ASTM D710-19
(Specification)Standard Specification for Vulcanized Fibre Sheets, Rolls, Rods, and Tubes Used for Electrical Insulation
Standard Specification for Vulcanized Fibre Sheets, Rolls, Rods, and Tubes Used for Electrical Insulation
ABSTRACT
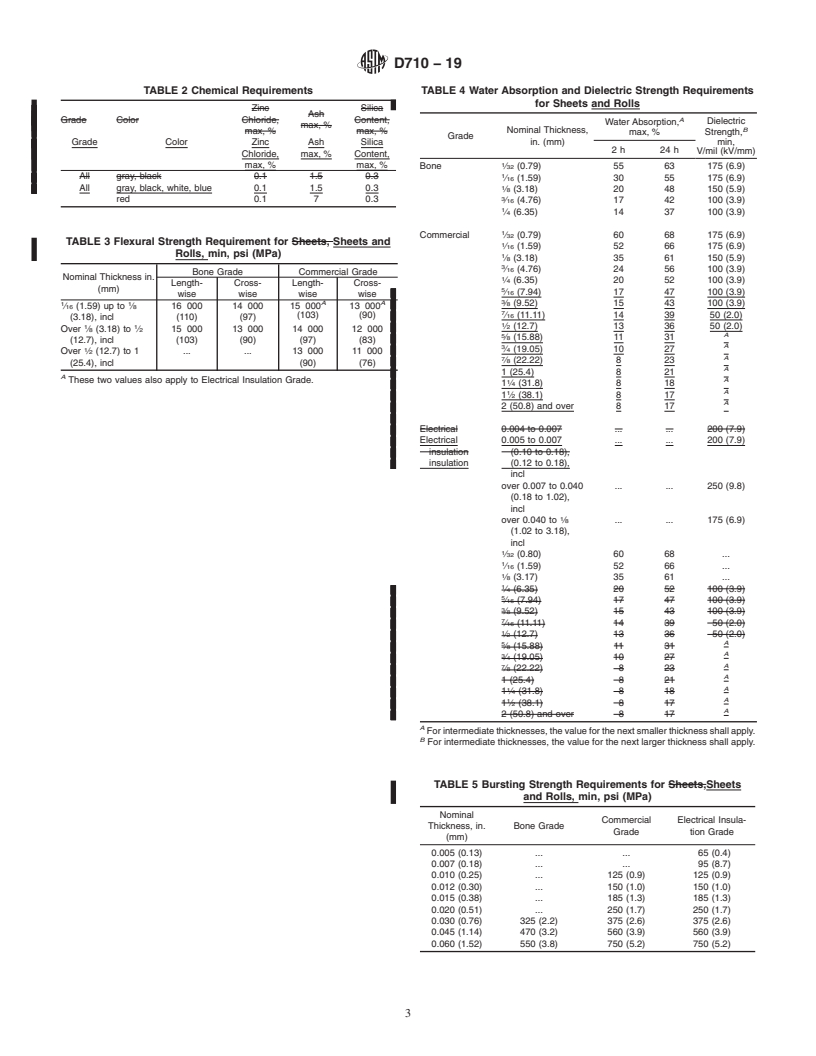
This specification covers vulcanized fibres in sheet, round rod, and round tube forms of bone, commercial, and electrical insulation grades. Fibres shall be tested appropriatedly and consequently conform to specified color, chemical composition, flexural strength, impact strength, tearing strength, compressive strength, water absorption, dielectric strength, bursting strength, density, Rockwell hardness, and dimensional and size requirements.
SCOPE
1.1 This specification covers vulcanized fibre (Note 1) sheets, rolls, round rods, and round tubes of such grades suitable for use as electrical insulation.
Note 1: The variant spelling “fibre” has been approved by Committee D09 for use in this standard.
1.2 The values stated in inch-pound units are to be regarded as standard. The values given in parentheses are mathematical conversions to SI units that are provided for information only and are not considered standard.
1.3 This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization established in the Decision on Principles for the Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
General Information
Relations
Buy Standard
Standards Content (Sample)
This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization established in the Decision on Principles for the
Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
Designation:D710 −19
Standard Specification for
Vulcanized Fibre Sheets, Rolls, Rods, and Tubes Used for
1
Electrical Insulation
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D710; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision.Anumber in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval.A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
This standard has been approved for use by agencies of the U.S. Department of Defense.
3
1. Scope* 2.2 Other Documents:
IEEE Publication No. 1,“General Principles for Tempera-
1.1 This specification covers vulcanized fibre (Note 1)
ture Limits in the Rating of Electrical Equipment.”
sheets, rolls, round rods, and round tubes of such grades
suitable for use as electrical insulation.
3. Terminology
NOTE 1—The variant spelling “fibre” has been approved by Committee
3.1 Definitions:
D09 for use in this standard.
3.1.1 vulcanized fibre, n—a material made from chemically
1.2 The values stated in inch-pound units are to be regarded
gelatinized cellulosic paper or board using zinc chloride as the
as standard. The values given in parentheses are mathematical
gelatinizing agent.
conversions to SI units that are provided for information only
3.1.1.1 Discussion—The zinc chloride is subsequently re-
and are not considered standard.
moved by leaching. The resulting product, after being dried
1.3 This international standard was developed in accor-
and finished by calendering, is a material of partially regener-
dance with internationally recognized principles on standard-
ated cellulose in which the fibrous structure is retained in
ization established in the Decision on Principles for the
varying degrees depending on the grade of paper used and on
Development of International Standards, Guides and Recom-
the processing conditions. Vulcanized fibre does not contain
mendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical
vulcanized rubber or sulfur as the name might imply. It is
Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
almost completely pure cellulose, with a trace amount of zinc
chloride.
2. Referenced Documents
2
4. Grades
2.1 ASTM Standards:
D495Test Method for High-Voltage, Low-Current, DryArc
4.1 Threegradesofvulcanizedfibrearecovered,asfollows:
Resistance of Solid Electrical Insulation
4.1.1 Bone Grade—This grade is characterized by the
D619Test Methods forVulcanized Fibre Used for Electrical
greater hardness and stiffness associated with higher density. It
Insulation
machinesmoresmoothlyandwithlesstendencytoseparatethe
D696TestMethodforCoefficientofLinearThermalExpan-
plies in difficult machining operations than the other grades. It
sion of Plastics Between −30°C and 30°C with a Vitreous 1 1
is made in thickness of ⁄64 to ⁄16in. (0.38 to 1.59 mm).
Silica Dilatometer
4.1.2 Commercial Grade—This grade is considered as the
D952Test Method for Bond or Cohesive Strength of Sheet
general-purpose grade and is sometimes referred to as me-
Plastics and Electrical Insulating Materials
chanical and electrical grade. It possesses good physical and
D3636Practice for Sampling and Judging Quality of Solid
electrical properties and can be fabricated satisfactorily by
Electrical Insulating Materials
punching, turning, and forming operations. It is made in
thicknesses from 0.005 to 0.100in. (0.12 to 2.54 mm).
4.1.3 Electrical Insulation Grade—This grade is intended
1
This specification is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D09 on
primarily for electrical applications and others involving diffi-
Electrical and Electronic Insulating Materials and is the direct responsibility of
cult bending or forming operations. It is made in thicknesses
Subcommittee D09.07 on Electrical Insulating Materials.
3
from 0.005 to ⁄32 in. (0.12 to 2.35 mm). Thin material of this
Current edition approved Nov. 1, 2019. Published December 2019. Originally
grade is sometimes referred to as “fish paper.”
approved in 1943. Last previous edition approved in 2013 as D710–97(2013).
DOI: 10.1520/D0710-19.
2
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
3
Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on Available from Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers, Inc. (IEEE),
the ASTM website. 445 Hoes Ln., P.O. Box 1331, Piscataway, NJ 08854-1331, http://www.ieee.org.
*A Summary of Changes section appears at the end of this standard
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
...
This document is not an ASTM standard and is intended only to provide the user of an ASTM standard an indication of what changes have been made to the previous version. Because
it may not be technically possible to adequately depict all changes accurately, ASTM recommends that users consult prior editions as appropriate. In all cases only the current version
of the standard as published by ASTM is to be considered the official document.
Designation: D710 − 13 D710 − 19
Standard Specification for
Vulcanized Fibre Sheets, Rolls, Rods, and Tubes Used for
1
Electrical Insulation
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D710; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
This standard has been approved for use by agencies of the U.S. Department of Defense.
1. Scope*
1.1 This specification covers vulcanized fibre (Note 1) sheets, rolls, round rods, and round tubes of such grades suitable for use
as electrical insulation.
NOTE 1—The variant spelling “fibre” has been approved by Committee D09 for use in this standard.
1.2 The values stated in inch-pound units are to be regarded as standard. The values given in parentheses are mathematical
conversions to SI units that are provided for information only and are not considered standard.
1.3 This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization
established in the Decision on Principles for the Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued
by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
2. Referenced Documents
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
D495 Test Method for High-Voltage, Low-Current, Dry Arc Resistance of Solid Electrical Insulation
D619 Test Methods for Vulcanized Fibre Used for Electrical Insulation
D696 Test Method for Coefficient of Linear Thermal Expansion of Plastics Between −30°C and 30°C with a Vitreous Silica
Dilatometer
D952 Test Method for Bond or Cohesive Strength of Sheet Plastics and Electrical Insulating Materials
D3636 Practice for Sampling and Judging Quality of Solid Electrical Insulating Materials
3
2.2 Other Documents:
IEEE Publication No. 1, “General Principles for Temperature Limits in the Rating of Electrical Equipment.”
3. Terminology
3.1 Definitions:
3.1.1 vulcanized fibre, n—a material made from chemically gelatinized cellulosic paper or board using zinc chloride as the
gelatinizing agent.
3.1.1.1 Discussion—
The zinc chloride is subsequently removed by leaching. The resulting product, after being dried and finished by calendering, is a
material of partially regenerated cellulose in which the fibrous structure is retained in varying degrees depending on the grade of
paper used and on the processing conditions. Material up to about 25 mm in thickness is produced by bonding multiple layers of
paper (or board) after chemical treatment. Vulcanized fibre does not contain vulcanized rubber or sulfur as the name might imply.
Thin vulcanized fibre has sometimes been termed “fish paper.”It is almost completely pure cellulose, with a trace amount of zinc
chloride.
1
This specification is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D09 on Electrical and Electronic Insulating Materials and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee
D09.07 on Flexible and Rigid Electrical Insulating Materials.
Current edition approved Nov. 1, 2013Nov. 1, 2019. Published November 2013December 2019. Originally approved in 1943. Last previous edition approved in 20092013
ε1
as D710 – 97 (2013).(2009) . DOI: 10.1520/D0710-13.10.1520/D0710-19.
2
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM Standards
volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on the ASTM website.
3
Available from Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers, Inc. (IEEE), 445 Hoes Ln., P.O. Box 1331, Piscataway, NJ 08854-1331, http://www.ieee.org.
*A Summary of Changes section appears at the end of this standard
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
D710 − 19
4. Grades
4.1 Three grades of vulcanized fibre are covered, as follows:
4.1.1 Bone Grade—This grade is characterized by the greater hardness and stiffness associated with higher density. It machines
more smoothly and with less tendency to separate the plies in difficult machining operations than the other grades. It is made in
1 1
thickness of ⁄64 to ⁄16 in. (0.79(0.38 to 6.351.59 mm).
4.1.2 Commercial Grade—This grade is considered as the general-purpose grade and is sometimes referred to as mechanical
and electrical grade. It posses
...









Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.