ASTM C591-11
(Specification)Standard Specification for Unfaced Preformed Rigid Cellular Polyisocyanurate Thermal Insulation
Standard Specification for Unfaced Preformed Rigid Cellular Polyisocyanurate Thermal Insulation
ABSTRACT
This specification covers the types, physical properties, and dimensions of unfaced, preformed rigid cellular polyurethane modified polyisocyanurate plastic material intended for use as thermal insulation on surfaces. This insulation can be classified into six types according to its compressive resistance: Types I, IV, II, III, V, and VI. Also this insulation can be classified as Grades 1 and 2 according to its service temperature range. The thermal insulation is produced by the polymerization of polymeric polyisocyanates in the presence of polyhydroxyl compounds, catalysts, cell stabilizers, and blowing agents. Different test methods shall be performed in order to determine the thermal insulation's following properties: density, compressive resistance, apparent thermal conductivity, hot-surface performance, water absorption, water vapor permeability, dimensional stability, closed-cell content, surface bearing characteristics, tensile strength, and leachable chloride, fluoride, silicate, and sodium ions.
SCOPE
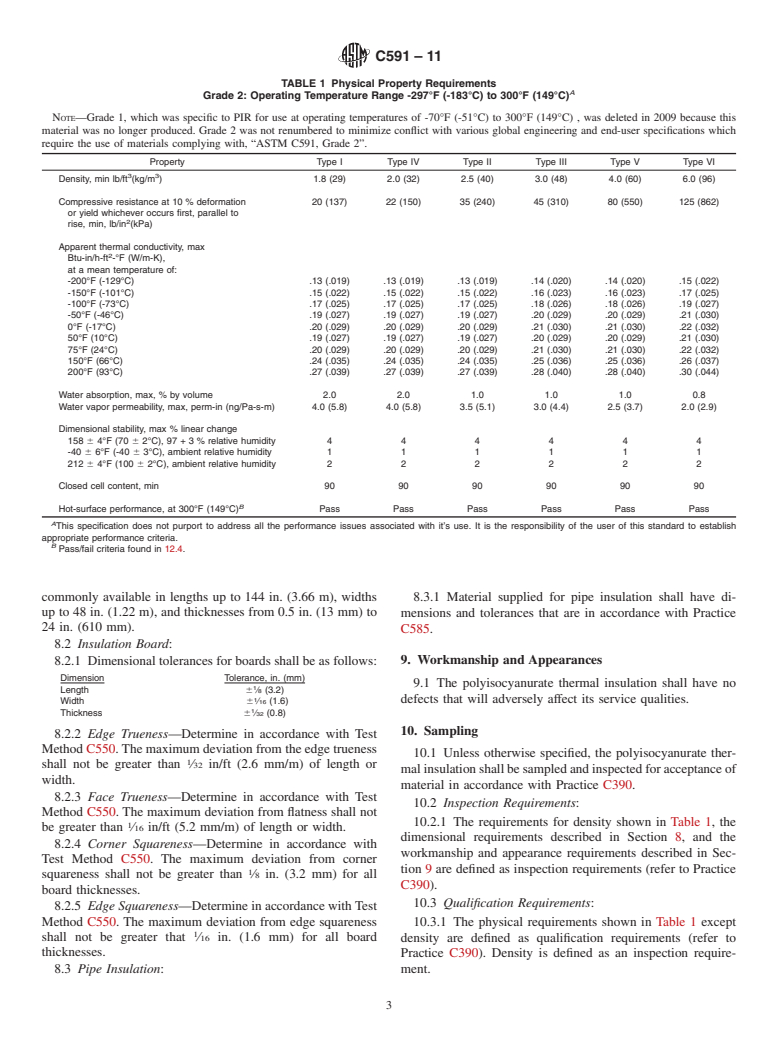
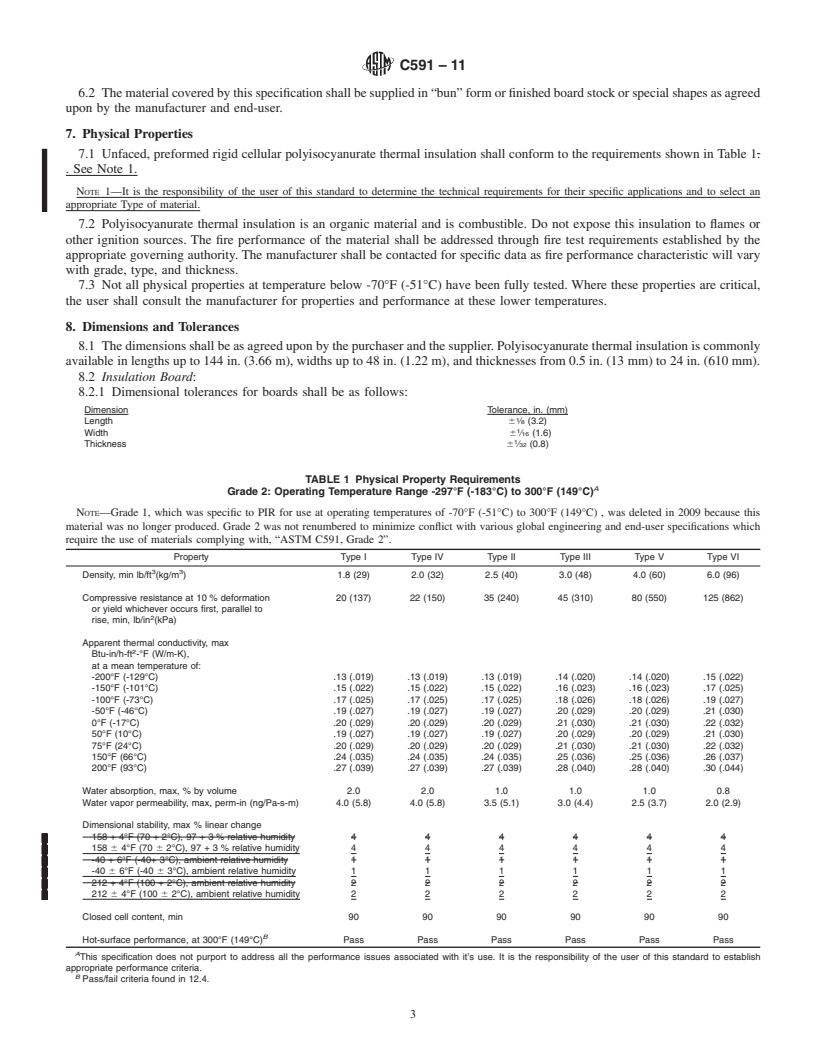
1.1 This specification covers the types, physical properties, and dimensions of unfaced, preformed rigid cellular polyisocyanurate plastic material intended for use as thermal insulation on surfaces from -297°F (-183°C) to 300°F (149°C). For specific applications, the actual temperature limits shall be agreed upon by the manufacturer and purchaser.
1.2 This specification only covers “polyurethane modified polyisocyanurate” thermal insulation which is commonly referred to as “polyisocyanurate” thermal insulation. This standard does not encompass all polyurethane modified materials. Polyurethane modified polyisocyanurate and other polyurethane materials are similar, but the materials will perform differently under some service conditions.
1.3 This standard is designed as a material specification, not a design document. Physical property requirements vary by application and temperature. At temperatures below -70°F (-51°C) the physical properties of the polyisocyanurate insulation at the service temperature are of particular importance. Below -70°F (-51°C) the manufacturer and the purchaser must agree on what additional cold temperature performance properties are required to determine if the material can function adequately for the particular application.
1.4 The main body of this standard addresses requirements of unfaced preformed rigid cellular polyisocyanurate thermal insulation manufactured using blowing agents with an ozone depletion potential of 0 (ODP 0).
1.5 The table in the Annex A1 addresses requirements of unfaced preformed rigid cellular polyisocyanurate thermal insulation manufactured with HCFC blowing agent.
1.6 When adopted by an authority having jurisdiction, codes that address fire properties in many applications regulate the use of the thermal insulation materials covered by this specification. Fire properties are controlled by job, project, or other specifications where codes or government regulations do not apply.
1.7 The values stated in inch-pound units are to be regarded as standard. The values given in parentheses are mathematical conversions to SI units that are provided for information only and are not considered standard.
1.8 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
General Information
Relations
Buy Standard
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Designation: C591 – 11
Standard Specification for
Unfaced Preformed Rigid Cellular Polyisocyanurate
1
Thermal Insulation
This standard is issued under the fixed designation C591; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision.Anumber in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval.A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
This standard has been approved for use by agencies of the Department of Defense.
1. Scope fication. Fire properties are controlled by job, project, or other
specifications where codes or government regulations do not
1.1 This specification covers the types, physical properties,
apply.
and dimensions of unfaced, preformed rigid cellular polyiso-
1.7 The values stated in inch-pound units are to be regarded
cyanurate plastic material intended for use as thermal insula-
as standard. The values given in parentheses are mathematical
tion on surfaces from -297°F (-183°C) to 300°F (149°C). For
conversions to SI units that are provided for information only
specific applications, the actual temperature limits shall be
and are not considered standard.
agreed upon by the manufacturer and purchaser.
1.8 This standard does not purport to address all of the
1.2 This specification only covers “polyurethane modified
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
polyisocyanurate” thermal insulation which is commonly re-
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
ferred to as “polyisocyanurate” thermal insulation. This stan-
priate safety and health practices and determine the applica-
dard does not encompass all polyurethane modified materials.
bility of regulatory limitations prior to use.
Polyurethane modified polyisocyanurate and other polyure-
thane materials are similar, but the materials will perform
2. Referenced Documents
differently under some service conditions.
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
1.3 Thisstandardisdesignedasamaterialspecification,not
C165 Test Method for Measuring Compressive Properties
a design document. Physical property requirements vary by
of Thermal Insulations
application and temperature. At temperatures below -70°F
C168 Terminology Relating to Thermal Insulation
(-51°C) the physical properties of the polyisocyanurate insula-
C177 Test Method for Steady-State Heat Flux Measure-
tion at the service temperature are of particular importance.
ments and Thermal Transmission Properties by Means of
Below -70°F (-51°C) the manufacturer and the purchaser must
the Guarded-Hot-Plate Apparatus
agree on what additional cold temperature performance prop-
C272 Test Method for Water Absorption of Core Materials
erties are required to determine if the material can function
for Structural Sandwich Constructions
adequately for the particular application.
C303 Test Method for Dimensions and Density of Pre-
1.4 The main body of this standard addresses requirements
formed Block and Board−Type Thermal Insulation
of unfaced preformed rigid cellular polyisocyanurate thermal
C335 Test Method for Steady-State Heat Transfer Proper-
insulation manufactured using blowing agents with an ozone
ties of Pipe Insulation
depletion potential of 0 (ODP 0).
C390 Practice for Sampling and Acceptance of Thermal
1.5 The table in the Annex A1 addresses requirements of
Insulation Lots
unfaced preformed rigid cellular polyisocyanurate thermal
C411 Test Method for Hot-Surface Performance of High-
insulation manufactured with HCFC blowing agent.
Temperature Thermal Insulation
1.6 Whenadoptedbyanauthorityhavingjurisdiction,codes
C518 Test Method for Steady-State Thermal Transmission
that address fire properties in many applications regulate the
Properties by Means of the Heat Flow Meter Apparatus
use of the thermal insulation materials covered by this speci-
C550 Test Method for Measuring Trueness and Squareness
of Rigid Block and Board Thermal Insulation
1
This specification is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee C16 on
Thermal Insulation and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee C16.22 on
2
Organic and Nonhomogeneous Inorganic Thermal Insulations. For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
Current edition approved May 15, 2011. Published June 2011. Originally contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
approved in 1966. Last previous edition approved in 2009 as C591–09. DOI: Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on
10.1520/C0591-11.
the ASTM website.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959, United States.
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
C591 – 11
2
C585 Practice for Inner and Outer Diameters of Thermal
...
This document is not an ASTM standard and is intended only to provide the user of an ASTM standard an indication of what changes have been made to the previous version. Because
it may not be technically possible to adequately depict all changes accurately, ASTM recommends that users consult prior editions as appropriate. In all cases only the current version
of the standard as published by ASTM is to be considered the official document.
Designation:C591–09 Designation: C591 – 11
Standard Specification for
Unfaced Preformed Rigid Cellular Polyisocyanurate
1
Thermal Insulation
This standard is issued under the fixed designation C591; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
This standard has been approved for use by agencies of the Department of Defense.
1. Scope
1.1 This specification covers the types, physical properties, and dimensions of unfaced, preformed rigid cellular polyisocya-
nurate plastic material intended for use as thermal insulation on surfaces from -297°F (-183°C) to 300°F (149°C). For specific
applications, the actual temperature limits shall be agreed upon by the manufacturer and purchaser.
1.2 This specification only covers “polyurethane modified polyisocyanurate” thermal insulation which is commonly referred to
as “polyisocyanurate” thermal insulation. This standard does not encompass all polyurethane modified materials. Polyurethane
modified polyisocyanurate and other polyurethane materials are similar, but the materials will perform differently under some
service conditions.
1.3 This standard is designed as a material specification, not a design document. Physical property requirements vary by
application and temperature.At temperatures below -70°F (-51°C) the physical properties of the polyisocyanurate insulation at the
service temperature are of particular importance. Below -70°F (-51°C) the manufacturer and the purchaser must agree on what
additional cold temperature performance properties are required to determine if the material can function adequately for the
particular application.
1.4The table in the
1.4 The main body of this standard addresses requirements of unfaced preformed rigid cellular polyisocyanurate thermal
insulation manufactured using blowing agents with an ozone depletion potential of 0 (ODP 0).
1.5 The table in theAnnexA1 addresses requirements of unfaced preformed rigid cellular polyisocyanurate thermal insulation
manufactured with HCFC blowing agent.
1.5When1.6 When adopted by an authority having jurisdiction, codes that address fire properties in many applications regulate
the use of the thermal insulation materials covered by this specification. Fire properties are controlled by job, project, or other
specifications where codes or government regulations do not apply.
1.6The1.7 The values stated in inch-pound units are to be regarded as standard. The values given in parentheses are
mathematical conversions to SI units that are provided for information only and are not considered standard.
1.71.8 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility
of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory
limitations prior to use.
2. Referenced Documents
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
C165 Test Method for Measuring Compressive Properties of Thermal Insulations
C168 Terminology Relating to Thermal Insulation
C177 Test Method for Steady-State Heat Flux Measurements and Thermal Transmission Properties by Means of the
Guarded-Hot-Plate Apparatus
C272 Test Method for Water Absorption of Core Materials for Structural Sandwich Constructions
C303 Test Method for Dimensions and Density of Preformed Block and BoardType Thermal Insulation
C335 Test Method for Steady-State Heat Transfer Properties of Pipe Insulation
1
This specification is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee C16 on Thermal Insulation and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee C16.22 on Organic and
Nonhomogeneous Inorganic Thermal Insulations.
Current edition approved Nov. 1, 2009. Published November 2009. Originally approved in 1966. Last previous edition approved in 2008 as C591–08. DOI:
10.1520/C0591-09.
CurrenteditionapprovedMay15,2011.PublishedJune2011.Originallyapprovedin1966.Lastpreviouseditionapprovedin2009asC591 – 09.DOI:10.1520/C0591-11.
2
For referencedASTM standards, visit theASTM website, www.astm.org, or contactASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM Standards
volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on the ASTM website.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959, United States.
1
--------------
...








Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.