ASTM D2782-02(2008)
(Test Method)Standard Test Method for Measurement of Extreme-Pressure Properties of Lubricating Fluids (Timken Method)
Standard Test Method for Measurement of Extreme-Pressure Properties of Lubricating Fluids (Timken Method)
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
This test method is used widely for the determination of extreme pressure properties for specification purposes. Users are cautioned to carefully consider the precision and bias statements herein when establishing specification limits.
SCOPE
1.1 This test method covers the determination of the load-carrying capacity of lubricating fluids by means of the Timken Extreme Pressure Tester.
Note 1—This test method is suitable for testing fluids having a viscosity of less than about 5000 cSt (5000 mm2/s) at 40°C. For testing fluids having a higher viscosity, refer to Note 5 in 9.1.
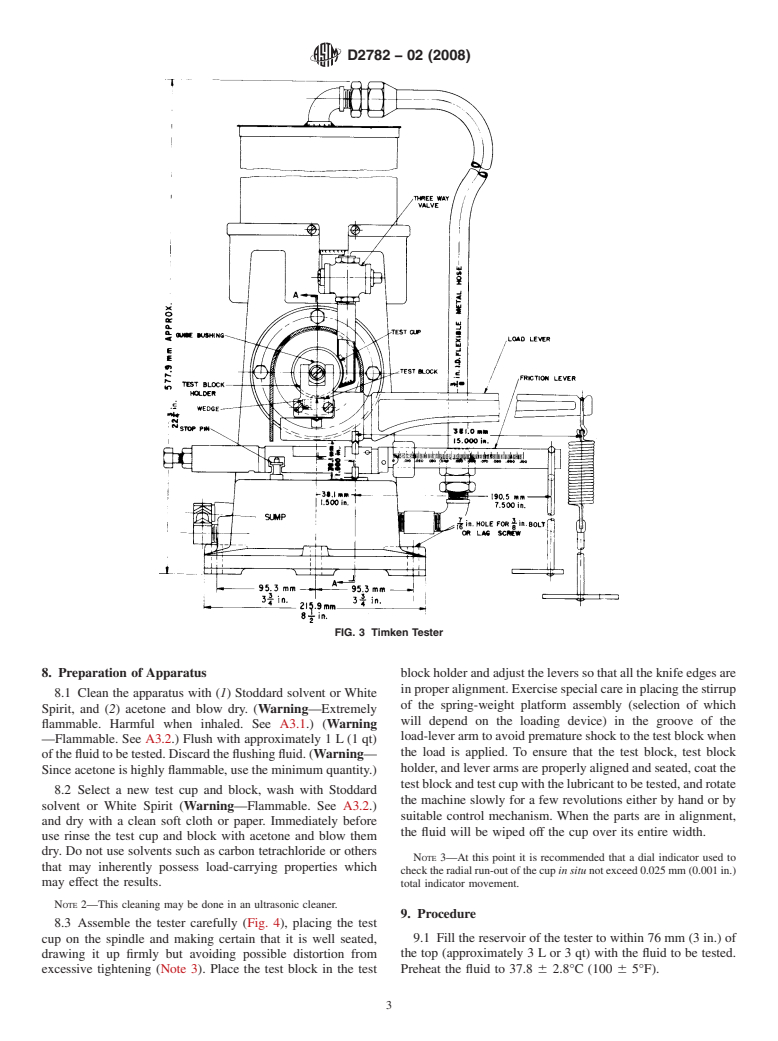
1.2 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as standard. Because the equipment used in this test method is available only in inch-pound units, SI units are omitted when referring to the equipment and the test specimens.
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use. Specific warning statements are given in 7.1, 7.2, 8.1, 8.2, 9.4, and 9.9.
General Information
Relations
Buy Standard
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Designation: D2782 − 02(Reapproved 2008)
240/84
Standard Test Method for
Measurement of Extreme-Pressure Properties of Lubricating
1
Fluids (Timken Method)
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D2782; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision.Anumber in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval.A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope 2.2 ASTM Adjuncts:
3
Photograph of Test Blocks Showing Scars
1.1 This test method covers the determination of the load-
carrying capacity of lubricating fluids by means of theTimken
3. Terminology
Extreme Pressure Tester.
3.1 Definitions:
NOTE 1—This test method is suitable for testing fluids having a
3.1.1 extreme pressure (EP) additive, n, in a lubricant—a
2
viscosity of less than about 5000 cSt (5000 mm /s) at 40°C. For testing
substance that minimizes damage to metal surfaces in contact
fluids having a higher viscosity, refer to Note 5 in 9.1.
under high-stress rubbing conditions. D4175
1.2 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as
3.1.2 lubricant, n—any substance interposed between two
standard. Because the equipment used in this test method is
surfaces for the purpose of reducing friction or wear between
available only in inch-pound units, SI units are omitted when
them. G40
referring to the equipment and the test specimens.
3.1.3 scoring, n, in tribology—a severe form of wear char-
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the
acterized by the formation of extensive grooves and scratches
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
in the direction of sliding. G40
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
3.1.4 wear, n—damage to a solid surface generally involv-
priate safety and health practices and determine the applica-
bility of regulatory limitations prior to use. Specific warning ingprogressivelossofmaterial,duetorelativemotionbetween
that surface and a contacting substance or substances. G40
statements are given in 7.1, 7.2, 8.1, 8.2, 9.4, and 9.9.
3.2 Definitions of Terms Specific to This Standard:
2. Referenced Documents
3.2.1 load-carrying capacity of a lubricant— as determined
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
by this test method, the maximum load or pressure that can be
D2509Test Method for Measurement of Load-Carrying
sustained by the lubricant (when used in the given system
Capacity of Lubricating Grease (Timken Method)
underspecificconditions)withoutfailureoftheslidingcontact
D4175 Terminology Relating to Petroleum, Petroleum
surfaces as evidenced by scoring or seizure or asperity weld-
Products, and Lubricants
ing.
G40Terminology Relating to Wear and Erosion
3.2.2 OK value, n—as determined by this test method, the
maximummass(weight)addedtotheloadleverweightpan,at
which no scoring or seizure occurs.
3.2.3 score value, n—as determined by this test method, the
minimum mass (weight) added to the load lever weight pan, at
1
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D02 on which scoring or seizure occurs.
PetroleumProductsandLubricantsandisthedirectresponsibilityofSubcommittee
3.2.3.1 Discussion—Whenthelubricantfilmissubstantially
D02.L0.11 on Tribiological Properties of Industrial Fluids and Lubricates.
maintained, a smooth scar is obtained on the test block, but
Current edition approved May 1, 2008. Published August 2008. Originally
´1
when there is a breakdown of the lubricant film, scoring or
approved in 1969. Last previous edition approved in 2002 as D2782–02 .
This test method was adopted as a joint ASTM-IP Standard.
surface failure of the test block takes place, as shown in Figs.
This test method was prepared under the joint sponsorship of the American
1 and 2. In its simplest and most recognized form, scoring is
Society of Lubrication Engineers.Accepted by STLE January 1969. DOI: 10.1520/
characterizedbythefurrowedappearanceofawidescaronthe
D2782-02R08.
2
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
3
Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on Available from ASTM International Headquarters. Order Adjunct No.
the ASTM website. ADJD2509. Original adjunct produced in 1972.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
D2782 − 02 (2008)
FIG. 1 Test Blocks Showing Various Types of Scar
are cautioned to carefully consider the precision and bias
statements herein when establishing specification limits.
6. Apparatus
4
6.1 Timken Extreme Pressure Tester, described in detail in
Annex A1 and illustrated
...
This document is not anASTM standard and is intended only to provide the user of anASTM standard an indication of what changes have been made to the previous version. Because
it may not be technically possible to adequately depict all changes accurately, ASTM recommends that users consult prior editions as appropriate. In all cases only the current version
of the standard as published by ASTM is to be considered the official document.
An American National Standard
Designation:D2782–01 Designation:D2782–02 (Reapproved 2008)
240/84
Standard Test Method for
Measurement of Extreme-Pressure Properties of Lubricating
1
Fluids (Timken Method)
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D2782; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision.Anumber in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval.A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval. This test method was adopted as a joint
ASTM-IP Standard.
This test method has been approved by the sponsoring committees and accepted by the cooperating societies in accordance with
established procedures.
1. Scope
1.1 This test method covers the determination of the load-carrying capacity of lubricating fluids by means of the Timken
Extreme Pressure Tester.
2
NOTE 1—This test method is suitable for testing fluids having a viscosity of less than about 5000 cSt (5000 mm /s) at 40°C. For testing fluids having
a higher viscosity, refer to Note 4 Note 5 in 9.1.
1.2 ThevaluesstatedinSIunitsaretoberegardedasstandard.Becausetheequipmentusedinthistestmethodisavailableonly
in inch-pound units, SI units are omitted when referring to the equipment and the test specimens.
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility
of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory
limitations prior to use. Specific precautionarywarning statements are given in 7.1, 7.2, 8.1, 8.2, 9.4, and 10.19.9.
2. Referenced Documents
2
2.1 ASTM Standards: D235Specification for Mineral Spirits (Petroleum Spirits) (Hydrocarbon Drycleaning Solvents)
2
D329Specification for Acetone
D2509 Test Method for Measurement of Extreme Pressure Properties Load-Carrying Capacity of Lubricating Grease (Timken
Method)
D4175 Terminology Relating to Petroleum, Petroleum Products, and Lubricants
G40 Terminology Relating to Wear and Erosion
1
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D02 on Petroleum Products and Lubricants and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee D02.L on
Industrial Lubricants.
Current edition approved Sept. 10, 2001. Published September 2001. Originally published as D2782–69T. Last previous edition D2782–94 (1996).
1
This test method is under the jurisdiction ofASTM Committee D02 on Petroleum Products and Lubricants and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee D02.L0.11
on Tribiological Properties of Industrial Fluids and Lubricants.
´1
Current edition approved May 1, 2008. Published August 2008. Originally approved in 1969. Last previous edition approved in 2002 as D2782–02 .
This test method was adopted as a joint ASTM-IP Standard.
This test method was prepared under the joint sponsorship of the American Society of Lubrication Engineers. Accepted by STLE January 1969.
2
ForreferencedASTMstandards,visittheASTMwebsite,www.astm.org,orcontactASTMCustomerServiceatservice@astm.org.For Annual Book of ASTM Standards
, Vol 06.04.volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on the ASTM website.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959, United States.
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
D2782–02 (2008)
2.2 ASTM Adjuncts: ASTM
Three Glossy Prints of Test Blocks Showing Scars (D2782)
3
Photograph of Test Blocks Showing Scars
3. Terminology
3.1 Definitions:
3.1.1 extreme pressure (EP) additive, n, in a lubricant—a substance that minimizes damage to metal surfaces in contact under
high-stress rubbing conditions. D4175
3.1.2 lubricant, n—any substance interposed between two surfaces for the purpose of reducing friction or wear between them.
G40
3.1.3 scoring, n, in tribology—a severe form of wear characterized by the formation of extensive grooves and scratches in the
direction of sliding. G40
3.1.4 wear, n—damage to a solid surface generally involving progressive loss of material, due to relative motion between that
surface and a contacting substance or substances. G40
3.2 Definitions of Terms Specific to This Standard:
3.2.1 load-carrying capacity of a lubricant— as determined by this test method, the maximum load or pressure that can be
sustained by the lubricant (when used in the given system under specific conditions) without failure of the sliding contact surfaces
as evidenced by scoring
...









Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.