ASTM G72/G72M-24
(Test Method)Standard Test Method for Autogenous Ignition Temperature of Liquids and Solids in a High-Pressure Oxygen-Enriched Environment
Standard Test Method for Autogenous Ignition Temperature of Liquids and Solids in a High-Pressure Oxygen-Enriched Environment
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
4.1 Most organic liquids and solids will ignite in a pressurized oxidizing gas atmosphere if heated to a sufficiently high temperature and pressure. This procedure provides a numerical value for the temperature at the onset of ignition under carefully controlled conditions. Means for extrapolation from this idealized situation to the description, appraisal, or regulation of fire and explosion hazards in specific field situations, are not established. Ranking of the ignition temperatures of several materials in the standard apparatus is generally in conformity with field experience.
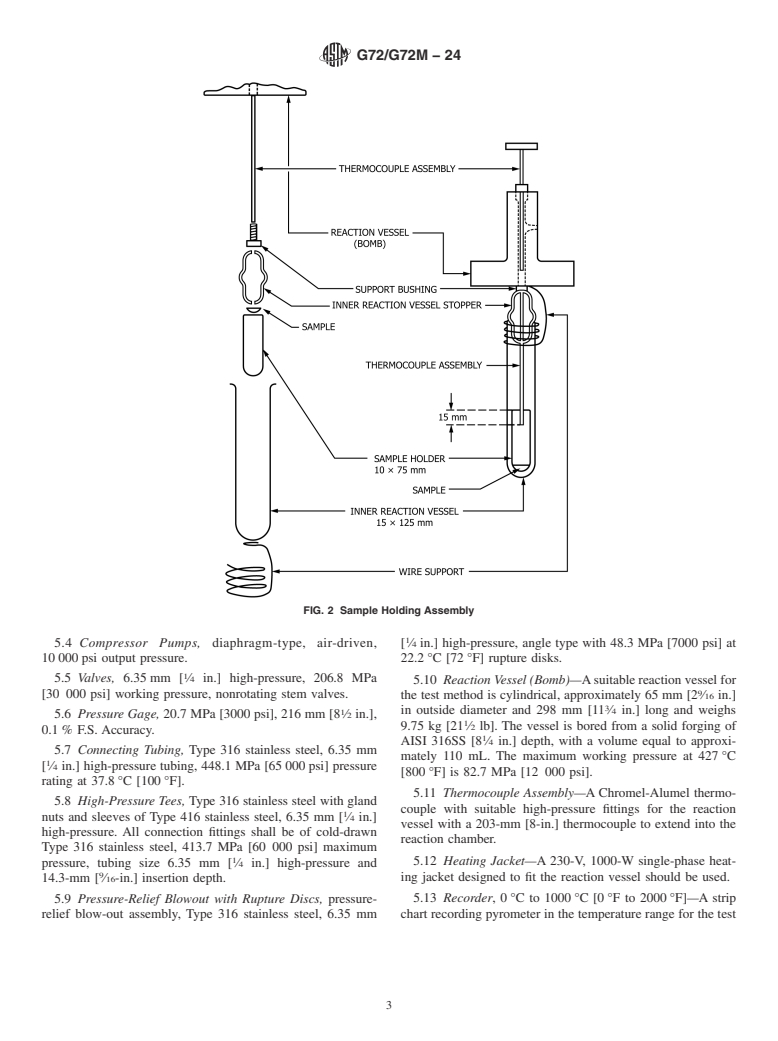
4.2 The temperature at which material will ignite spontaneously (AIT) will vary greatly with the geometry of the test system and the rate of heating. To achieve good interlaboratory agreement of ignition temperatures, it is necessary to use equipment of approximately the dimensions described in the test method. It is also necessary to follow the described procedure as closely as possible.
4.3 The decomposition and oxidation of some fully fluorinated materials releases so little energy that there is no clear-cut indication of ignition. Nor will there be a clear indication of ignition if a sample volatilizes, distilling to another part of the reaction vessel, before reaching ignition temperature.
SCOPE
1.1 This test method covers the determination of the temperature at which liquids and solids will spontaneously ignite. These materials must ignite without application of spark or flame in a high-pressure oxygen-enriched environment.
1.2 This test method is intended for use at pressures of 2.1 MPa to 20.7 MPa [300 psi to 3000 psi]. The pressure used in the description of the method is 10.3 MPa [1500 psi], and is intended for applicability to high pressure conditions. The test method, as described, is for liquids or solids with ignition temperature in the range from 60 °C to 500 °C [140 °F to 932 °F].
Note 1: Test Method G72/G72M normally utilizes samples of approximately 0.20 ± 0.03-g mass, a starting pressure of 10.3 MPa [1500 psi] and a temperature ramp rate of 5 °C/min. However, Autogenous Ignition Temperatures (AIT) can also be obtained under other test conditions. Testing experience has shown that AIT testing of volatile liquids can be influenced by the sample pre-conditioning and the sample mass. This will be addressed in the standard as Special Case 1 in subsection 8.2.2. Testing experience has also shown that AIT testing of solid or non-volatile liquid materials at low pressures (that is, 8.2.3. Since the AIT of a material is dependent on the sample mass/configuration and test conditions, any departure from the standard conditions normally used for Test Method G72/G72M testing should be clearly indicated in the test report.
1.3 This test method is for high-pressure pure oxygen. The test method may be used in atmospheres from 0.5 % to 100 % oxygen.
1.4 An apparatus suitable for these requirements is described. This test method could be applied to higher pressures and materials of higher ignition temperature. If more severe requirements or other oxidizers than those described are desired, care must be taken in selecting an alternative safe apparatus capable of withstanding the conditions.
1.5 The values stated in either SI units or inch-pound units are to be regarded separately as standard. The values stated in each system may not be exact equivalents; therefore, each system shall be used independently of the other. Combining values from the two systems may result in non-conformance with the standard.
1.6 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety, health, and environmental practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
1.7 This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognize...
General Information
Relations
Buy Standard
Standards Content (Sample)
This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization established in the Decision on Principles for the
Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
Designation: G72/G72M − 24
Standard Test Method for
Autogenous Ignition Temperature of Liquids and Solids in a
1
High-Pressure Oxygen-Enriched Environment
This standard is issued under the fixed designation G72/G72M; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year
of original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval.
A superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope 1.5 The values stated in either SI units or inch-pound units
are to be regarded separately as standard. The values stated in
1.1 This test method covers the determination of the tem-
each system may not be exact equivalents; therefore, each
perature at which liquids and solids will spontaneously ignite.
system shall be used independently of the other. Combining
These materials must ignite without application of spark or
values from the two systems may result in non-conformance
flame in a high-pressure oxygen-enriched environment.
with the standard.
1.2 This test method is intended for use at pressures of
1.6 This standard does not purport to address all of the
2.1 MPa to 20.7 MPa [300 psi to 3000 psi]. The pressure used
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
in the description of the method is 10.3 MPa [1500 psi], and is
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
intended for applicability to high pressure conditions. The test
priate safety, health, and environmental practices and deter-
method, as described, is for liquids or solids with ignition
mine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
temperature in the range from 60 °C to 500 °C [140 °F to
1.7 This international standard was developed in accor-
932 °F].
dance with internationally recognized principles on standard-
ization established in the Decision on Principles for the
NOTE 1—Test Method G72/G72M normally utilizes samples of ap-
proximately 0.20 6 0.03-g mass, a starting pressure of 10.3 MPa
Development of International Standards, Guides and Recom-
[1500 psi] and a temperature ramp rate of 5 °C ⁄min. However, Autog-
mendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical
enous Ignition Temperatures (AIT) can also be obtained under other test
Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
conditions. Testing experience has shown that AIT testing of volatile
liquids can be influenced by the sample pre-conditioning and the sample
2. Referenced Documents
mass. This will be addressed in the standard as Special Case 1 in
2
subsection 8.2.2. Testing experience has also shown that AIT testing of
2.1 ASTM Standards:
solid or non-volatile liquid materials at low pressures (that is, < 2.1 MPa)
D1193 Specification for Reagent Water
can be significantly influenced by the sample mass and the temperature
E177 Practice for Use of the Terms Precision and Bias in
ramp rate. This will be addressed in the standard as Special Case 2, in
ASTM Test Methods
subsection 8.2.3. Since the AIT of a material is dependent on the sample
mass/configuration and test conditions, any departure from the standard E691 Practice for Conducting an Interlaboratory Study to
conditions normally used for Test Method G72/G72M testing should be
Determine the Precision of a Test Method
clearly indicated in the test report.
G93 Guide for Cleanliness Levels and Cleaning Methods for
1.3 This test method is for high-pressure pure oxygen. The
Materials and Equipment Used in Oxygen-Enriched En-
test method may be used in atmospheres from 0.5 % to 100 %
vironments
oxygen.
2.2 Federal Specification:
3
BB-O-925 Oxygen, Technical, Gas and Liquid
1.4 An apparatus suitable for these requirements is de-
2.3 Other Documents:
scribed. This test method could be applied to higher pressures
MNL 36 Safe Use of Oxygen and Oxygen Systems: Guide-
and materials of higher ignition temperature. If more severe
lines for Oxygen System Design, Materials, Selection,
requirements or other oxidizers than those described are
4
Operations, Storage, and Transportation
desired, care must be taken in selecting an alternative safe
apparatus capable of withstanding the conditions.
2
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on
1
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee G04 on the ASTM website.
3
Compatibility and Sensitivity of Materials in Oxygen Enriched Atmospheres and is Available from U.S. Government Printing Office Superintendent of Documents,
the direc
...
This document is not an ASTM standard and is intended only to provide the user of an ASTM standard an indication of what changes have been made to the previous version. Because
it may not be technically possible to adequately depict all changes accurately, ASTM recommends that users consult prior editions as appropriate. In all cases only the current version
of the standard as published by ASTM is to be considered the official document.
Designation: G72/G72M − 15 G72/G72M − 24
Standard Test Method for
Autogenous Ignition Temperature of Liquids and Solids in a
1
High-Pressure Oxygen-Enriched Environment
This standard is issued under the fixed designation G72/G72M; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year
of original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval.
A superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope
1.1 This test method covers the determination of the temperature at which liquids and solids will spontaneously ignite. These
materials must ignite without application of spark or flame in a high-pressure oxygen-enriched environment.
1.2 This test method is intended for use at pressures of 2.1 to 20.7 MPa [300 to 3000 psi]. 2.1 MPa to 20.7 MPa [300 psi to
3000 psi]. The pressure used in the description of the method is 10.3 MPa [1500 psi], 10.3 MPa [1500 psi], and is intended for
applicability to high pressure conditions. The test method, as described, is for liquids or solids with ignition temperature in the
range from 6060 °C to 500 °C [140[140 °F to 932 °F].
NOTE 1—Test Method G72/G72M normally utilizes samples of approximately 0.20 +/-6 0.03-g mass, a starting pressure of 10.3 MPa 10.3 MPa
[1500 psi] and a temperature ramp rate of 5 °C ⁄min. However, Autogenous Ignition Temperatures (AIT) can also be obtained under other test conditions.
Testing experience has shown that AIT testing of volatile liquids can be influenced by the sample pre-conditioning and the sample mass. This will be
addressed in the standard as Special Case 1 in subsection 8.2.2. Testing experience has also shown that AIT testing of solid or non-volatile liquid materials
at low pressures (i.e., < 2.1 MPa) (that is, < 2.1 MPa) can be significantly influenced by the sample mass and the temperature ramp rate. This will be
addressed in the standard as Special Case 2, in subsection 8.2.3. Since the AIT of a material is dependent on the sample mass/configuration and test
conditions, any departure from the standard conditions normally used for Test Method G72/G72M testing should be clearly indicated in the test report.
1.3 This test method is for high-pressure pure oxygen. The test method may be used in atmospheres from 0.5 % to 100 % oxygen.
1.4 An apparatus suitable for these requirements is described. This test method could be applied to higher pressures and materials
of higher ignition temperature. If more severe requirements or other oxidizers than those described are desired, care must be taken
in selecting an alternative safe apparatus capable of withstanding the conditions.
1.5 The values stated in either SI units or inch-pound units are to be regarded separately as standard. The values stated in each
system may not be exact equivalents; therefore, each system shall be used independently of the other. Combining values from the
two systems may result in non-conformance with the standard.
1.6 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility
of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and healthsafety, health, and environmental practices and determine
the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
1.7 This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization
established in the Decision on Principles for the Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued
by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
1
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee G04 on Compatibility and Sensitivity of Materials in Oxygen Enriched Atmospheres and is the direct
responsibility of Subcommittee G04.01 on Test Methods.
Current edition approved Oct. 1, 2015Jan. 1, 2024. Published October 2015February 2024. Originally approved in 1982. Last previous edition approved in 20092015 as
G72/G72M – 09.G72/G72M – 15. DOI: 10.1520/G0072_G0072M-15.10.1520/G0072_G0072M-24.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
G72/G72M − 24
2. Referenced Documents
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
D1193 Specification for Reagent Water
E177 Practice for Use of the Terms Precision and Bias in ASTM Test Methods
E691 Practice for Conducting an Interlaboratory Study to Determi
...









Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.