ASTM E70-07(2015)
(Test Method)Standard Test Method for pH of Aqueous Solutions With the Glass Electrode
Standard Test Method for pH of Aqueous Solutions With the Glass Electrode
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
4.1 pH is, within the limits described in 1.1, an accurate measurement of the hydrogen ion concentration and thus is widely used for the characterization of aqueous solutions.
4.2 pH measurement is one of the main process control variables in the chemical industry and has a prominent place in pollution control.
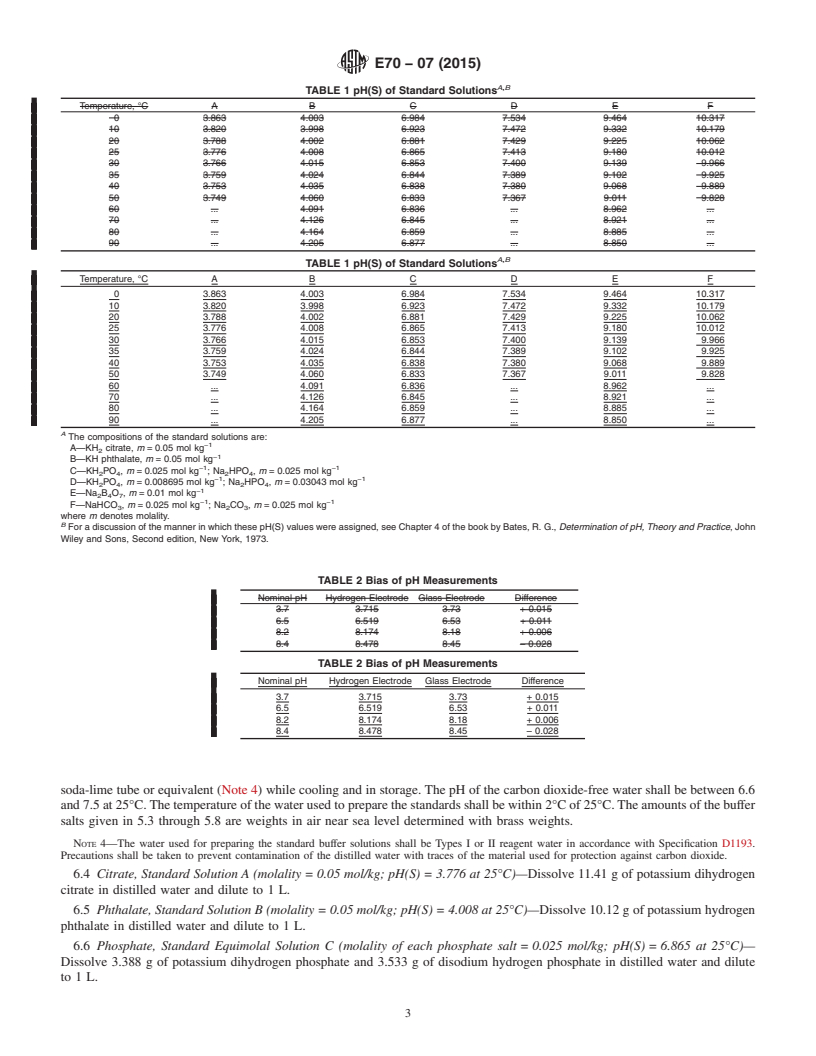
SCOPE
1.1 This test method specifies the apparatus and procedures for the electrometric measurement of pH values of aqueous solutions with the glass electrode. It does not deal with the manner in which the solutions are prepared. pH measurements of good precision can be made in aqueous solutions containing high concentrations of electrolytes or water-soluble organic compounds, or both. It should be understood, however, that pH measurements in such solutions are only a semiquantitative indication of hydrogen ion concentration or activity. The measured pH will yield an accurate result for these quantities only when the composition of the medium matches approximately that of the standard reference solutions. In general, this test method will not give an accurate measure of hydrogen ion activity unless the pH lies between 2 and 12 and the concentration of neither electrolytes nor nonelectrolytes exceeds 0.1 mol/L (M).
1.2 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as standard. The values in parentheses are for information only.
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
General Information
Relations
Buy Standard
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Designation: E70 − 07 (Reapproved 2015)
Standard Test Method for
1
pH of Aqueous Solutions With the Glass Electrode
ThisstandardisissuedunderthefixeddesignationE70;thenumberimmediatelyfollowingthedesignationindicatestheyearoforiginal
adoptionor,inthecaseofrevision,theyearoflastrevision.Anumberinparenthesesindicatestheyearoflastreapproval.Asuperscript
epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
This standard has been approved for use by agencies of the U.S. Department of Defense.
1. Scope* 2. Referenced Documents
2
1.1 This test method specifies the apparatus and procedures 2.1 ASTM Standards:
for the electrometric measurement of pH values of aqueous D1193Specification for Reagent Water
solutions with the glass electrode. It does not deal with the E180Practice for Determining the Precision of ASTM
manner in which the solutions are prepared. pH measurements Methods for Analysis and Testing of Industrial and Spe-
3
ofgoodprecisioncanbemadeinaqueoussolutionscontaining cialty Chemicals (Withdrawn 2009)
high concentrations of electrolytes or water-soluble organic E691Practice for Conducting an Interlaboratory Study to
compounds,orboth.Itshouldbeunderstood,however,thatpH Determine the Precision of a Test Method
measurements in such solutions are only a semiquantitative
3. Terminology
indication of hydrogen ion concentration or activity. The
measured pH will yield an accurate result for these quantities 3.1 Definitions:
only when the composition of the medium matches approxi- 3.1.1 pH—defined formally as the negative logarithm to the
mately that of the standard reference solutions. In general, this base 10 of the conventional hydrogen ion activity. See Appen-
test method will not give an accurate measure of hydrogen ion dix X1.
activity unless the pH lies between 2 and 12 and the concen-
3.2 Definitions of Terms Specific to This Standard:
tration of neither electrolytes nor nonelectrolytes exceeds 0.1
3.2.1 For the purpose of this test method, the term “meter”
mol/L (M).
shall apply to the instrument used for the measurement of
1.2 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as potential (either in millivolts or in terms of pH units), the term
standard. The values in parentheses are for information only.
“electrodes” to the glass electrode and the reference electrode,
and the term “assembly” to the combination of the meter and
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the
the electrodes. The performance of the meter shall be differ-
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
entiated from that of the electrodes.
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
priate safety, health, and environmental practices and deter-
4. Significance and Use
mine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
4.1 pH is, within the limits described in 1.1, an accurate
1.4 This international standard was developed in accor-
measurement of the hydrogen ion concentration and thus is
dance with internationally recognized principles on standard-
widely used for the characterization of aqueous solutions.
ization established in the Decision on Principles for the
Development of International Standards, Guides and Recom-
4.2 pH measurement is one of the main process control
mendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical
variablesinthechemicalindustryandhasaprominentplacein
Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
pollution control.
1 2
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D16 on For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
Aromatic, Industrial, Specialty and Related Chemicals and is the direct responsi- contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
bility of Subcommittee D16.04 on Instrumental Analysis. Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on
Current edition approved June 1, 2015. Published June 2015. Originally the ASTM website.
3
approved in 1952. Last previous edition approved in 2007 as E70–07. DOI: The last approved version of this historical standard is referenced on
10.1520/E0070-07R15. www.astm.org.
*A Summary of Changes section appears at the end of this standard
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
E70 − 07 (2015)
5. Apparatus 5.2.4 If the assembly is in intermittent use, the ends of the
electrodes shall be immersed in distilled water between mea-
5.1 pH meters—Many excellent pH meters are available
surements. The high-alkalinity type of glass electrode shall be
from commercial sources. To some extent, the choice of meter
storedintheboraxbuffersolution.Forprolongedstorage,glass
will depend on the desired precision of measu
...
This document is not an ASTM standard and is intended only to provide the user of an ASTM standard an indication of what changes have been made to the previous version. Because
it may not be technically possible to adequately depict all changes accurately, ASTM recommends that users consult prior editions as appropriate. In all cases only the current version
of the standard as published by ASTM is to be considered the official document.
Designation: E70 − 07 E70 − 07 (Reapproved 2015)
Standard Test Method for
1
pH of Aqueous Solutions With the Glass Electrode
This standard is issued under the fixed designation E70; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of original
adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A superscript
epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
This standard has been approved for use by agencies of the U.S. Department of Defense.
1. Scope*
1.1 This test method specifies the apparatus and procedures for the electrometric measurement of pH values of aqueous
solutions with the glass electrode. It does not deal with the manner in which the solutions are prepared. pH measurements of good
precision can be made in aqueous solutions containing high concentrations of electrolytes or water-soluble organic compounds, or
both. It should be understood, however, that pH measurements in such solutions are only a semiquantitative indication of hydrogen
ion concentration or activity. The measured pH will yield an accurate result for these quantities only when the composition of the
medium matches approximately that of the standard reference solutions. In general, this test method will not give an accurate
measure of hydrogen ion activity unless the pH lies between 2 and 12 and the concentration of neither electrolytes nor
nonelectrolytes exceeds 0.1 mol/L (M).
1.2 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as standard. The values in parentheses are for information only.
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility
of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory
limitations prior to use.
2. Referenced Documents
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
D1193 Specification for Reagent Water
E180 Practice for Determining the Precision of ASTM Methods for Analysis and Testing of Industrial and Specialty Chemicals
3
(Withdrawn 2009)
E691 Practice for Conducting an Interlaboratory Study to Determine the Precision of a Test Method
3. Terminology
3.1 Definitions:
3.1.1 pH—defined formally as the negative logarithm to the base 10 of the conventional hydrogen ion activity. See Appendix
X1.
3.2 Definitions of Terms Specific to This Standard:
3.2.1 For the purpose of this test method, the term “meter” shall apply to the instrument used for the measurement of potential
(either in millivolts or in terms of pH units), the term “electrodes” to the glass electrode and the reference electrode, and the term
“assembly” to the combination of the meter and the electrodes. The performance of the meter shall be differentiated from that of
the electrodes.
4. Significance and Use
4.1 pH is, within the limits described in 1.1, an accurate measurement of the hydrogen ion concentration and thus is widely used
for the characterization of aqueous solutions.
1
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee E15 on Industrial and Specialty Chemicals and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee E15.01 on
General Standards.
Current edition approved April 1, 2007June 1, 2015. Published May 2007June 2015. Originally approved in 1952. Last previous edition approved in 20022007 as E70 – 97
(2002).E70 – 07. DOI: 10.1520/E0070-07.10.1520/E0070-07R15.
2
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM Standards
volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on the ASTM website.
3
The last approved version of this historical standard is referenced on www.astm.org.
*A Summary of Changes section appears at the end of this standard
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
E70 − 07 (2015)
4.2 pH measurement is one of the main process control variables in the chemical industry and has a prominent place in pollution
control.
5. Apparatus
5.1 pH meters—Many excellent pH meters are available from commercial sources. To some extent, the choice of meter will
depend on the desired precision of measurement. The meter may operate on a null-detection principle or may utilize digital readout
or a direct deflection meter with a large scale. Power may be supplied by batteries or a-c operation may be provided.
...









Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.