ASTM D909-01
(Test Method)Standard Test Method for Knock Characteristics of Aviation Gasoline's by the Supercharge Method
Standard Test Method for Knock Characteristics of Aviation Gasoline's by the Supercharge Method
SCOPE
1.1 This test method covers the determination of the knock-limited power, under supercharge rich-mixture conditions, of fuels for use in spark-ignition reciprocating aircraft engines, in terms of ASTM supercharge octane or performance number. By operational considerations, this test method is restricted to testing fuels of 85 ASTM supercharge octane number and over.
1.2 The values stated in inch-pound units are to be regarded as the standard. The values in parentheses are for information only.
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use. Specific precautionary statements are given in Annex 7.
General Information
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
An American National Standard
Designation: D 909 – 01 Method 6012.6—Federal Test
Method Standard No. 791b
Designation: 119/96
Standard Test Method for
Knock Characteristics of Aviation Gasolines by the
1
Supercharge Method
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D909; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision.Anumber in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval.A
superscript epsilon (e) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
This standard has been approved for use by agencies of the Department of Defense.
6
1. Scope Absorption Spectrometry
D3341 Test Method for Lead in Gasoline by the Iodine
1.1 This test method covers the determination of the knock-
6
Monochloride Method
limited power, under supercharge rich-mixture conditions, of
D4057 Practice for Manual Sampling of Petroleum and
fuels for use in spark-ignition reciprocating aircraft engines, in
6
Petroleum Products
terms of ASTM supercharge octane or performance number.
7
E1 Specifications for ASTM Thermometers
By operational considerations, this test method is restricted to
testingfuelsof85ASTMsuperchargeoctanenumberandover.
3. Terminology
1.2 The values stated in inch-pound units are to be regarded
3.1 Definitions:
as the standard. The values in parentheses are for information
3.1.1 ASTM supercharge octane number of a fuel below
only.
100—the whole number nearest the percentage by volume of
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the
isooctane(equals100)inablendwithn-heptane(equals0)that
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
matches the knock characteristics of the fuel when compared
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
by this test method.
priate safety and health practices and determine the applica-
3.1.2 ASTM supercharge rating of a fuel above 100—the
bility of regulatory limitations prior to use. Specific precau-
amount of tetraethyllead (TEL) in isooctane, expressed in
tionary statements are given in Annex A7.
millilitres per U.S. gallon.
2. Referenced Documents 3.2 ASTM supercharge ratings are normally expressed as
octanenumbersbelow100andasperformancenumbersabove
2.1 ASTM Standards:
100. At 100, a rating may be expressed either as 100 octane
D1368 Test Method for Trace Concentrations of Lead in
2
number or as 100 performance number. Sometimes it is
Primary Reference Fuels
3 desirable to convert the ASTM supercharge octane number to
D2268 Test Method for Analysis of High Purity
performancenumber.ThiscanbedonebyusingTable 1.Table
D2599 Test Method for Lead in Gasoline by X-Ray Spec-
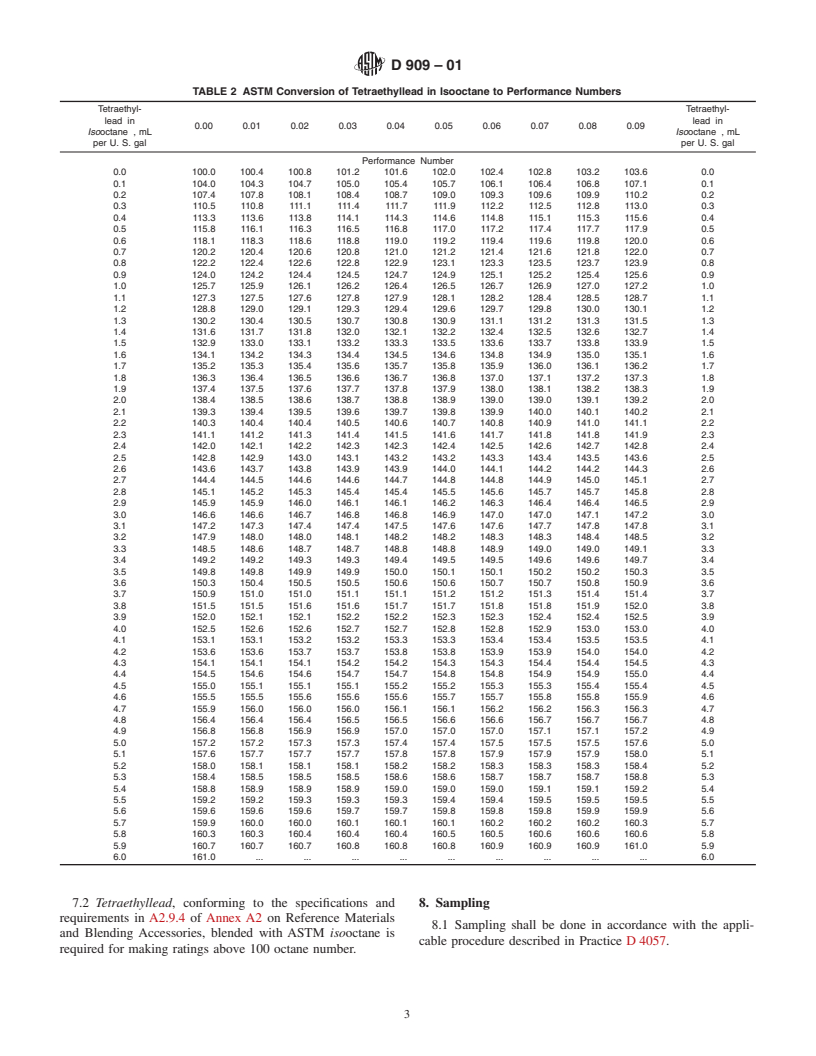
4 2 lists the corresponding performance numbers for various
trometry
concentrations of tetraethyllead in isooctane.
D2699 Test Method for Research Octane Number of
5
Spark-Ignition Engine Fuel
4. Summary of Test Method
D2700 Test Method for Motor Octane Number of Spark-
5 4.1 ASTM supercharge octane or performance number of a
Ignition Engine Fuel
fuel is determined by comparing its knock-limited power with
D3237 Test Method for Lead in Gasoline by Atomic
those for bracketing blends of reference fuels under standard
operating conditions. This is done at constant compression
ratio by varying the manifold pressure and fuel flow rate, the
1
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D02 on
independent variables of the test, and measuring indicated
Petroleum Products and Lubricants and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee
mean effective pressure (imep) at enough points to define the
D02.01 on Combustion Characteristics.
mixtureresponsecurvesforthesampleandthereferencefuels.
Current edition approved Dec. 10, 2001. Published February 2002. Originally
e1
published as D909–58. Last previous edition D909–00 . When the knock-limited power for the sample is bracketed
2
Discontinued, see 1994 Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 05.01.
3
Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 05.01.
4
Discontinued, Replaced by Test Method D5059, see 1992 Annual Book of
6
ASTM Standards, Vol 05.02. Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 05.02.
5 7
Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 05.05. Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 14.03.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959, United States.
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
D909–01
TABLE 1 ASTM Conversion of Octane Numbers to Performance Numbers
Octane Octane
0.0 0.1 0.2 0.3 0.4 0.5 0.6 0.7 0.8 0.9
Number Number
Performance Number
70 48.3 48.4 48.4 48.5 48.6 48.7 48.8 48.9 49.0 49.0 70
71 49.1 49.2 49.3 49.4 49.5 49.6 49.6 49.7 49.8 49.9 71
72 50.0 50.1 50.2 50.3 50.4 50.5 50.5 50.6 50.7 50.8 72
73 50.9 51.0 51.1 51.2 51.3 51.4 51.5 51.6 51.7 51.8 73
74 51.9 51.9 52.0 52.1 52.2 52.3 52.4 5
...







Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.