.20 Grade 23—Titanium alloy (6 % aluminum, 4 % vanadium with extra low interstitials, ELI),
1.1.21 Grade 24—Titanium alloy (6 % aluminum, 4 % vanadium) plus 0.4 to 0.8 % palladium,
1.1.22 Grade 25—Titanium alloy (6 % aluminum, 4 % vanadium) plus 0.3 to 0.8 % nickel and 0.04 to 0.08 % palladium,
1.1.23 Grade 26—Unalloyed titanium plus 0.08 to 0.14 % ruthenium,
1.1.24 Grade 27—Unalloyed titanium plus 0.08 to 0.14 % ruthenium,
1.1.25 Grade 28—Titanium alloy (3 % aluminum, 2.5 % vanadium) plus 0.08 to 0.14 % ruthenium,
1.1.26 Grade 29—Titanium alloy (6 % aluminum, 4 % vanadium, extra low interstitial elements, ELI) plus 0.08 to 0.14 % ruthenium,
1.1.27 Grade 30—Titanium alloy (0.3 % cobalt, 0.05 % palladium),
1.1.28 Grade 31—Titanium alloy (0.3 % cobalt, 0.05 % palladium),
1.1.29 Grade 32—Titanium alloy (5 % aluminum, 1 % tin, 1 % zirconium, 1 % vanadium, 0.8 % molybdenum),
1.1.30 Grade 33—Titanium alloy (0.4 % nickel, 0.015 % palladium, 0.025 % ruthenium, 0.15 % chromium),
1.1.31 Grade 34—Titanium alloy (0.4 % nickel, 0.015 % palladium, 0.025 % ruthenium, 0.15 % chromium),
1.1.32 Grade 35—Titanium alloy (4.5 % aluminum, 2 % molybdenum, 1.6 % vanadium, 0.5 % iron, 0.3 % silicon),
1.1.33 Grade 36—Titanium alloy (45 % niobium),
1.1.34 Grade 37—Titanium alloy (1.5 % aluminum), and
1.1.35 Grade 38—Titanium alloy (4 % aluminum, 2.5 % vanadium, 1.5 % iron).
1.2 The values stated in either SI units or inch-pound units are to be regarded separately as standard. The values stated in each system may not be exact equivalents; therefore, each system shall be used independently of the other. Combining values from the two systems may result in non-conformance with the standard.
1.3 The following caveat pertains only to the test method portions of this specification: This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
General Information
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Designation:B977 −11
StandardSpecification for
Titanium and Titanium Ingots
This standard is issued under the fixed designation B977; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope 1.1.20 Grade 23—Titanium alloy (6 % aluminum, 4 % va-
nadium with extra low interstitials, ELI),
1.1 This specification covers titanium and titanium alloy
1.1.21 Grade 24—Titanium alloy (6 % aluminum, 4 % va-
ingots as follows:
nadium) plus 0.4 to 0.8 % palladium,
1.1.1 Grade 1—Unalloyed titanium,
1.1.22 Grade 25—Titanium alloy (6 % aluminum, 4 % va-
1.1.2 Grade 2—Unalloyed titanium,
nadium)plus0.3to0.8 %nickeland0.04to0.08 %palladium,
1.1.3 Grade 3—Unalloyed titanium,
1.1.23 Grade 26—Unalloyed titanium plus 0.08 to 0.14 %
1.1.4 Grade 4—Unalloyed titanium,
ruthenium,
1.1.5 Grade 5—Titanium alloy (6 % aluminum, 4 %
1.1.24 Grade 27—Unalloyed titanium plus 0.08 to 0.14 %
vanadium),
ruthenium,
1.1.6 Grade 6—Titanium alloy (5 % aluminum, 2.5 % tin),
1.1.25 Grade 28—Titanium alloy (3 % aluminum, 2.5 %
1.1.7 Grade 7—Unalloyed titanium plus 0.12 to 0.25 %
vanadium) plus 0.08 to 0.14 % ruthenium,
palladium,
1.1.26 Grade 29—Titanium alloy (6 % aluminum, 4 %
1.1.8 Grade 9—Titanium alloy (3 % aluminum, 2.5 %
vanadium, extra low interstitial elements, ELI) plus 0.08 to
vanadium),
0.14 % ruthenium,
1.1.9 Grade 11—Unalloyed titanium plus 0.12 to 0.25 %
1.1.27 Grade 30—Titanium alloy (0.3 % cobalt, 0.05 %
palladium,
palladium),
1.1.10 Grade 12—Titanium alloy (0.3 % molybdenum,
1.1.28 Grade 31—Titanium alloy (0.3 % cobalt, 0.05 %
0.8 % nickel),
palladium),
1.1.11 Grade 13—Titanium alloy (0.5 % nickel, 0.05 %
1.1.29 Grade 32—Titanium alloy (5 % aluminum, 1 % tin,
ruthenium),
1 % zirconium, 1 % vanadium, 0.8 % molybdenum),
1.1.12 Grade 14—Titanium alloy (0.5 % nickel, 0.05 %
1.1.30 Grade 33—Titanium alloy (0.4 % nickel, 0.015 %
ruthenium),
palladium, 0.025 % ruthenium, 0.15 % chromium),
1.1.13 Grade 15—Titanium alloy (0.5 % nickel, 0.05 %
1.1.31 Grade 34—Titanium alloy (0.4 % nickel, 0.015 %
ruthenium),
palladium, 0.025 % ruthenium, 0.15 % chromium),
1.1.14 Grade 16—Unalloyed titanium plus 0.04 to 0.08 %
1.1.32 Grade 35—Titanium alloy (4.5 % aluminum, 2 %
palladium,
molybdenum, 1.6 % vanadium, 0.5 % iron, 0.3 % silicon),
1.1.15 Grade 17—Unalloyed titanium plus 0.04 to 0.08 %
1.1.33 Grade 36—Titanium alloy (45 % niobium),
palladium,
1.1.34 Grade 37—Titanium alloy (1.5 % aluminum), and
1.1.16 Grade 18—Titanium alloy (3 % aluminum, 2.5 %
1.1.35 Grade 38—Titanium alloy (4 % aluminum, 2.5 %
vanadium) plus 0.04 to 0.08 % palladium,
vanadium, 1.5 % iron).
1.1.17 Grade 19—Titanium alloy (3 % aluminum, 8 %
vanadium, 6 % chromium, 4 % zirconium, 4 % molybdenum),
1.2 The values stated in either SI units or inch-pound units
1.1.18 Grade 20—Titanium alloy (3 % aluminum, 8 %
are to be regarded separately as standard. The values stated in
vanadium, 6 % chromium, 4 % zirconium, 4 % molybdenum)
each system may not be exact equivalents; therefore, each
plus 0.04 to 0.08 % palladium,
system shall be used independently of the other. Combining
1.1.19 Grade 21—Titanium alloy (15 % molybdenum, 3 %
values from the two systems may result in non-conformance
aluminum, 2.7 % niobium, 0.25 % silicon),
with the standard.
1.3 The following caveat pertains only to the test method
portions of this specification: This standard does not purport to
This specification is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee B10 on
address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its
Reactive and Refractory Metals and Alloys and is the direct responsibility of
use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to
Subcommittee B10.01 on Titanium.
establish appropriate safety and health practices and deter-
Current edition approved July 1, 2011. Published August 2011. DOI:10.1520/
B0977–11. mine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
B977−11
2. Referenced Documents 5.1.3 electron beam cold hearth melting followed by
2 vacuum arc melting,
2.1 ASTM Standards:
5.1.4 plasma arc cold hearth melting followed by vacuum
E29 Practice for Using Significant Digits in Test Data to
arc melting,
Determine Conformance with Specifications
5.1.5 electron beam cold hearth melting,
E178 Practice for Dealing With Outlying Observations
5.1.6 plasma arc cold hearth melting or
E539 TestMethodforAnalysisofTitaniumAlloysbyX-Ray
5.1.7 other melting process as agreed upon by the purchaser
Fluorescence Spectrometry
and producer.
E1409 Test Method for Determination of Oxygen and Nitro-
gen in Titanium and Titanium Alloys by the Inert Gas 5.2 The melting method used to produce the ingot shall be
Fusion Technique reported to the purchaser on the certification.
E1447 Test Method for Determination of Hydrogen in Tita-
5.3 The melting method shall be at the discretion of the
nium and Titanium Alloys by Inert Gas Fusion Thermal
producer, unless specified in the purchase order.
Conductivity/Infrared Detection Method
E1941 Test Method for Determination of Carbon in Refrac-
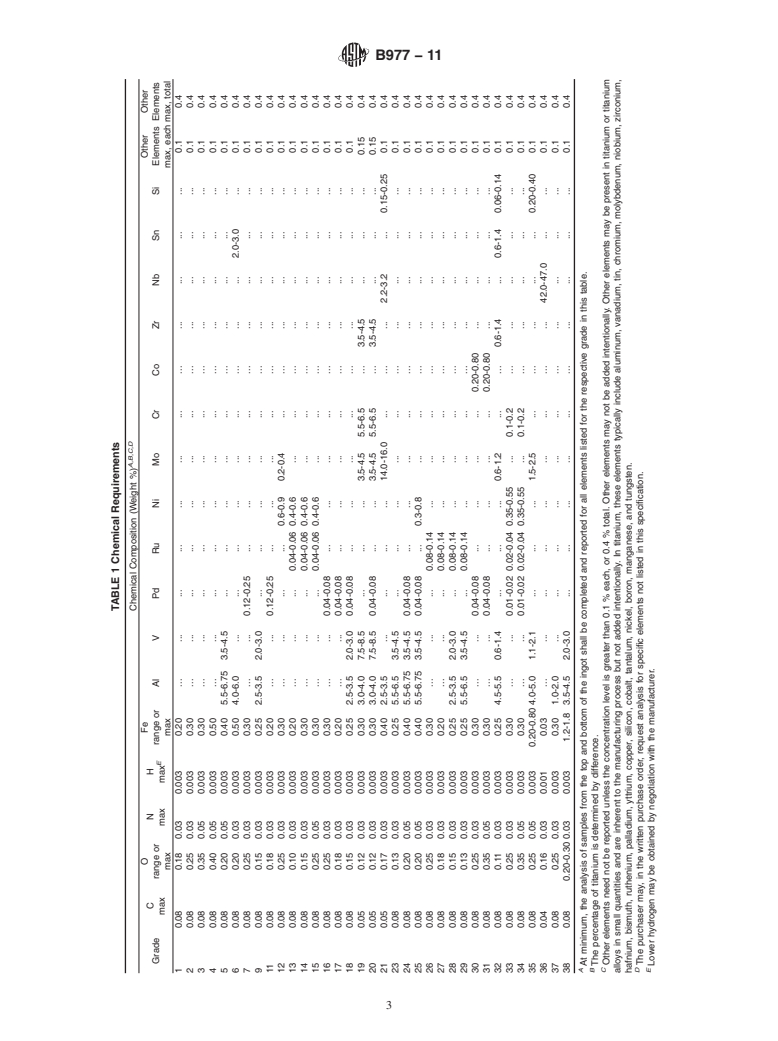
6. Chemical Composition
tory and Reactive Metals andTheirAlloys by Combustion
6.1 The chemistry of titanium and titanium alloy ingot
Analysis
covered by this specification shall conform to the requirements
E2371 Test Method for Analysis of Titanium and Titanium
for the specified grade as prescribed in Table 1.
Alloys by Atomic Emission Plasma Spectrometry
6.1.1 The elements listed for each grade in Table 1 are
E2626 Guide for Spectrometric Analysis of Reactive and
intentional alloy additions or elements that are inherent to the
Refractory Metals
manufacture of titanium sponge or ingot.
6.1.2 Elements intentionally added to the melt, including
3. Terminology
additions made via revert additions, must be identified, ana-
3.1 Lot Definitions:
lyzedandreportedinthechemicalanalysis.Elementsnotlisted
3.2 ingot, n—a quantity of metal cast into a shape suitable
in Table 1 for the specified grade shall not be required.
for subsequent processing to various mill products.
6.1.3 When agreed upon by the producer and purchaser and
requested by the purchaser in the written purchase order,
4. Ordering Information
chemical analysis shall be completed for specific elements not
4.1 Orders for material under this specification shall include
listed in this specification.
the following information as required to describe adequately
6.2 The chemical analysis shall normally be conducted
the desired material:
using theASTM standard test methods referenced in 2.1. Other
4.1.1 Grade number (1.1),
industry standard methods may be used where the ASTM test
4.1.2 Nominal weight in the unit system regarded as stan-
methods in 2.1 do not adequately cover the elements in the
dard (inch-pound or SI),
material or by other methods acceptable to the purchaser.
4.1.3 Nominal size (width and gauge or diameter, length) in
Alternate techniques are discussed in Guide E2626.
the unit system regarded as standard (inch-pound or SI),
6.3 Product Check Analysis—Product check analysis is an
4.1.4 ASTM designation and year of issue.
analysis made by or for the purchaser for the purpose of
4.2 Orders for material under this specification may include
verifying the composition of the ingot. The check analysis
(at the discretion of the purchaser) the following additional
tolerances reflect the variation between laboratories in the
information:
measurement of chemical composition. The permissible varia-
4.2.1 Method of manufacture (5.1),
tion in the product check analysis from the specified range is as
4.2.2 Surface condition (7.1 and 7.2),
prescribed in Table 2.
4.2.3 Product analysis (6.2),
4.2.4 Additional chemical analysis (6.1.3),
7. Condition
4.2.5 Requirements for purchaser inspection/witness (11.1),
7.1 Surface Finish—The surface finish shall be at the
and
discretion of the producer, unless specified in the purchase
4.2.6 Packaging (Section 15).
order.
5. Materials and Manufacture
7.2 When specified, the ingots shall be conditioned on the
5.1 Materials covered by this specification are produced by surfacetostandardsagreeduponbetweenthemanufacturerand
one of the following methods: the purchaser.
5.1.1 double vacuum arc melting,
7.3 Titanium and titanium alloy ingots shall be free of
5.1.2 triple vacuum arc melting,
imperfections that would be deemed injurious by the standards
of acceptability agreed upon between the purchaser and the
manufacturer.
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
7.3.1 The manufacturer shall be permitted to remove minor
contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
surface imperfections. Surface imperfections may be removed
Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on
the ASTM website. up to 1 in. (25 mm) deep from the ingot surface.Areas adjacent
B977−11
TABLE 1 Chemical Requirements
A,B,C,D
Chemical Composition (Weight %)
O Fe Other Other
C N H
Grade range or range or Al V Pd RuNi Mo Cr CoZrNb Sn Si Elements Elements
E
max max max
max max max, each max, total
1 0.08 0.18 0.03 0.003 0.20 . . . . . . . . . . . . 0.1 0.4
2 0.08 0.25 0.03 0.003 0.30 . . . . . . . . . . . . 0.1 0.4
3 0.08 0.35 0.05 0.003 0.30 . . . . . . . . . . . . 0.1 0.4
4 0.08 0.40 0.05 0.003 0.50 . . . . . . . . . . . . 0.1 0.4
5 0.08 0.20 0.05 0.003 0.40 5.5-6.75 3.5-4.5 . . . . . . . . . . 0.1 0.4
6 0.08 0.20 0.03 0.003 0.50 4.0-6.0 . . . . . . . . . 2.0-3.0 . 0.1 0.4
7 0.08 0.25 0.03 0.003 0.30 . . 0.12-0.25 . . . . . . . . . 0.1 0.4
9 0.08 0.15 0.03 0.003 0.25 2.5-3.5 2.0-3.0 . . . . . . . . . . 0.1 0.4
11 0.08 0.18 0.03 0.003 0.20 . . 0.12-0.25 . . . . . . . . . 0.1 0.4
12 0.08 0.25 0.03 0.003 0.30 . . . . 0.6-0.9 0.2-0.4 . . . . . . 0.1 0.4
13 0.08 0.10 0.03 0.003 0.20 . . . 0.04-0.06 0.4-0.6 . . . . . . . 0.1 0.4
14 0.08 0.15 0.03 0.003 0.30 . . . 0.04-0.06 0.4-0.6 . . . . . . . 0.1 0.4
15 0.08 0.25 0.05 0.003 0.30 . . . 0.04-0.06 0.4-0.6 . . . . . . . 0.1 0.4
16 0.08 0.25 0.03 0.003 0.30 . . 0.04-0.08 . . . . . . . . . 0.1 0.4
17 0.08 0.18 0.03 0.003 0.20 . . 0.04-0.08 . . . . . . . . . 0.1 0.4
18 0.08 0.15 0.03 0.003 0.25 2.5-3.5 2.0-3.0 0.04-0.08 . . . . . . . . . 0.1 0.4
19 0.05 0.12 0.03 0.003 0.30 3.0-4.0 7.5-8.5 . . . 3.5-4.5 5.5-6.5 . 3.5-4.5 . . . 0.15 0.4
20 0.05 0.12 0.03 0.003 0.30 3.0-4.0 7.5-8.5 0.04-0.08 . . 3.5-4.5 5.5-6.5 . 3.5-4.5 . . . 0.15 0.4
21 0.05 0.17 0.03 0.003 0.40 2.5-3.5 . . . . 14.0-16.0 . . . 2.2-3.2 . 0.15-0.25 0.1 0.4
23 0.08 0.13 0.03 0.003 0.25 5.5-6.5 3.5-4.5 . . . . . . . . . . 0.1 0.4
24 0.08 0.20 0.05 0.003 0.40 5.5-6.75 3.5-4.5 0.04-0.08 . . . . . . . . . 0.1 0.4
25 0.08 0.20 0.05 0.003 0.40 5.5-6.75 3.5-4.5 0.04-0.08 . 0.3-0.8 . . . . . . . 0.1 0.4
26 0.08 0.25 0.03 0.003 0.30 . . . 0.08-0.14 . . . . . . . . 0.1 0.4
27 0.08 0.18 0.03 0.003 0.20 . . . 0.08-0.14 . . . . . . . . 0.1 0.4
28 0.08 0.15 0.03 0.003 0.25 2.5-3.5 2.0-3.0 . 0.08-0.14 . . . . . . . . 0.1 0.4
29 0.08 0.13 0.03 0.003 0.25 5.5-6.5 3.5-4.5 . 0.08-0.14 . . . . . . . . 0.1 0.4
30 0.08 0.25 0.03 0.003 0.30 . . 0.04-0.08 . . . . 0.20-0.80 . . . . 0.1 0.4
31 0.08 0.35 0.05 0.003 0.30 . . 0.04-0.08 . . . . 0.20-0.80 . . . . 0.1 0.4
32 0.08 0.11 0.03 0.003 0.25 4.5-5.5 0.6-1.4 . . . 0.6-1.2 . . 0.6-1.4 . 0.6-1.4 0.06-0.14 0.1 0.4
33 0.08 0.25 0.03 0.003 0.30 . . 0.01-0.02 0.02-0.04 0.35-0.55 . 0.1-0.2 . . . . . 0.1 0.4
34 0.08 0.35 0.05 0.003 0.30 . . 0.01-0.02 0.02-0.04 0.35-0.55 . 0.1-0.2 . . . . . 0.1 0.4
35 0.08 0.25 0.05 0.003 0.20-0.80 4.0-5.0 1.1-2.1 . . . 1.5-2.5 . . . . . 0.20-0.40 0.1 0.4
36 0.04 0.16 0.03 0.001 0.03 . . . . . . . . . 42.0-47.0 . . 0.1 0.4
37 0.08 0.25 0.03 0.003 0.30 1.0-2.0 . . . . . . . . . . . 0.1 0.4
38 0.08 0.20-0.30 0.03 0.003 1.2-1.8 3.5-4.5 2.0-3.0 . . . . . . . . . . 0.1 0.4
A
At minimum, the analysis of samples from the top and bottom of the ingot shall be completed and reported for all elements listed for the respective grade in this table.
B
The percentage of titanium is determined by difference.
C
Other elements need not be reported unless the concentration level is greater than 0.1 % each, or 0.4 % total. Other elements may not be added intentionally. Other elements may be present in titanium or titanium
alloys in small quantities and are inherent to the manufacturing process but not added intentionally. In titanium, these elements typically include aluminum, vanadium, tin, chromium, molybdenum, niobium, zirconium,
hafnium, bismuth, ruthenium, palladium, yttrium, copper, silicon, cobalt, tantalum, nickel, boron, manganese, and tungsten.
D
The purchaser may, in the written purchase order, request analysis for specific elements not listed in this specification.
E
Lower hydrogen may be obtained by negotiation with the manufacturer.
B977−11
TABLE 2 Permissible Variations in Product Analysis
location. The frequency of the resample will be at least double
Product Analysis Limits, Permissible Variation in the initial number of tests. If the results of the resample
Element Max or Range, (%) Product Analysis
conform to the specification, then the resample values become
Aluminum 0.5 to 2.5 ±0.20
the test values for certification.
Aluminum 2.5 to 6.75 ±0.40
Carbon 0.10 ±0.02
8.3 The manufacturer may scalp or crop the ingot to remove
Chromium 0.1 to 0.2 ±0.02
nonconforming material then sample the remaining ingot
Chromium 5.5 to 6.5 ±0.30
Cobalt 0.2 to 0.8 ±0.05
position(s). The ingot shall be acceptable if all results of the
Hydrogen 0.02 ±0.002
tests on the ingot conform to this specification.
Iron 0.80 ±0.15
Iron 1.2 to 1.8 ±0.20
9. Sampling
Molybdenum 0.2 to 0.4 ±0.03
Molybdenum 0.6 to 1.2 ±0.15
9.1 Samples for chemical analyses shall be representative of
Molybdenum 1.5 to 4.5 ±0.20
the material bein
...







Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.