ASTM F1122-22
(Specification)Standard Specification for Quick Disconnect Couplings (6 in. NPS and Smaller)
Standard Specification for Quick Disconnect Couplings (6 in. NPS and Smaller)
ABSTRACT
This specification covers the manufacturing data required to produce a variety of styles and sizes of quick disconnect couplings up to and including NPS 6 for marine use that ensure interchangeability and safety of operation. Quick disconnect couplings shall consist of the following types: Standard class and Class I. Adapters and couplers are to be produced as castings or forgings. Cam handles may be produced by casting, forging, or sintered metal processes. Maximum allowable working pressure (MAWP) for a Standard Class coupling shall be 25 % of its burst pressure. Maximum allowable working pressure for a Class I coupling shall be 20 % of its burst pressure. The following test shall be performed: pressure tests and production test.
SCOPE
1.1 This specification covers the manufacturing data required to produce a variety of styles and sizes of quick disconnect couplings up to and including NPS 6 for marine use that ensure interchangeability and safety of operation.
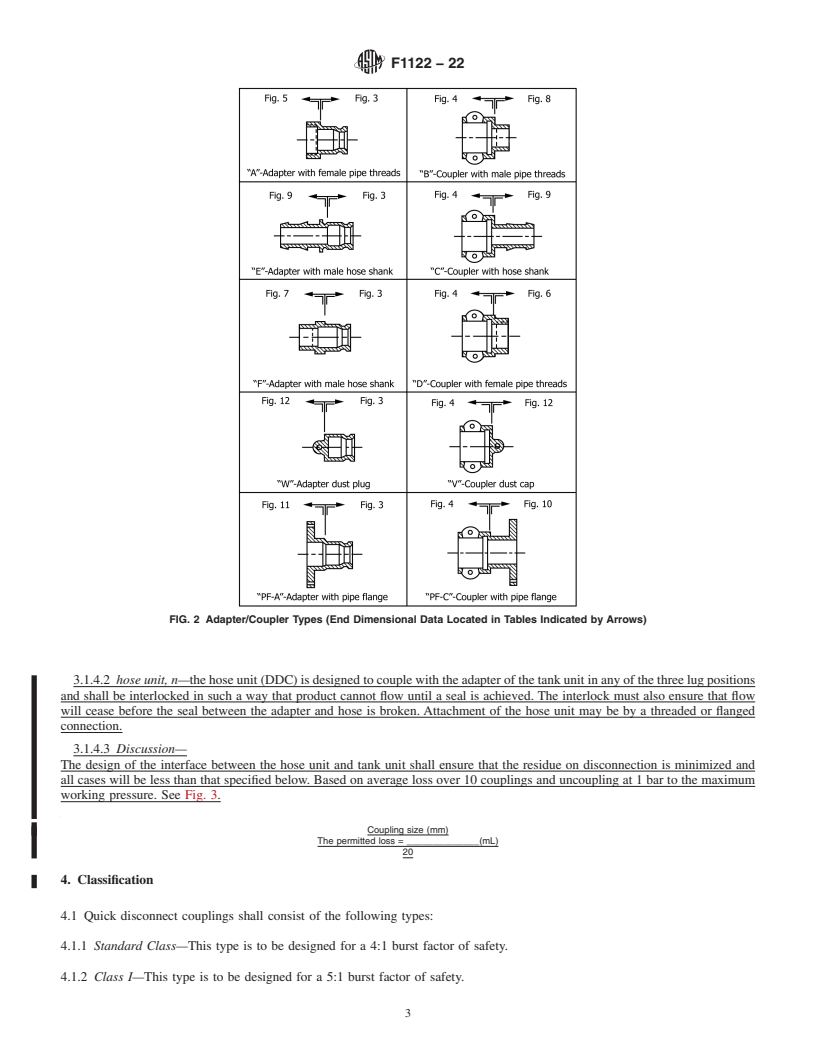
1.2 In general, quick disconnect couplings are hose and pipe end fittings that permit quick mechanical attachment by means other than bolted or threaded fittings. The method of attachment is a male coupling half (adapter, tank unit) that fits into a female coupling half (coupler, hose unit) of the same size.
1.2.1 By closing attached cam handles on cam and groove couplings, the coupling halves seal, permitting fluids to be transported under pressure through the quick disconnect coupling.
1.2.2 By aligning the rollers on the hose unit coupler with the notches on the tank unit adapter on the dry disconnect coupling (DDC), push the coupler onto the adapter and rotate past 100°. This will lock the couplings together, create a seal and open the internal valves for full flow with low pressure drop. The dual poppet design shut-off mechanism seals liquids and gases behind the valve, eliminating fugitive emissions and the danger of a spill upon disconnection.
1.3 The values stated in inch-pound units are to be regarded as standard. The values given in parentheses are mathematical conversions to SI units that are provided for information only and are not considered standard.
1.4 The following safety hazards caveat pertains only to the test method described in this specification: This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety, health, and environmental practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
1.5 This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization established in the Decision on Principles for the Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
General Information
Buy Standard
Standards Content (Sample)
This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization established in the Decision on Principles for the
Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
Designation:F1122 −22 An American National Standard
Standard Specification for
1
Quick Disconnect Couplings (6 in. NPS and Smaller)
This standard is issued under the fixed designation F1122; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision.Anumber in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval.A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope Development of International Standards, Guides and Recom-
mendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical
1.1 This specification covers the manufacturing data re-
Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
quired to produce a variety of styles and sizes of quick
disconnectcouplingsuptoandincludingNPS6formarineuse
2. Referenced Documents
that ensure interchangeability and safety of operation.
2
2.1 MSS Standards:
1.2 Ingeneral,quickdisconnectcouplingsarehoseandpipe
MSS-SP-6 Standard Finish for Contact Faces of Pipe
end fittings that permit quick mechanical attachment by means
Flanges and Connecting End Flanges of Valves and
other than bolted or threaded fittings. The method of attach-
Fittings
ment is a male coupling half (adapter, tank unit) that fits into a
MSS-SP-25Standard Marking System for Valves, Fittings,
female coupling half (coupler, hose unit) of the same size.
Flanges, and Unions
1.2.1 By closing attached cam handles on cam and groove
MSS-SP-55Quality Standard for Steel Castings for Valves,
couplings, the coupling halves seal, permitting fluids to be
Flanges, and Fittings and Other Piping Components (Vi-
transported under pressure through the quick disconnect cou-
sual Method)
pling.
3
2.2 ASME Standards:
1.2.2 By aligning the rollers on the hose unit coupler with
the notches on the tank unit adapter on the dry disconnect ASME Boiler and Pressure Vessel CodeSection VIII, Divi-
sion 1
coupling (DDC), push the coupler onto the adapter and rotate
past 100°. This will lock the couplings together, create a seal ASME Boiler and Pressure Vessel CodeSection IX
ASME/ANSI B2.1Pipe Threads (Except Dryseal)
and open the internal valves for full flow with low pressure
drop.The dual poppet design shut-off mechanism seals liquids B16.5Pipe Flanges and Flanged Fittings: NPS 1/2 through
NPS 24 Metric/Inch Standard
and gases behind the valve, eliminating fugitive emissions and
the danger of a spill upon disconnection. B16.24Cast Copper Alloy Pipe Flanges, Flanged Fittings,
and Valves: Classes 150, 300, 600, 900, 1500, and 2500
1.3 The values stated in inch-pound units are to be regarded
B16.42Ductile Iron Pipe Flanges and Flanged Fittings:
as standard. The values given in parentheses are mathematical
Classes 150 and 300
conversions to SI units that are provided for information only
B31.1Power Piping
and are not considered standard.
2.3 Other Standards:
1.4 The following safety hazards caveat pertains only to the
STANAG 3756Facilities and Equipment for Receipt and
test method described in this specification: This standard does
4
Delivery of Aviation Kerosene and Diesel Fuels
not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any,
5
ISO 3601Fluid power systems — O-rings
associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this
5
ISO 2230Rubber products — Guidelines for storage
standard to establish appropriate safety, health, and environ-
mental practices and determine the applicability of regulatory
3. Terminology
limitations prior to use.
3.1 Definitions of Terms Specific to This Standard:
1.5 This international standard was developed in accor-
dance with internationally recognized principles on standard-
ization established in the Decision on Principles for the
2
AvailablefromManufacturersStandardizationSocietyoftheValveandFittings
Industry(MSS),127ParkSt.,NE,Vienna,VA22180-4602,http://www.mss-hq.org.
3
Available from American Society of Mechanical Engineers (ASME), ASME
1
This specification is under the jurisdiction ofASTM Committee F25 on Ships International Headquarters, Two Park Ave., New York, NY 10016-5990, http://
and Marine Technology and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee F25.11 on www.asme.org.
4
Machinery and Piping Systems. Available from SAI Global, 205 West Wacker Dr., Suite 1800, Chicago, IL
Current edition approved June 1, 2022. Published August 2022. Originally 60606, https://infostore.saiglobal.com.
5
approved in 1987. Last previous edition approved in 2021 as F1122–04 (2021). Available fromAmerican National Standards Institute (ANSI), 25 W. 43rd St.,
DOI: 10.1520/F1122-22. 4th Floor, New York, NY 10036, http://www.ansi.org.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Dr
...
This document is not an ASTM standard and is intended only to provide the user of an ASTM standard an indication of what changes have been made to the previous version. Because
it may not be technically possible to adequately depict all changes accurately, ASTM recommends that users consult prior editions as appropriate. In all cases only the current version
of the standard as published by ASTM is to be considered the official document.
Designation: F1122 − 04 (Reapproved 2021) F1122 − 22 An American National Standard
Standard Specification for
1
Quick Disconnect Couplings (6 in. NPS and Smaller)
This standard is issued under the fixed designation F1122; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope
1.1 This specification covers the manufacturing data required to produce a variety of styles and sizes of quick disconnect couplings
up to and including NPS 6 for marine use that ensure interchangeability and safety of operation.
1.2 In general, quick disconnect couplings are hose and pipe end fittings that permit quick mechanical attachment by means other
than bolted or threaded fittings. The method of attachment is a male coupling half (adapter) (adapter, tank unit) that fits into a
female coupling half (coupler) (coupler, hose unit) of the same size. By closing attached cam handles, the coupling halves seal,
permitting fluids to be transported under pressure through the quick disconnect coupling.
1.2.1 By closing attached cam handles on cam and groove couplings, the coupling halves seal, permitting fluids to be transported
under pressure through the quick disconnect coupling.
1.2.2 By aligning the rollers on the hose unit coupler with the notches on the tank unit adapter on the dry disconnect coupling
(DDC), push the coupler onto the adapter and rotate past 100°. This will lock the couplings together, create a seal and open the
internal valves for full flow with low pressure drop. The dual poppet design shut-off mechanism seals liquids and gases behind
the valve, eliminating fugitive emissions and the danger of a spill upon disconnection.
1.3 The values stated in inch-pound units are to be regarded as standard. The values given in parentheses are mathematical
conversions to SI units that are provided for information only and are not considered standard.
1.4 The following safety hazards caveat pertains only to the test method described in this specification: This standard does not
purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to
establish appropriate safety, health, and environmental practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior
to use.
1.5 This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization
established in the Decision on Principles for the Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued
by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
2. Referenced Documents
2
2.1 MSS Standards:
MSS-SP-6 Standard Finish for Contact Faces of Pipe Flanges and Connecting End Flanges of Valves and Fittings
MSS-SP-25 Standard Marking System for Valves, Fittings, Flanges, and Unions
MSS-SP-55 Quality Standard for Steel Castings for Valves, Flanges, and Fittings and Other Piping Components (Visual Method)
1
This specification is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee F25 on Ships and Marine Technology and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee F25.11 on
Machinery and Piping Systems.
Current edition approved June 1, 2021June 1, 2022. Published June 2021August 2022. Originally approved in 1987. Last previous edition approved in 20152021 as
F1122 – 04 (2015).(2021). DOI: 10.1520/F1122-04R21.10.1520/F1122-22.
2
Available from Manufacturers Standardization Society of the Valve and Fittings Industry (MSS), 127 Park St., NE, Vienna, VA 22180-4602, http://www.mss-hq.org.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
F1122 − 22
3
2.2 ASME Standards:
ASME Boiler and Pressure Vessel Code Section VIII, Division 1
ASME Boiler and Pressure Vessel Code Section IX
ASME/ANSI B2.1 Pipe Threads (Except Dryseal)
B16.5 Pipe Flanges and Flanged Fittings: NPS 1/2 through NPS 24 Metric/Inch Standard
B16.24 Cast Copper Alloy Pipe Flanges, Flanged Fittings, and Valves: Classes 150, 300, 600, 900, 1500, and 2500
B16.42 Ductile Iron Pipe Flanges and Flanged Fittings: Classes 150 and 300
B31.1 Power Piping
2.3 Other Standards:
4
STANAG 3756 Facilities and Equipment for Receipt and Delivery of Aviation Kerosene and Diesel Fuels
5
ISO 3601 Fluid
...










Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.