ASTM D1623-09
(Test Method)Standard Test Method for Tensile and Tensile Adhesion Properties of Rigid Cellular Plastics
Standard Test Method for Tensile and Tensile Adhesion Properties of Rigid Cellular Plastics
ABSTRACT
This test method establishes standard procedure for determining the tensile and tensile adhesion properties of rigid cellular plastics in the form of test specimens of standard shape under defined conditions of temperature, humidity, and testing machine speed. Tensile properties shall be measured using any of three types of specimens: Type A shall be the preferred specimen in those cases where enough sample material exists to form the necessary specimen; Type B shall be the preferred specimen when only smaller specimens are available, as in sandwich panels, etc.; Type C shall be the preferred specimen for the determination of tensile adhesive properties of a cellular plastic to a substrate as in a sandwich panel or the bonding strength of a cellular plastic to a single substrate. This test method requires the use of the following apparatuses: a constant-rate-of-crosshead-movement type testing machine; self-aligning type grips for holding test specimens; an extension indicator; and a lathe specimen cutter.
SCOPE
1.1 This test method covers the determination of the tensile and tensile adhesion properties of rigid cellular materials in the form of test specimens of standard shape under defined conditions of temperature, humidity, and testing machine speed.
1.2 Tensile properties shall be measured using any of three types of specimens:
1.2.1 Type A shall be the preferred specimen in those cases where enough sample material exists to form the necessary specimen.
1.2.2 Type B shall be the preferred specimen when only smaller specimens are available, as in sandwich panels, etc.
1.2.3 Type C shall be the preferred specimen for the determination of tensile adhesive properties of a cellular plastic to a substrate as in a sandwich panel or the bonding strength of a cellular plastic to a single substrate.
1.3 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as standard. The values given in parentheses are mathematical conversions to inch-pound units that are provided for information only and are not considered standard.
Note 1—There is no known ISO equivalent to this test method.
General Information
Relations
Buy Standard
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Designation: D1623 − 09
Standard Test Method for
Tensile and Tensile Adhesion Properties of Rigid Cellular
1
Plastics
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D1623; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
This standard has been approved for use by agencies of the U.S. Department of Defense.
1. Scope* 3. Terminology
3.1 Definitions of terms applying to this test method appear
1.1 This test method covers the determination of the tensile
in the Appendix to Test Method D638.
and tensile adhesion properties of rigid cellular materials in the
form of test specimens of standard shape under defined
conditions of temperature, humidity, and testing machine 4. Apparatus
speed.
4.1 Testing Machine—A testing machine of the constant-
rate-of-crosshead-movement type, comprising essentially the
1.2 Tensile properties shall be measured using any of three
following:
types of specimens:
4.1.1 Grips—Grips for holding the test specimen shall be
1.2.1 Type A shall be the preferred specimen in those cases
theself-aligningtype;thatis,theymustbeattachedtothefixed
where enough sample material exists to form the necessary
and movable members of the testing machine in such a way
specimen.
that they will move freely into alignment as soon as any load
1.2.2 Type B shall be the preferred specimen when only
is applied, so that the long axis of the test specimen will
smaller specimens are available, as in sandwich panels, etc.
coincide with the direction of the applied pull through the
1.2.3 Type C shall be the preferred specimen for the deter-
center line of the grip assembly. Universal-type joints imme-
mination of tensile adhesive properties of a cellular plastic to a
diately above and below the specimen grips are recommended.
substrate as in a sandwich panel or the bonding strength of a
The test specimen shall be held in such a way that slippage
cellular plastic to a single substrate.
relative to the grips is prevented, insofar as possible. For Type
1.3 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as
Aspecimens, use a grip assembly like the one shown in Fig. 1
standard. The values given in parentheses are mathematical and Fig. 2. For Type B specimens, one suitable grip assembly
conversions to inch-pound units that are provided for informa-
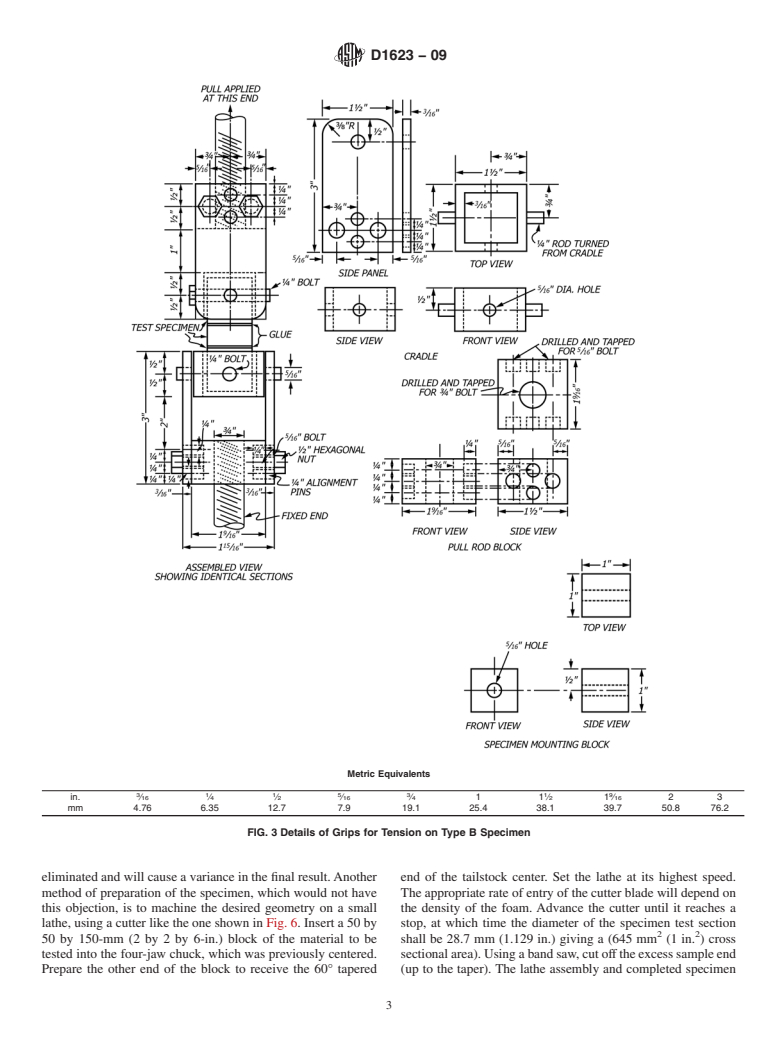
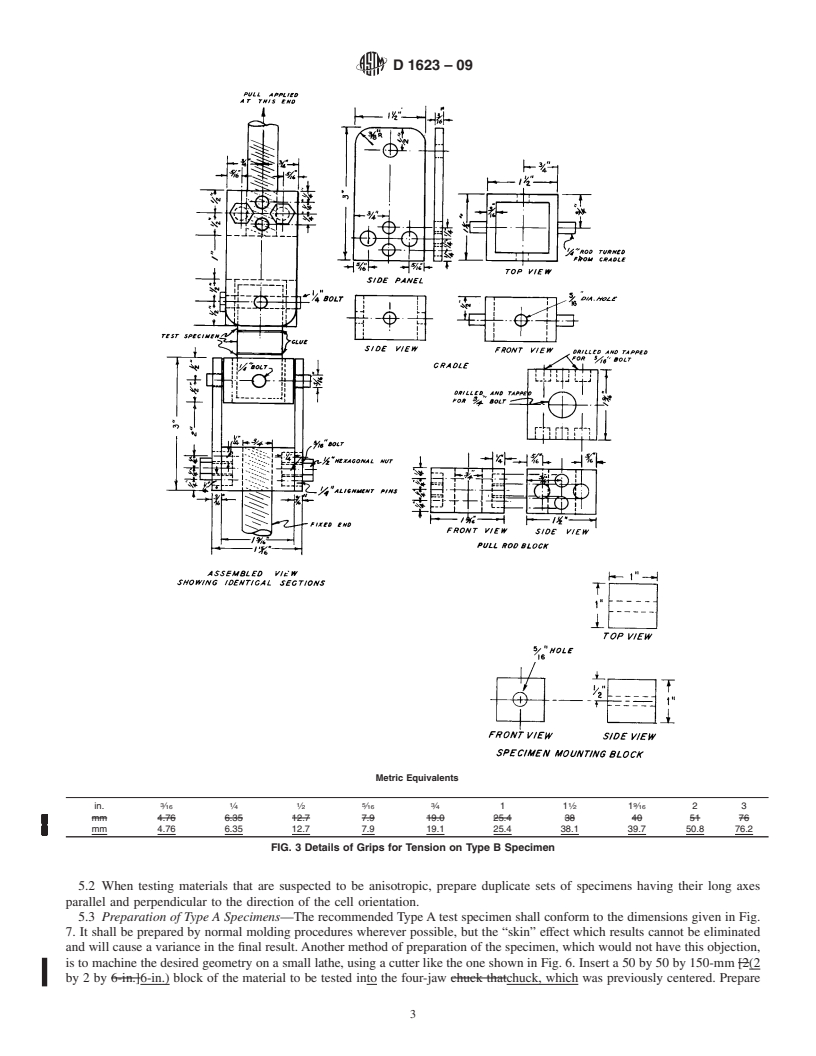
is shown in Fig. 3 and Fig. 4. For Type C specimen, a suitable
tion only and are not considered standard.
grip assembly is shown in Fig. 5.
NOTE 1—There is no known ISO equivalent to this test method.
4.1.2 Load Indicator—Use a load cell or suitable load-
indicating mechanism capable of showing the total tensile load
2. Referenced Documents
exerted on the test specimen when held in the grips. Choose an
2 indicator that will permit precision to within 61%.
2.1 ASTM Standards:
4.1.3 Extension Indicator—If measurement of the extension
D638 Test Method for Tensile Properties of Plastics
is desired, use a suitable instrument for determining the
D883 Terminology Relating to Plastics
distance between two fixed points on the test specimen, or
E691 Practice for Conducting an Interlaboratory Study to
similarly by grip separation or extensometer at any time during
Determine the Precision of a Test Method
the test.
4.2 Specimen Cutter—For TypeAspecimens, use a suitable
lathe cutter (see Fig. 6).
1
This test method is under the jurisdiction ofASTM Committee D20 on Plastics
and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee D20.22 on Cellular Materials -
Plastics and Elastomers.
5. Test Specimen
Current edition approved Sept. 1, 2009. Published September 2009. Originally
5.1 Allsurfacesofthespecimenshallbefreeoflargevisible
approved in 1959. Last previous edition approved in 2003 as D1623 – 03. DOI:
10.1520/D1623-09.
flawsorimperfections.Ifitisnecessarytoplacegagemarkson
2
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
the specimen, do this in such a way as not to affect the surfaces
contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
of the test specimen. Gage marks shall not be scratched,
Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on
the ASTM website. punched, or impressed on the specimen.
*A Summary of Changes section appears at the end of this standard
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
D1623 − 09
Metric Equivalents
1 1 1 9 11 1 1 1 5
in. ⁄8 ⁄4 ⁄2 ⁄16 ⁄16 1 1.130 1 ⁄2 22 ⁄4 2 ⁄2 33 ⁄16
mm 3.18 6.35 12.7 14.3 17.5 25.4 28.7 38.1 50.8 57.2 63.5 76.2 84.1
FIG. 1 Details
...
This document is not an ASTM standard and is intended only to provide the user of an ASTM standard an indication of what changes have been made to the previous version. Because
it may not be technically possible to adequately depict all changes accurately, ASTM recommends that users consult prior editions as appropriate. In all cases only the current version
of the standard as published by ASTM is to be considered the official document.
Designation:D1623–03 Designation:D1623–09
Standard Test Method for
Tensile and Tensile Adhesion Properties of Rigid Cellular
1
Plastics
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D 1623; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
This standard has been approved for use by agencies of the Department of Defense.
1. Scope*
1.1 Thistestmethodcoversthedeterminationofthetensileandtensileadhesionpropertiesofrigidcellularmaterialsintheform
of test specimens of standard shape under defined conditions of temperature, humidity, and testing machine speed.
1.2 Tensile properties shall be measured using any of three types of specimens:
1.2.1 Type A shall be the preferred specimen in those cases where enough sample material exists to form the necessary
specimen, specimen.
1.2.2 Type B shall be the preferred specimen when only smaller specimens are available, as in sandwich panels, etc.
1.2.3 Type C shall be the preferred specimen for the determination of tensile adhesive properties of a cellular plastic to a
substrate as in a sandwich panel or the bonding strength of a cellular plastic to a single substrate.
1.3 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as standard. The values given in parentheses are mathematical conversions
to inch-pound units that are provided for information only and are not considered standard.
NOTE1—The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as the standard.
NOTE2—There is no equivalent ISO standard. 1—There is no known ISO equivalent to this test method.
2. Referenced Documents
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
D 638 Test Method for Tensile Properties of Plastics
D 883 Terminology Relating to Plastics
E 691 Practice for Conducting an Interlaboratory Study to Determine the Precision of a Test Method
3. Terminology
3.1 Definitions of terms applying to this test method appear in the Appendix to Test Method D 638.
4. Apparatus
4.1 Testing Machine—A testing machine of the constant-rate-of-crosshead-movement type, comprising essentially the
following:
4.1.1 Grips—Grips for holding the test specimen shall be the self-aligning type; that is, they must be attached to the fixed and
movable members of the testing machine in such a way that they will move freely into alignment as soon as any load is applied,
so that the long axis of the test specimen will coincide with the direction of the applied pull through the center line of the grip
assembly. Universal-type joints immediately above and below the specimen grips are recommended. The test specimen shall be
held in such a way that slippage relative to the grips is prevented, insofar as possible. For TypeAspecimens, use a grip assembly
like the one shown in Fig. 1 and Fig. 2. For Type B specimens, one suitable grip assembly is shown in Fig. 3 and Fig. 4. For Type
C specimen, a suitable grip assembly is shown in Fig. 5.
4.1.2 Load Indicator—Use a load cell or suitable load-indicating mechanism capable of showing the total tensile load exerted
on the test specimen when held in the grips. Choose an indicator that will permit precision to within 61%.
4.1.3 Extension Indicator—If measurement of the extension is desired, use a suitable instrument for determining the distance
between two fixed points on the test specimen, or similarly by grip separation or extensometer at any time during the test.
1
This test method is under the jurisdiction ofASTM Committee D20 on Plastics and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee D20.22 on Cellular Materials - Plastics
and Elastomers.
Current edition approved March 10, 2003. Published April 2003. Originally approved in 1959. Last previous edition approved in 1995 as D1623–78 (1995).
Current edition approved Sept. 1, 2009. Published September 2009. Originally approved in 1959. Last previous edition approved in 2003 as D 1623 – 03.
2
For referencedASTM standards, visit theASTM website, www.astm.org, or contactASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book ofASTM Standards
, Vol 08.01.volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on the ASTM website.
*ASummary of Changes section appears at the end of this standard.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959, United States.
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
D1623–09
FIG.
...








Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.