ASTM D4468-23
(Test Method)Standard Test Method for Total Sulfur in Gaseous Fuels by Hydrogenolysis and Rateometric Colorimetry
Standard Test Method for Total Sulfur in Gaseous Fuels by Hydrogenolysis and<brk/> Rateometric Colorimetry
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
5.1 This test method can be used to determine specification, or regulatory compliance to requirements, for total sulfur in gaseous fuels. In gas processing plants, sulfur can be a contaminant and must be removed before gas is introduced into gas pipelines. In petrochemical plants, sulfur is a poison for many catalysts and must be reduced to acceptable levels, usually in the range from 0.01 ppm/v to 1 ppm/v. This test method may also be used as a quality-control tool for sulfur determination in finished products, such as propane, butane, ethane, and ethylene.
SCOPE
1.1 This test method covers the determination of sulfur gaseous fuels in the range from 0.001 to 20 parts per million by volume (ppm/v).
1.2 This test method may be extended to higher concentration by dilution.
1.3 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as standard. No other units of measurement are included in this standard.
1.4 This standard may involve hazardous materials, operations, and equipment. This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety, health, and environmental practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use. Specific precautionary statements are given in 7.7, 7.8, and 8.3.
1.5 This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization established in the Decision on Principles for the Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
General Information
Relations
Buy Standard
Standards Content (Sample)
This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization established in the Decision on Principles for the
Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
Designation: D4468 − 23
Standard Test Method for
Total Sulfur in Gaseous Fuels by Hydrogenolysis and
1
Rateometric Colorimetry
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D4468; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope 3. Terminology
1.1 This test method covers the determination of sulfur 3.1 For definitions of general terms used in D03 Gaseous
gaseous fuels in the range from 0.001 to 20 parts per million by Fuels standards, refer to Terminology D4150.
volume (ppm/v).
4. Summary of Test Method
1.2 This test method may be extended to higher concentra-
tion by dilution. 4.1 The sample is introduced at a constant rate into a
flowing hydrogen stream in a hydrogenolysis apparatus. The
1.3 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as
sample and hydrogen are pyrolyzed at a temperature of
standard. No other units of measurement are included in this
1000 °C or above, to convert sulfur compounds to hydrogen
standard.
sulfide (H S). Readout is by the rateometric detection of the
2
1.4 This standard may involve hazardous materials,
colorimetric reaction of H S with lead acetate. Units used are
2
operations, and equipment. This standard does not purport to
ppm/v, which is equivalent to micromoles/mole.
address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its
use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to
5. Significance and Use
establish appropriate safety, health, and environmental prac-
5.1 This test method can be used to determine specification,
tices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations
or regulatory compliance to requirements, for total sulfur in
prior to use. Specific precautionary statements are given in 7.7,
gaseous fuels. In gas processing plants, sulfur can be a
7.8, and 8.3.
contaminant and must be removed before gas is introduced into
1.5 This international standard was developed in accor-
gas pipelines. In petrochemical plants, sulfur is a poison for
dance with internationally recognized principles on standard-
many catalysts and must be reduced to acceptable levels,
ization established in the Decision on Principles for the
usually in the range from 0.01 ppm ⁄v to 1 ppm ⁄v. This test
Development of International Standards, Guides and Recom-
method may also be used as a quality-control tool for sulfur
mendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical
determination in finished products, such as propane, butane,
Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
ethane, and ethylene.
2. Referenced Documents
6. Apparatus
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
6.1 Pyrolysis Furnace—A furnace that can provide an
D1193 Specification for Reagent Water
adjustable temperature of 900 °C to 1300 °C in a quartz or
D1914 Practice for Conversion Units and Factors Relating to
ceramic tube of 5 mm or larger tube (ID) is required for
Sampling and Analysis of Atmospheres
pyrolysis of the sample. (See Fig. 1.) The flow system is to be
D4045 Test Method for Sulfur in Petroleum Products by
a fluorocarbon or other material inert to H S and other sulfur
Hydrogenolysis and Rateometric Colorimetry
2
compounds. (See Fig. 1.)
D4150 Terminology Relating to Gaseous Fuels
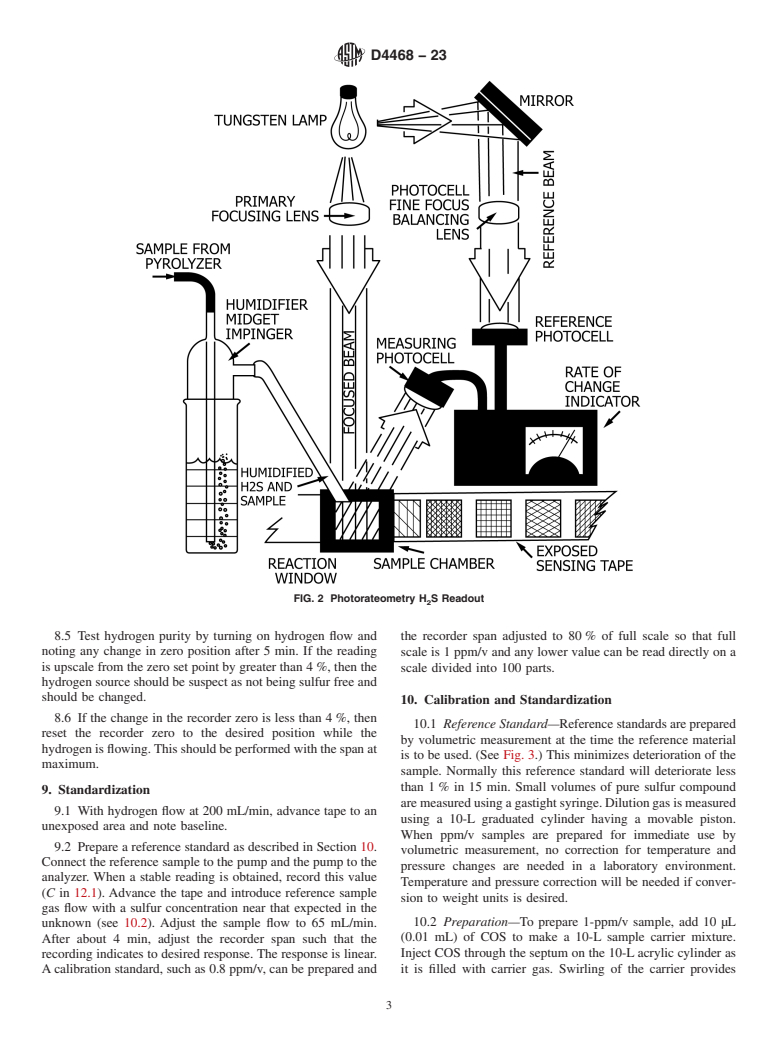
6.2 Rateometric H S Readout—Hydrogenolysis products
2
contain H S in proportion to sulfur in the sample. The H S
1
2 2
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D03 on Gaseous
concentration is determined by measuring rate of change of
Fuels and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee D03.06.03 on Analysis by
Spectroscopy.
reflectance of a tape impregnated with lead acetate caused by
Current edition approved June 1, 2023. Published June 2023. Originally
darkening when lead sulfide is formed. Rateometric
approved in 1985. Last previous edition approved in 2015 as D4468 – 85 (2015).
electronics, adapted to provide first derivative output, allows
DOI: 10.1520/D4468-23.
2
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or sufficient sensitivity to measure to 0.001 ppm/v. (See Fig. 2.)
contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
6.3 Recorder—A suitable chart recorder may be used for a
Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on
the ASTM website. permanent record of analysis.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
D4468 − 23
FIG. 1 H
...
This document is not an ASTM standard and is intended only to provide the user of an ASTM standard an indication of what changes have been made to the previous version. Because
it may not be technically possible to adequately depict all changes accurately, ASTM recommends that users consult prior editions as appropriate. In all cases only the current version
of the standard as published by ASTM is to be considered the official document.
Designation: D4468 − 85 (Reapproved 2015) D4468 − 23
Standard Test Method for
Total Sulfur in Gaseous Fuels by Hydrogenolysis and
1
Rateometric Colorimetry
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D4468; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope
1.1 This test method covers the determination of sulfur gaseous fuels in the range from 0.001 to 20 parts per million by volume
(ppm/v).
1.2 This test method may be extended to higher concentration by dilution.
1.3 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as standard. No other units of measurement are included in this standard.
1.4 This standard may involve hazardous materials, operations, and equipment. This standard does not purport to address all
of the safety concerns concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish
appropriate safety and healthsafety, health, and environmental practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations
prior to use. Specific precautionary statements are given in 6.77.7, 6.87.8, and 7.38.3.
1.5 This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization
established in the Decision on Principles for the Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued
by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
2. Referenced Documents
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
D1193 Specification for Reagent Water
D1914 Practice for Conversion Units and Factors Relating to Sampling and Analysis of Atmospheres
D4045 Test Method for Sulfur in Petroleum Products by Hydrogenolysis and Rateometric Colorimetry
D4150 Terminology Relating to Gaseous Fuels
3. Terminology
3.1 For definitions of general terms used in D03 Gaseous Fuels standards, refer to Terminology D4150.
4. Summary of Test Method
4.1 The sample is introduced at a constant rate into a flowing hydrogen stream in a hydrogenolysis apparatus. The sample and
1
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D03 on Gaseous Fuels and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee D03.05 on Determination of
Special Constituents of Gaseous Fuels.
Current edition approved Nov. 1, 2015June 1, 2023. Published December 2015June 2023. Originally approved in 1985. Last previous edition approved in 20112015 as
D4468–85D4468 – 85 (2015). (2011). DOI: 10.1520/D4468-85R15.10.1520/D4468-23.
2
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM Standards
volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on the ASTM website.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
D4468 − 23
hydrogen are pyrolyzed at a temperature of 1000°C1000 °C or above, to convert sulfur compounds to hydrogen sulfide (H S).
2
Readout is by the rateometric detection of the colorimetric reaction of H S with lead acetate. Units used are ppm/v, which is
2
equivalent to micromoles/mole.
5. Significance and Use
5.1 This test method can be used to determine specification, or regulatory compliance to requirements, for total sulfur in gaseous
fuels. In gas processing plants, sulfur can be a contaminant and must be removed before gas is introduced into gas pipelines. In
petrochemical plants, sulfur is a poison for many catalysts and must be reduced to acceptable levels, usually in the range from
0.010.01 ppm ⁄v to 11 ppm ppm/v. ⁄v. This test method may also be used as a quality-control tool for sulfur determination in
finished products, such as propane, butane, ethane, and ethylene.
6. Apparatus
6.1 Pyrolysis Furnace—A furnace that can provide an adjustable temperature of 900 to 1300°C900 °C to 1300 °C in a quartz or
ceramic tube of 5 mm mm or larger tube (ID) is required for pyrolysis of the sample. (See Fig. 1.) The flow system is to be a
fluorocarbon or other material inert to H S and other sulfur compounds. (See Fig. 1.)
2
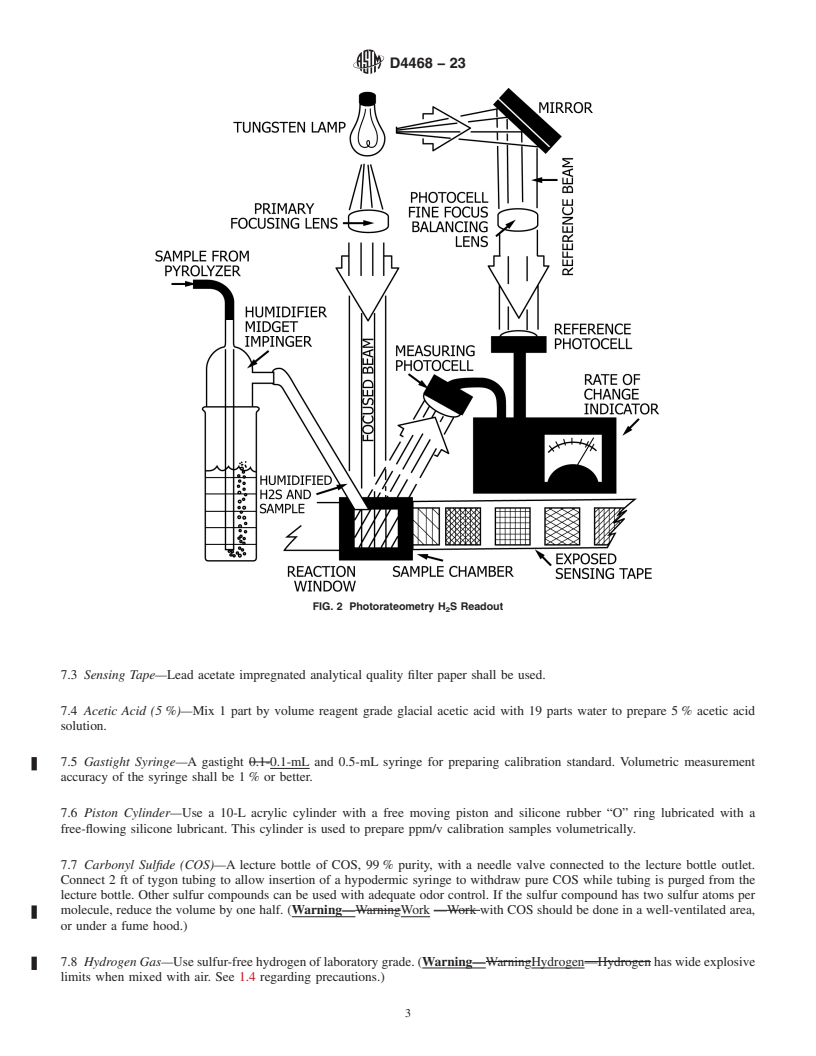
6.2 Rateometric H S Readout—Hydrogenolysis products contain H S in proportion to sulfur in the sample. The H S concentration
2 2 2
is determined by measuring rate of change of reflectance of a tape impregnate
...








Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.