ASTM D6174-01(2006)
(Test Method)Standard Test Method for Inorganic Sulfate in Surfactants by Potentiometric Lead Titration (Withdrawn 2015)
Standard Test Method for Inorganic Sulfate in Surfactants by Potentiometric Lead Titration (Withdrawn 2015)
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
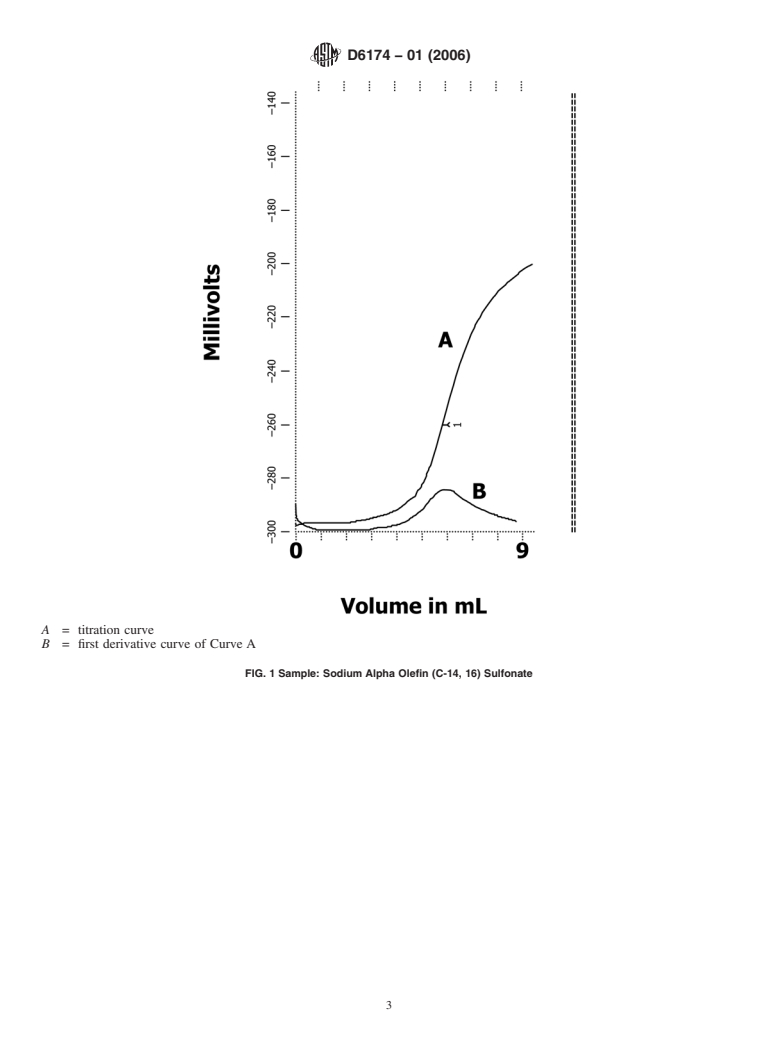
Anionic surfactants, such as those listed in 1.1, commonly are used in detergent formulations. Their acceptability for use depends on their purity. Sulfate content, as measured by this test method, can be used to estimate the purity of an anionic surfactant under test.
SCOPE
1.1 This test method describes a potentiometric titration procedure for determining the inorganic sulfate content of surfactants. It is intended for the analysis of -olefin sulfonates, alkane sulfonates, alcohol sulfates, alcohol ether sulfates, alkylbenzenesulfonates, and the like.
This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use. Material Safety Data Sheets are available for reagents and materials. Review them for hazards prior to usage.
WITHDRAWN RATIONALE
This test method describes a potentiometric titration procedure for determining the inorganic sulfate content of surfactants.
Formerly under the jurisdiction of Committee D12 on Soaps and Other Detergents, this test method was withdrawn in January 2015 in accordance with section 10.6.3 of the Regulations Governing ASTM Technical Committees, which requires that standards shall be updated by the end of the eighth year since the last approval date.
General Information
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Designation: D6174 − 01(Reapproved 2006)
Standard Test Method for
Inorganic Sulfate in Surfactants by Potentiometric Lead
Titration
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D6174; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope forusedependsontheirpurity.Sulfatecontent,asmeasuredby
this test method, can be used to estimate the purity of an
1.1 This test method describes a potentiometric titration
anionic surfactant under test.
procedure for determining the inorganic sulfate content of
surfactants.Itisintendedfortheanalysisofα-olefinsulfonates,
6. Apparatus
alkane sulfonates, alcohol sulfates, alcohol ether sulfates,
6.1 Potentiometric Titration Assembly, consisting of an
alkylbenzenesulfonates, and the like.
automatic titrator fitted with a lead ion-selective electrode, a
1.2 This standard does not purport to address all of the
double-junction reference electrode, and a 10-mL buret. The
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
reference electrode should be filled with the standard inner and
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
outer filling solutions supplied with it. A TFE-fluorocarbon-
priate safety and health practices and determine the applica-
coated magnetic stirring bar should be used for mixing during
bility of regulatory limitations prior to use. Material Safety
titration, with a separate magnetic stirring motor if the autoti-
Data Sheets are available for reagents and materials. Review
trator is not so equipped.
them for hazards prior to usage.
NOTE 1—Proper care of the lead-selective electrode is essential for
2. Referenced Documents obtaining high-quality titration curves. Follow manufacturer’s instruc-
tions.
2.1 ASTM Standards:
D1193 Specification for Reagent Water
7. Reagents
7.1 Glacial Acetic Acid.
3. Terminology
7.2 Lead Nitrate, reagent grade.
3.1 Definitions of Terms Specific to This Standard:
3.1.1 inorganic sulfate, n—sulfate species present as sulfu-
7.3 Sodium Sulfate, anhydrous, reagent grade.
ric acid, ionic salts of this acid, or mixtures of these.
7.4 Sodium Perchlorate, reagent grade.
4. Summary of Test Method
7.5 Ethanol, denatured, formula 3A.
4.1 A surfactant sample containing inorganic sulfate is
7.6 Water, Type III reagent water conforming to Specifica-
titrated in ethanolic medium with a standard lead solution.
tion D1193.
Lead sulfate precipitate is formed during the titration. Ethanol
8. Preparation of Standard Solutions
and sodium perchlorate are present to decrease the solubility of
lead sulfate, thus sharpening the endpoint.Acetic acid is added
8.1 10 % Acetic Acid—Dilute glacial acetic acid 1/10 with
to remove possible interference from carbonate. The endpoint
water.
is signaled by an increase in lead ion activity, as measured by
8.2 Lead Titrant, 0.05 M—Dissolve 16.6 g lead nitrate in
a lead-selective electrode.
300 mL water. Pour into a 1-L bottle and fill with 3A ethanol.
Mix well. Standardize according to 9.1.
5. Significance and Use
8.3 Sulfate Standard, 0.05 M—Dry 5 g anhydrous sodium
5.1 Anionic surfactants, such as those listed in 1.1, com-
sulfate at 110°C for 1 h. Accurately weigh about 3.5 g into a
monly are used in detergent formulations. Their acceptability
1 2
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D12 on Soaps Reagent Chemicals, American Chemical Society Specifications, American
and Other Detergents and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee D12.12 on Chemical Society, Washington, DC. For suggestions on the testing of reagents not
Analysis of Soaps and Synthetic Detergents. listed by the American Chemical Society, see Analar Standards for Laboratory
Current edition approved Feb. 1, 2006. Published March 2006. Originally Chemicals, BDH Ltd., Poole, Dorset, U.K., and the United States Pharmacopeia
approved in 1997. Last previous edition approved in 2001 as D6174-01. DOI: and National Formulary, U.S. Pharmacopeial Convention, Inc. (USPC), Rockville,
10.1520/D6174-01R06. MD.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
D6174 − 01 (2006)
500-mLvolumetric flask, dilute to volume with water, and mix 10.2 Transfer a portion of test surfactant, equivalent to
to dissolve. Calculate the exact concentration as follows: 30–50 mg sodium sulfate, to a 50-mL beaker. For example, if
a surfactant is expected to contain 1 % sodium sulfate, weigh
G
5 Molarity (1)
3–5 g to analytical precision into
...







Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.