ASTM D2622-21
(Test Method)Standard Test Method for Sulfur in Petroleum Products by Wavelength Dispersive X-ray Fluorescence Spectrometry
Standard Test Method for Sulfur in Petroleum Products by Wavelength Dispersive X-ray Fluorescence Spectrometry
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
5.1 This test method provides rapid and precise measurement of total sulfur in petroleum and petroleum products with a minimum of sample preparation. A typical analysis time is 1 min to 2 min per sample.
5.2 The quality of many petroleum products is related to the amount of sulfur present. Knowledge of sulfur concentration is necessary for processing purposes. There are also regulations promulgated in federal, state, and local agencies that restrict the amount of sulfur present in some fuels.
5.3 This test method provides a means of determining whether the sulfur content of petroleum or a petroleum product meets specification or regulatory limits.
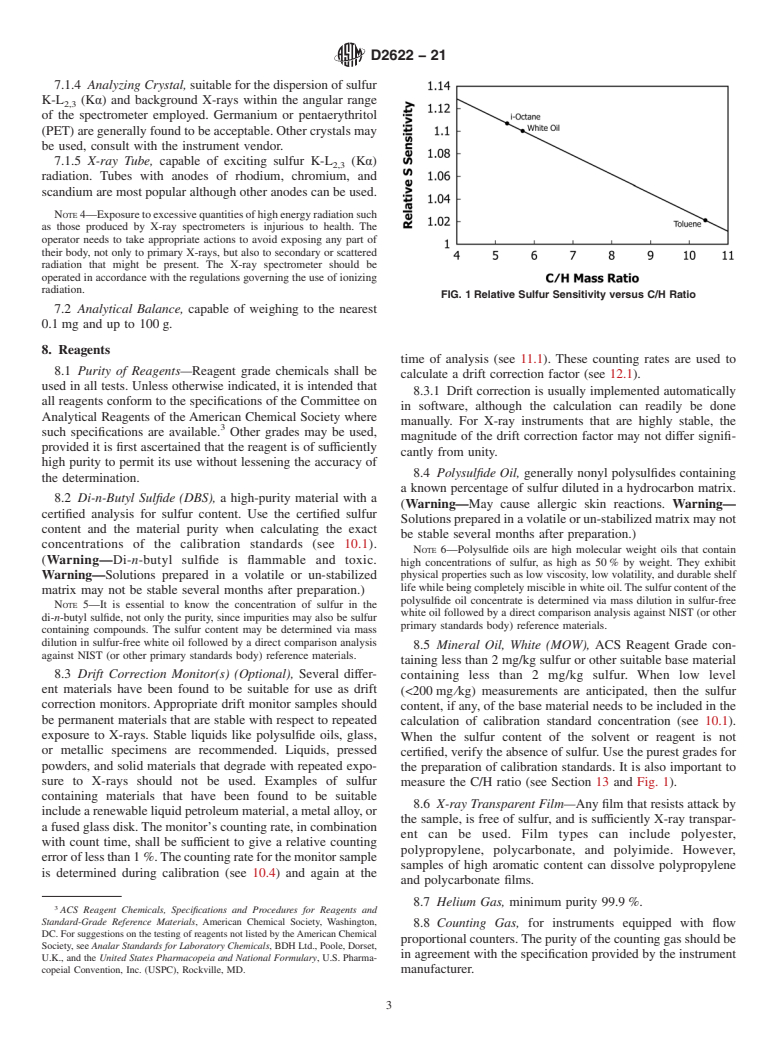
5.4 When this test method is applied to petroleum materials with matrices significantly different from the white oil calibration materials specified in this test method, the cautions and recommendations in Section 6 should be observed when interpreting results.
Note 2: The equipment specified for Test Method D2622 tends to be more expensive than that required for alternative test methods, such as Test Method D4294. Consult the Index to ASTM Standards for alternative test methods.
SCOPE
1.1 This test method covers the determination of total sulfur in petroleum and petroleum products that are single-phase and either liquid at ambient conditions, liquefiable with moderate heat, or soluble in hydrocarbon solvents. These materials can include diesel fuel, jet fuel, kerosene, other distillate oil, naphtha, residual oil, lubricating base oil, hydraulic oil, crude oil, unleaded gasoline, gasoline-ethanol blends, and biodiesel.
1.2 The range of this test method is between the PLOQ value (calculated by procedures consistent with Practice D6259) of 3 mg/kg total sulfur and the highest level sample in the round robin, 4.6 % by weight total sulfur.
Note 1: Instrumentation covered by this test method can vary in sensitivity. The applicability of the test method at sulfur concentrations below 3 mg/kg may be determined on an individual basis for WDXRF instruments capable of measuring lower levels, but precision in this test method does not apply.
1.2.1 The values of the limit of quantitation (LOQ) and method precision for a specific laboratory’s instrument depends on instrument source power (low or high power), sample type, and the practices established by the laboratory to perform the method.
1.3 Samples containing more than 4.6 % by mass sulfur should be diluted to bring the sulfur concentration of the diluted material within the scope of this test method. Samples that are diluted can have higher errors than indicated in Section 15 than non-diluted samples.
1.4 Volatile samples (such as high vapor pressure gasolines or light hydrocarbons) may not meet the stated precision because of selective loss of light materials during the analysis.
1.5 A fundamental assumption in this test method is that the standard and sample matrices are well matched, or that the matrix differences are accounted for (see 13.2). Matrix mismatch can be caused by C/H ratio differences between samples and standards or by the presence of other interfering heteroatoms or species (see Table 1).
1.6 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as standard. No other units of measurement are included in this standard.
1.7 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety, health, and environmental practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
1.8 This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization established in the Decision on Principles for the Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
General Information
Buy Standard
Standards Content (Sample)
This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization established in the Decision on Principles for the
Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
Designation: D2622 − 21
Standard Test Method for
Sulfur in Petroleum Products by Wavelength Dispersive
1
X-ray Fluorescence Spectrometry
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D2622; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
This standard has been approved for use by agencies of the U.S. Department of Defense.
1. Scope* match can be caused by C/H ratio differences between samples
and standards or by the presence of other interfering heteroa-
1.1 This test method covers the determination of total sulfur
toms or species (see Table 1).
in petroleum and petroleum products that are single-phase and
either liquid at ambient conditions, liquefiable with moderate 1.6 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as
heat, or soluble in hydrocarbon solvents. These materials can standard. No other units of measurement are included in this
include diesel fuel, jet fuel, kerosene, other distillate oil, standard.
naphtha, residual oil, lubricating base oil, hydraulic oil, crude
1.7 This standard does not purport to address all of the
oil, unleaded gasoline, gasoline-ethanol blends, and biodiesel.
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
1.2 The range of this test method is between the PLOQ
priate safety, health, and environmental practices and deter-
value (calculated by procedures consistent with Practice
mine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
D6259) of 3 mg/kg total sulfur and the highest level sample in
1.8 This international standard was developed in accor-
the round robin, 4.6 % by weight total sulfur.
dance with internationally recognized principles on standard-
NOTE 1—Instrumentation covered by this test method can vary in
ization established in the Decision on Principles for the
sensitivity. The applicability of the test method at sulfur concentrations
Development of International Standards, Guides and Recom-
below 3 mg⁄kg may be determined on an individual basis for WDXRF
instruments capable of measuring lower levels, but precision in this test mendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical
method does not apply.
Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
1.2.1 The values of the limit of quantitation (LOQ) and
2. Referenced Documents
methodprecisionforaspecificlaboratory’sinstrumentdepends
2
on instrument source power (low or high power), sample type,
2.1 ASTM Standards:
and the practices established by the laboratory to perform the
D4057 Practice for Manual Sampling of Petroleum and
method.
Petroleum Products
1.3 Samples containing more than 4.6 % by mass sulfur D4175 Terminology Relating to Petroleum Products, Liquid
Fuels, and Lubricants
should be diluted to bring the sulfur concentration of the
diluted material within the scope of this test method. Samples D4177 Practice for Automatic Sampling of Petroleum and
Petroleum Products
thataredilutedcanhavehighererrorsthanindicatedinSection
D4294 Test Method for Sulfur in Petroleum and Petroleum
15 than non-diluted samples.
Products by Energy Dispersive X-ray Fluorescence Spec-
1.4 Volatile samples (such as high vapor pressure gasolines
trometry
or light hydrocarbons) may not meet the stated precision
D4927 Test Methods for Elemental Analysis of Lubricant
because of selective loss of light materials during the analysis.
and Additive Components—Barium, Calcium,
1.5 Afundamental assumption in this test method is that the
Phosphorus, Sulfur, and Zinc by Wavelength-Dispersive
standard and sample matrices are well matched, or that the
X-Ray Fluorescence Spectroscopy
matrix differences are accounted for (see 13.2). Matrix mis-
D6259 Practice for Determination of a Pooled Limit of
Quantitation for a Test Method
1
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D02 on
Petroleum Products, Liquid Fuels, and Lubricants and is the direct responsibility of
2
Subcommittee D02.03 on Elemental Analysis. For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
Current edition approved Dec. 1, 2021. Published January 2022. Originally contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
approved in 1967. Last previous edition approved in 2016 as D2622 – 16. DOI: Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on
10.1520/D2622-21. the ASTM website.
*A Summary of Changes section appears at the end of this standard
Co
...
This document is not an ASTM standard and is intended only to provide the user of an ASTM standard an indication of what changes have been made to the previous version. Because
it may not be technically possible to adequately depict all changes accurately, ASTM recommends that users consult prior editions as appropriate. In all cases only the current version
of the standard as published by ASTM is to be considered the official document.
Designation: D2622 − 16 D2622 − 21
Standard Test Method for
Sulfur in Petroleum Products by Wavelength Dispersive
1
X-ray Fluorescence Spectrometry
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D2622; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
This standard has been approved for use by agencies of the U.S. Department of Defense.
1. Scope*
1.1 This test method covers the determination of total sulfur in petroleum and petroleum products that are single-phase and either
liquid at ambient conditions, liquefiable with moderate heat, or soluble in hydrocarbon solvents. These materials can include diesel
fuel, jet fuel, kerosene, other distillate oil, naphtha, residual oil, lubricating base oil, hydraulic oil, crude oil, unleaded gasoline,
gasoline-ethanol blends, and biodiesel.
1.2 The range of this test method is between the PLOQ value (calculated by procedures consistent with Practice D6259) of 3
mg/kg total sulfur and the highest level sample in the round robin, 4.6 weight % 4.6 % by weight total sulfur.
NOTE 1—Instrumentation covered by this test method can vary in sensitivity. The applicability of the test method at sulfur concentrations below 3 mg ⁄kg
may be determined on an individual basis for WDXRF instruments capable of measuring lower levels, but precision in this test method does not apply.
1.2.1 The values of the limit of quantitation (LOQ) and method precision for a specific laboratory’s instrument depends on
instrument source power (low or high power), sample type, and the practices established by the laboratory to perform the method.
1.3 Samples containing more than 4.6 mass % 4.6 % by mass sulfur should be diluted to bring the sulfur concentration of the
diluted material within the scope of this test method. Samples that are diluted can have higher errors than indicated in Section 1415
than non-diluted samples.
1.4 Volatile samples (such as high vapor pressure gasolines or light hydrocarbons) may not meet the stated precision because of
selective loss of light materials during the analysis.
1.5 A fundamental assumption in this test method is that the standard and sample matrices are well matched, or that the matrix
differences are accounted for (see 12.213.2). Matrix mismatch can be caused by C/H ratio differences between samples and
standards or by the presence of other interfering heteroatoms or species (see Table 1).
1.6 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as standard. No other units of measurement are included in this standard.
1.7 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility
of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety safety, health, and healthenvironmental practices and determine the
applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
1
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D02 on Petroleum Products, Liquid Fuels, and Lubricants and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee
D02.03 on Elemental Analysis.
Current edition approved Jan. 1, 2016Dec. 1, 2021. Published February 2016January 2022. Originally approved in 1967. Last previous edition approved in 20102016 as
D2622 – 10.D2622 – 16. DOI: 10.1520/D2622-16.10.1520/D2622-21.
*A Summary of Changes section appears at the end of this standard
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
D2622 − 21
TABLE 1 Concentrations of Interfering Species
Species Mass % Tolerated
Phosphorus 0.3
Zinc 0.6
Barium 0.8
Lead 0.9
Calcium 1
Chlorine 3
Oxygen 2.8
FAME (see Note 16) 25
Ethanol (see Note 16) 8.6
Methanol (see Note 16) 6
1.8 This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization
established in the Decision on Principles for the Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued
by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
2. Referenced Documents
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
D4057 Practice for Manual Sampling of Petroleum and Petroleum Products
D4175 Terminology Relating to Petroleum Products, Liquid Fuels, and Lubricants
D4177 Practice for Automatic Sampling of Petroleum and Petroleum
...










Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.