ASTM D7493-22
(Test Method)Standard Test Method for Online Measurement of Sulfur Compounds in Natural Gas and Gaseous Fuels by Gas Chromatograph and Electrochemical Detection
Standard Test Method for Online Measurement of Sulfur Compounds in Natural Gas and Gaseous Fuels by Gas Chromatograph and Electrochemical Detection
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
5.1 Gaseous fuels, such as natural gas, petroleum gases and bio-gases, contain sulfur compounds that are naturally occurring or that are added as odorants for safety purposes. These sulfur compounds are odorous, toxic, corrosive to equipment, and can inhibit or destroy catalysts employed in gas processing and other end uses. Their accurate continuous measurement is important to gas processing, operation and use, and is frequently of regulatory interest.
5.2 Small amounts (typically, total of 4 to 6 ppm(v)) of sulfur odorants are added to natural gas and other fuel gases for safety purposes. Some sulfur odorants are reactive and may be oxidized to form more stable sulfur compounds having higher odor thresholds which adversely impact the potential safety of the gas delivery systems and gas users. Gaseous fuels are analyzed for sulfur compounds and odorant levels to assist in pipeline integrity surveillance and to ensure appropriate odorant levels for public safety.
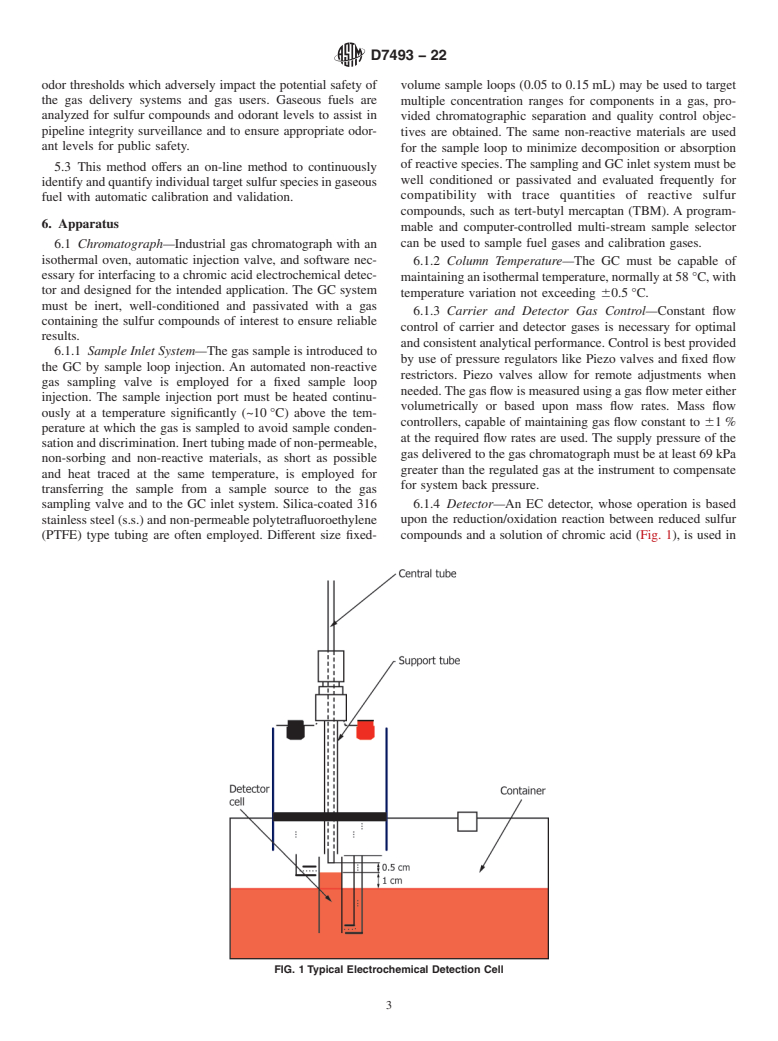
5.3 This method offers an on-line method to continuously identify and quantify individual target sulfur species in gaseous fuel with automatic calibration and validation.
SCOPE
1.1 This test method is for on-line measurement of gas phase sulfur-containing compounds in gaseous fuels by gas chromatography (GC) and electrochemical (EC) detection. This test method is applicable to hydrogen sulfide, C1 to C4 mercaptans, sulfides, and tetrahydrothiophene (THT).
1.1.1 Carbonyl sulfide (COS) is not measured according to this test method.
1.1.2 The detection range for sulfur compounds is approximately from 0.1 to 100 ppm(v) (mL/m3) or 0.1 to 100 mg/m3 at 25 °C, 101.3 kPa. The detection range will vary depending on the sample injection volume, chromatographic peak separation, and the sensitivity of the specific EC detector.
1.2 This test method describes a GC-EC method using capillary GC columns and a specific detector for natural gas and other gaseous fuels composed of mainly light (C4 and smaller) hydrocarbons. Alternative GC columns including packed columns, detector designs, and instrument parameters may be used, provided that chromatographic separation, quality control, and measurement objectives needed to comply with user or regulator needs, or both, are achieved.
1.3 This test method does not intend to identify and measure all individual sulfur species and is mainly employed for monitoring naturally occurring reduced sulfur compounds commonly found in natural gas and fuel gases or employed as an odorant in these gases.
1.4 This test method is typically employed in repetitive or continuous on-line monitoring of sulfur components in natural gas and fuel gases using a single sulfur calibration standard. Guidance for producing calibration curves specific to particular analytes or enhanced quality control procedures can be found in Test Methods D5504, D5623, D6228, D6968, ISO 19739, or GPA 2199.
1.5 The test method can be used for measuring sulfur compounds listed in Table 1 in air or other gaseous matrices, provided that compounds that can interfere with the GC separation and electrochemical detection are not present.
1.6 This test method is written as a companion to Practices D5287, D7165 and D7166.
1.7 Units—The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as standard. No other units of measurement are included in this standard.
1.8 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety, health, and environmental practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
1.9 This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization established in the Decision on Principles for the Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued by the World Trade Organization Tec...
General Information
Buy Standard
Standards Content (Sample)
This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization established in the Decision on Principles for the
Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
Designation: D7493 − 22
Standard Test Method for
Online Measurement of Sulfur Compounds in Natural Gas
and Gaseous Fuels by Gas Chromatograph and
1
Electrochemical Detection
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D7493; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope 1.5 The test method can be used for measuring sulfur
compounds listed in Table 1 in air or other gaseous matrices,
1.1 This test method is for on-line measurement of gas
provided that compounds that can interfere with the GC
phase sulfur-containing compounds in gaseous fuels by gas
separation and electrochemical detection are not present.
chromatography (GC) and electrochemical (EC) detection.
This test method is applicable to hydrogen sulfide, C1 to C4 1.6 This test method is written as a companion to Practices
mercaptans, sulfides, and tetrahydrothiophene (THT). D5287, D7165 and D7166.
1.1.1 Carbonyl sulfide (COS) is not measured according to
1.7 Units—The values stated in SI units are to be regarded
this test method.
as standard. No other units of measurement are included in this
1.1.2 The detection range for sulfur compounds is approxi-
standard.
3 3
mately from 0.1 to 100 ppm(v) (mL/m ) or 0.1 to 100 mg/m
1.8 This standard does not purport to address all of the
at 25 °C, 101.3 kPa. The detection range will vary depending
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
on the sample injection volume, chromatographic peak
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
separation, and the sensitivity of the specific EC detector.
priate safety, health, and environmental practices and deter-
1.2 This test method describes a GC-EC method using
mine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
capillary GC columns and a specific detector for natural gas
1.9 This international standard was developed in accor-
and other gaseous fuels composed of mainly light (C4 and
dance with internationally recognized principles on standard-
smaller) hydrocarbons. Alternative GC columns including
ization established in the Decision on Principles for the
packed columns, detector designs, and instrument parameters
Development of International Standards, Guides and Recom-
may be used, provided that chromatographic separation, qual-
mendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical
ity control, and measurement objectives needed to comply with
Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
user or regulator needs, or both, are achieved.
2. Referenced Documents
1.3 This test method does not intend to identify and measure
2
all individual sulfur species and is mainly employed for
2.1 ASTM Standards:
monitoring naturally occurring reduced sulfur compounds
D3609 Practice for Calibration Techniques Using Perme-
commonly found in natural gas and fuel gases or employed as
ation Tubes
an odorant in these gases.
D4150 Terminology Relating to Gaseous Fuels
D4626 Practice for Calculation of Gas Chromatographic
1.4 This test method is typically employed in repetitive or
Response Factors
continuous on-line monitoring of sulfur components in natural
D5287 Practice for Automatic Sampling of Gaseous Fuels
gas and fuel gases using a single sulfur calibration standard.
D5504 Test Method for Determination of Sulfur Compounds
Guidance for producing calibration curves specific to particular
in Natural Gas and Gaseous Fuels by Gas Chromatogra-
analytes or enhanced quality control procedures can be found
phy and Chemiluminescence
in Test Methods D5504, D5623, D6228, D6968, ISO 19739, or
D5623 Test Method for Sulfur Compounds in Light Petro-
GPA 2199.
leum Liquids by Gas Chromatography and Sulfur Selec-
tive Detection
1
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D03 on Gaseous
Fuels and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee D03.12 on On-Line/At-Line
2
Analysis of Gaseous Fuels. For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
Current edition approved Nov. 1, 2022. Published April 2023. Originally contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
approved in 2008. Last previous edition approved in 2018 as D7493 – 14 (2018). Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on
DOI: 10.1520/D7493-22. the ASTM website.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ------------
...
This document is not an ASTM standard and is intended only to provide the user of an ASTM standard an indication of what changes have been made to the previous version. Because
it may not be technically possible to adequately depict all changes accurately, ASTM recommends that users consult prior editions as appropriate. In all cases only the current version
of the standard as published by ASTM is to be considered the official document.
Designation: D7493 − 14 (Reapproved 2018) D7493 − 22
Standard Test Method for
Online Measurement of Sulfur Compounds in Natural Gas
and Gaseous Fuels by Gas Chromatograph and
1
Electrochemical Detection
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D7493; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope
1.1 This test method is for on-line measurement of volatile gas phase sulfur-containing compounds in gaseous fuels by gas
chromatography (GC) and electrochemical (EC) detection. This test method is applicable to hydrogen sulfide, C1 to C4
mercaptans, sulfides, and tetrahydrothiophene (THT).
1.1.1 Carbonyl sulfide (COS) is not covered in measured according to this test method.
3 3
1.1.2 The detection range for sulfur compounds is approximately from 0.1 to 100 ppmvppm(v) (mL/m ) or 0.1 to 100 mg/m . at
25 °C, 101.3 kPa. The detection range maywill vary depending on the sample injection volume, chromatographic peak separation,
and the sensitivity toof the specific EC detector.
1.2 This test method describes a GC-EC method employing packedusing capillary GC columns and a specific detector for natural
gas and other gaseous fuelfuels composed of mainly light (C4 and smaller) hydrocarbons. Alternative GC columns including
packed columns, detector designs, and instrument parameters may be used, provided that chromatographic separation, quality
control, and measurement objectives needed to comply with user,user or regulator needs, or both, are achieved.
1.3 This test method does not intend to identify and measure all individual sulfur species,species and is mainly employed for
monitoring naturally occurring reduced sulfur compounds commonly found in natural gas and fuel gases or employed as an odorant
in these gases.
1.4 TheThis test method is typically employed in repetitive or continuous on-line monitoring of sulfur components in natural gas
and fuel gases using a single sulfur calibration standard. Need for a multipoint calibration curve or Guidance for producing
calibration curves specific to particular analytes or enhanced quality control procedures can be satisfied by making use of
procedures delineated found in Test Methods D5504, D5623, D6228, D6968, ISO 19739, or GPA 2199.
1.5 The test method can be used for measurement of all measuring sulfur compounds listed in Table 1 in air or other gaseous
matrices, provided that no compounds that can interfere with the GC separation and electrochemical detection are not present.
1.6 This test method is written as a companion to Practices D5287, D7165 and D7166.
1
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D03 on Gaseous Fuels and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee D03.12 on On-Line/At-Line
Analysis of Gaseous Fuels.
Current edition approved July 1, 2018Nov. 1, 2022. Published July 2018April 2023. Originally approved in 2008. Last previous edition approved in 20142018 as
D7493D7493 – 14 (2018).-14. DOI: 10.1520/D7493-14R18.10.1520/D7493-22.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
D7493 − 22
TABLE 1 Typical Retention Times of Sulfur Components of Different GC-ECD Runs
GC-EC instrument GC-EC #1 GC-EC #2 GC-EC #3
1
GC-Column and ⁄8 in. ID× 70 cm L, 1.6 mm ID× 1200 mm L, 4 mm ID× 400 mm L,
parameters N , 12 mL/min, 65 °C N , 100 mL/min, 20 °C N , 100 mL/min, 20 °C
2 2 2
Detector Size 5×20 mm 5×20 mm 30×25 mm
Sulfur Compound RT (sec.) RT (sec.) RT (sec.)
Hydrogen sulfide, H S 30 30 30
2
Methyl mercaptan (MeSH) 70 66 60
Ethyl mercaptan (EtSH) 105 150 80
Dimethyl sulfide (DMS) 120 200 80
i-Propyl mercaptan (IPM) 160 240 160
t-Butyl mercaptan (TBM) 220 342 240
n-Propyl mercaptan (NPM) 265 426 290
i-Butyl mercaptan (IBM) 440 . 560
n-Butyl mercaptan (NBM) 585 . .
A A
Thiophane (THT) 900 720 2100
TABLE 1 Example Retention Times of Sulfur Components Observed for Several Column and Detector Sizes
GC-EC instrument GC-EC #1 GC-EC #2 GC-EC #3 GC-EC #4
1
GC-Column and ⁄8 in. ID × 70 cm L, 1.6 mm ID×1200 mm L, 4 mm ID× 400 mm L, 0.53 mm IDx 30 m, N , 4 mL/
2
parameters N , 12 mL/min, 65 °C N , 100 mL/min, 20 °C N , 100 mL/min, 20 °C min, 58 °C
2 2 2
Detector Size 5×20 mm 5×20 mm 30×25 mm 5x20 mm
Sulfur Compound RT (sec.) RT (sec.) RT
...










Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.