ASTM A952/A952M-02(2016)
(Specification)Standard Specification for Forged Grade 80 and Grade 100 Steel Lifting Components and Welded Attachment Links
Standard Specification for Forged Grade 80 and Grade 100 Steel Lifting Components and Welded Attachment Links
ABSTRACT
This specification covers forged alloy steel lifting components and welded coupling and master links for Grade 80 and Grade 100 alloy chain slings. The steel materials shall be melt processed either by electric process or oxygen blown process. The steel shall be fully killed and shall conform to the required austenitic grain size. Product analysis shall be performed on and the steel specimens shall conform to the required chemical compositions of nickel, chromium, molybdenum, phosphorus and sulfur. Proof tests shall be performed and the materials shall conform to the required values of working load and breaking force. Deformation test, breaking force test and fatigue test shall be performed on the steel materials.
SCOPE
1.1 This specification covers the requirements for forged alloy steel lifting components and welded coupling and master links for Grade 80 and Grade 100 alloy chain slings as described in Specification A906/A906M.
1.2 Two grades of components and welded links are covered:
1.2.1 Grade 80.
1.2.2 Grade 100.
1.3 This specification is a performance standard. Other standards apply to use of these products. Some of these standards are: OSHA 1910.184, ASME B30.9, and ASME B30.10.
1.4 The values stated in either inch-pound or SI units are to be regarded separately as standard. Within the text, the SI units are shown in brackets. The values stated in each system are not exact equivalents; therefore, each system shall be used independently of the other. Combining values from the two systems may result in nonconformance with the specification.
General Information
Buy Standard
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Designation:A952/A952M −02 (Reapproved 2016)
Standard Specification for
Forged Grade 80 and Grade 100 Steel Lifting Components
1
and Welded Attachment Links
This standard is issued under the fixed designationA952/A952M; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year
of original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval.
A superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope E44 Definitions for Terms Relating to Heat Treatment of
3
Metals (Withdrawn 1993)
1.1 This specification covers the requirements for forged
E165/E165M Practice for Liquid Penetrant Testing for Gen-
alloy steel lifting components and welded coupling and master
eral Industry
links for Grade 80 and Grade 100 alloy chain slings as
E709 Guide for Magnetic Particle Testing
described in Specification A906/A906M.
2.2 Other Standards:
1.2 Two grades of components and welded links are cov-
4
OSHA 1910.184 Slings
ered:
5
ASME B30.9 Slings
1.2.1 Grade 80.
5
ASME B30.10 Hooks
1.2.2 Grade 100.
1.3 This specification is a performance standard. Other 3. Terminology
standards apply to use of these products. Some of these
3.1 Definitions of Terms Specific to This Standard:
standards are: OSHA 1910.184, ASME B30.9, and ASME
3.1.1 breaking force, minimum—the minimum force in
B30.10.
pounds or newtons at which the component has been found by
1.4 The values stated in either inch-pound or SI units are to verification testing to break when a constantly increasing force
was applied in direct tension. This test is a manufacturer’s
be regarded separately as standard.Within the text, the SI units
design verification test and shall not be used as criteria for
are shown in brackets.The values stated in each system are not
service.
exact equivalents; therefore, each system shall be used inde-
pendentlyoftheother.Combiningvaluesfromthetwosystems
3.1.2 chain sling—an assembly consisting of alloy steel
may result in nonconformance with the specification.
chain joined to upper and lower end components for attaching
loads to be lifted by a crane or lifting machine.
2. Referenced Documents
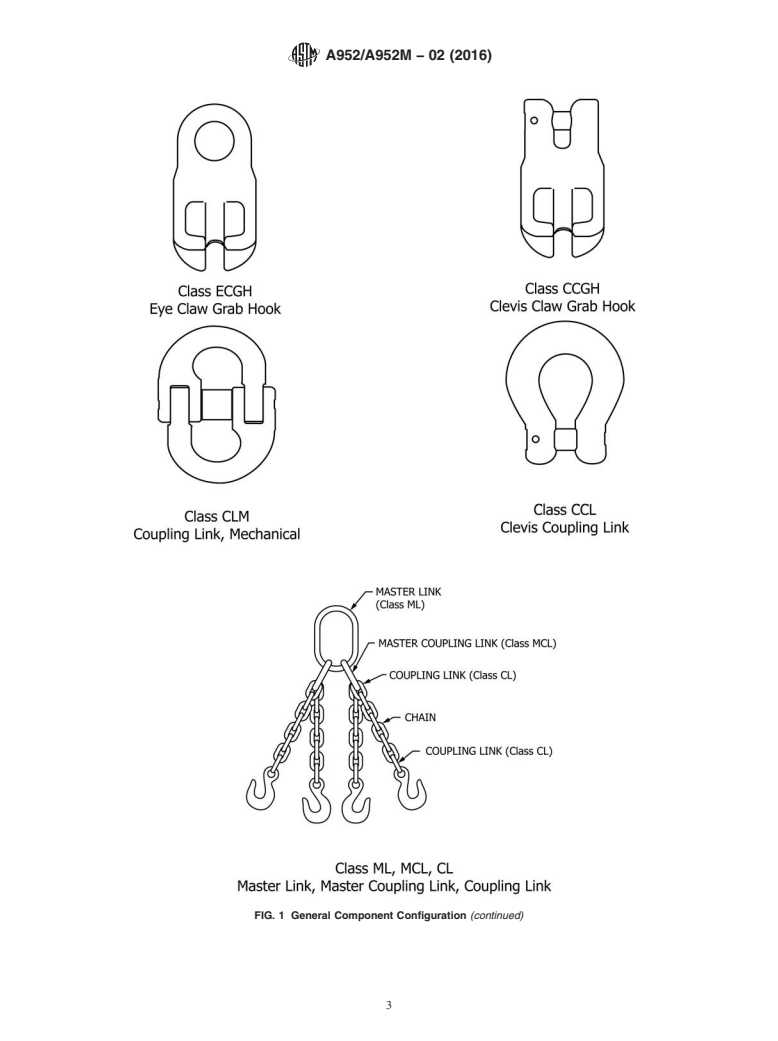
3.1.3 coupling link—a link fitted to the end of the chain to
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
connect to another component of the sling. See Fig. 1.
A29/A29M SpecificationforGeneralRequirementsforSteel
3.1.4 masterlink—alinkusedasanupperendcomponentof
Bars, Carbon and Alloy, Hot-Wrought
a chain sling and by means of which the sling may be attached
A391/A391M Specification for Grade 80 Alloy Steel Chain
to a crane or other device. See Fig. 1.
A751 Test Methods and Practices for Chemical Analysis of
3.1.5 master coupling link (secondary or intermediate
Steel Products
link)—a link used on three and four leg slings to connect the
A906/A906M Specification for Grade 80 and Grade 100
legs to a master link. See Fig. 1.
Alloy Steel Chain Slings for Overhead Lifting
A973/A973M Specification for Grade 100Alloy Steel Chain 3.1.6 proof test—a quality control tensile test applied to
components for the purpose of verifying manufacturing and
E4 Practices for Force Verification of Testing Machines
material quality. It is the minimum force in pounds or newtons
which the component has withstood at the time it left the
1
This specification is under the jurisdiction ofASTM Committee A01 on Steel,
Stainless Steel and Related Alloys and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee
3
A01.27 on Steel Chain. The last approved version of this historical standard is referenced on
Current edition approved Sept. 1, 2016. Published September 2016. Originally www.astm.org.
4
approved in 1996. Last previous edition approved in 2010 as A952/ Available from Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA), 200
A952M–02(2010). DOI: 10.1520/A0952_A0952M-02R16. Constitution Ave., NW, Room Number N3626, Washington, DC 20210, http://
2
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or www.osha.gov.
5
contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM Available from American Society of Mechanical Engineers (ASME), ASME
Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on International Headquarters, Two Park Ave., New York, NY 10016-5990, http://
the ASTM website. www.asme.org.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
A952/A952M−02 (2016)
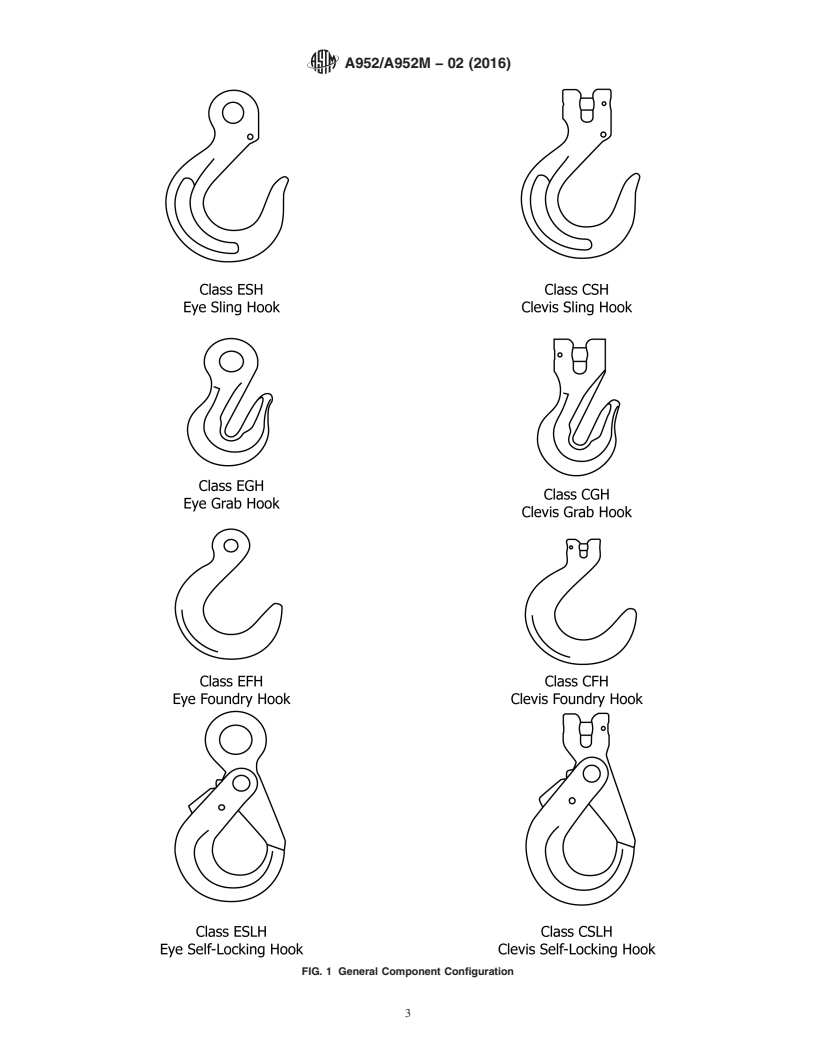
FIG. 1 General Component Configuration
2
---------------------- Page: 2 ----------------------
A952/A952M−02 (2016)
FIG. 1 General Component Configuration (continued)
3
---------------------- Page: 3 ----------------------
A952/A952M−02 (2016)
producer, under a test in which a constantly increasing
...
This document is not an ASTM standard and is intended only to provide the user of an ASTM standard an indication of what changes have been made to the previous version. Because
it may not be technically possible to adequately depict all changes accurately, ASTM recommends that users consult prior editions as appropriate. In all cases only the current version
of the standard as published by ASTM is to be considered the official document.
Designation: A952/A952M − 02 (Reapproved 2010) A952/A952M − 02 (Reapproved 2016)
Standard Specification for
Forged Grade 80 and Grade 100 Steel Lifting Components
1
and Welded Attachment Links
This standard is issued under the fixed designation A952/A952M; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year
of original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval.
A superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope
1.1 This specification covers the requirements for forged alloy steel lifting components and welded coupling and master links
for Grade 80 and Grade 100 alloy chain slings as described in Specification A906/A906M.
1.2 Two grades of components and welded links are covered:
1.2.1 Grade 80.
1.2.2 Grade 100.
1.3 This specification is a performance standard. Other standards apply to use of these products. Some of these standards are:
OSHA 1910.184, ASME B30.9, and ASME B30.10.
1.4 The values stated in either inch-pound or SI units are to be regarded separately as standard. Within the text, the SI units are
shown in brackets. The values stated in each system are not exact equivalents; therefore, each system shall be used independently
of the other. Combining values from the two systems may result in nonconformance with the specification.
2. Referenced Documents
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
A29/A29M Specification for General Requirements for Steel Bars, Carbon and Alloy, Hot-Wrought
A391/A391M Specification for Grade 80 Alloy Steel Chain
A751 Test Methods, Practices, and Terminology for Chemical Analysis of Steel Products
A906/A906M Specification for Grade 80 and Grade 100 Alloy Steel Chain Slings for Overhead Lifting
A973/A973M Specification for Grade 100 Alloy Steel Chain
E4 Practices for Force Verification of Testing Machines
3
E44 Definitions for Terms Relating to Heat Treatment of Metals (Withdrawn 1993)
E165E165/E165M Practice for Liquid Penetrant Examination for General Industry
E709 Guide for Magnetic Particle Testing
2.2 Other Standards:
4
OSHA 1910.184 Slings
5
ASME B30.9 Slings
5
ASME B30.10 Hooks
3. Terminology
3.1 Definitions of Terms Specific to This Standard:
1
This specification is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee A01 on Steel, Stainless Steel and Related Alloys and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee A01.27
on Steel Chain.
Current edition approved April 1, 2010Sept. 1, 2016. Published May 2010September 2016. Originally approved in 1996. Last previous edition approved in 20022010 as
A952/A952MA952/A952M–02(2010). – 02. DOI: 10.1520/A0952_A0952M-02R10.10.1520/A0952_A0952M-02R16.
2
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM Standards
volume information, refer to the standard’sstandard’s Document Summary page on the ASTM website.
3
The last approved version of this historical standard is referenced on www.astm.org.
4
Available from Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA), 200 Constitution Ave., NW, Room Number N3626, Washington, DC 20210, http://
www.osha.gov.
5
Available from American Society of Mechanical Engineers (ASME), ASME International Headquarters, ThreeTwo Park Ave., New York, NY 10016-5990,
http://www.asme.org.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
A952/A952M − 02 (2016)
3.1.1 breaking force, minimum—the minimum force in pounds or newtons at which the component has been found by
verification testing to break when a constantly increasing force was applied in direct tension. This test is a
manufacturer’smanufacturer’s design verification test and shall not be used as criteria for service.
3.1.2 chain sling—an assembly consisting of alloy steel chain joined to upper and lower end components for attaching loads
to be lifted by a crane or lifting machine.
3.1.3 coupling link—a link fitted to the end of the chain to connect to another component of the sling. See Fig. 1.
3.1.4 master link—a link used as an upper end component of a chain sling and by means of which the sling may be attached
to a crane or other device. See Fig. 1.
3.1.5 master coupling link (secondary or intermediate link)—a link used on three and four leg slings to connect the legs to a
master link. See Fig. 1.
3.1.6 proof test—a quality control tensile test applied to components for the purpose of
...








Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.