ASTM F1632-03(2010)
(Test Method)Standard Test Method for Particle Size Analysis and Sand Shape Grading of Golf Course Putting Green and Sports Field Rootzone Mixes
Standard Test Method for Particle Size Analysis and Sand Shape Grading of Golf Course Putting Green and Sports Field Rootzone Mixes
ABSTRACT
These test methods establish the apparatus required, standard procedures, and associated calculations for determining the particle size distribution and shape grading of sand in golf course putting green and other sand-based sports field rootzone mixtures assumed to have sand contents of 80 % by weight or greater. Particles large enough to be retained on a No. 270 sieve are determined by sieving, while, the silt and clay percentages are determined by a sedimentation process using the pipet method.
SCOPE
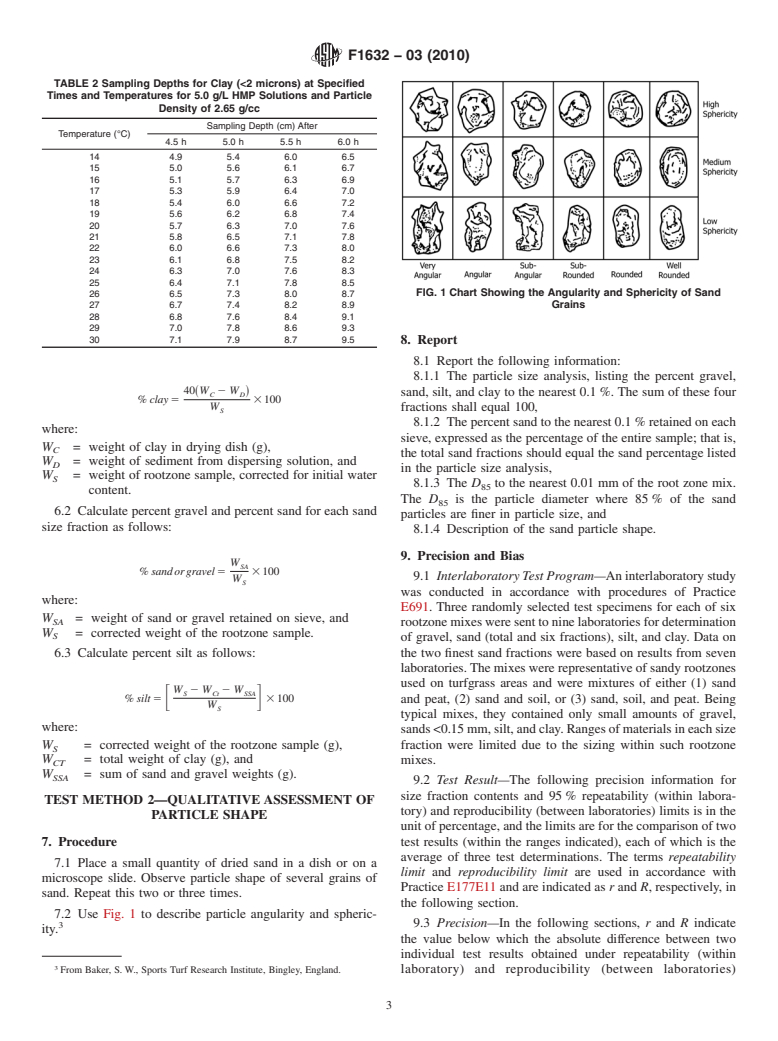
1.1 This test method covers the determination of particle size distribution of putting green and other sand-based rootzone mixes. Particles larger than 0.05 mm (retained on a No. 270 sieve) are determined by sieving. The silt and clay percentages are determined by a sedimentation process, using the pipet method. This procedure was developed for putting green rootzone mixes, those assumed to have sand contents of 80 % by weight or greater. Particle size analysis of soils may be performed by this test method or Test Method D422. This test method also describes a qualitative evaluation of sand particle shape.
1.2 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
General Information
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Designation: F1632 − 03 (Reapproved 2010) An American National Standard
Standard Test Method for
Particle Size Analysis and Sand Shape Grading of Golf
Course Putting Green and Sports Field Rootzone Mixes
This standard is issued under the fixed designation F1632; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision.Anumber in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval.A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope 3.2.1 For MethodA—An Electric Mixer, made for mechani-
cal mixing of soils, or
1.1 This test method covers the determination of particle
3.2.2 For Method B—A Horizontal Reciprocating Shaker,
size distribution of putting green and other sand-based root-
with holder for 250 mL flasks or bottles.
zone mixes. Particles larger than 0.05 mm (retained on a No.
270 sieve) are determined by sieving. The silt and clay
3.3 Sedimentation Cylinder, a glass cylinder marked for a
percentages are determined by a sedimentation process, using
volume of 1000 mL. The height of the 1000 mL must be
the pipet method. This procedure was developed for putting
36 62 cm from the bottom on the inside.
green rootzone mixes, those assumed to have sand contents of
3.4 Thermometer, accurate to 0.5°C.
80%byweightorgreater.Particlesizeanalysisofsoilsmaybe
performed by this test method or Test Method D422. This test 3.5 Pipet Rack, a device for lowering a pipet to a precise
depth in the sedimentation cylinder.
method also describes a qualitative evaluation of sand particle
shape.
3.6 Pipets,Lowyorotherwidetippedtype,25mLcapacity.
1.2 This standard does not purport to address all of the
3.7 Weighing Bottles or Beakers, glass with a capacity of
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
100 mL.
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
3.8 Sieves, square mesh with woven wire (brass or stainless
priate safety and health practices and determine the applica-
steel). The sieves shall conform to the requirements of Speci-
bility of regulatory limitations prior to use.
fication E11. A full set of sieves shall include the following:
2. Referenced Document
3.8.1 No. 10—2 mm,
3.8.2 No. 18—1 mm,
2.1 ASTM Standards:
3.8.3 No. 35—500 µm,
D422Test Method for Particle-Size Analysis of Soils
3.8.4 No. 60—250 µm,
E11Specification forWovenWireTest Sieve Cloth andTest
Sieves 3.8.5 No. 100—149 µm,
E177Practice for Use of the Terms Precision and Bias in 3.8.6 No. 140—105 µm, and
ASTM Test Methods
3.8.7 No. 270—53 µm.
E691Practice for Conducting an Interlaboratory Study to
3.9 Sieve Shaker, type that provides vertical tapping action
Determine the Precision of a Test Method
as well as horizontal shaking.
3. Apparatus
3.10 Desiccator.
3.1 Balance, sensitive to 0.001 g.
3.11 Dispersing Agent, a 5% sodium hexametaphosphate
(HMP) solution, made by dissolving 50 g of reagent or
3.2 Stirring Apparatus, may be either of the following
technical grade HMPin 1000 mLof distilled or demineralized
types:
water.
3.12 Oven, capable of maintaining a temperature of 105 6
This test method is under the jurisdiction ofASTM Committee F08 on Sports
5°C.
Equipment, Playing Surfaces, and Facilitiesand is the direct responsibility of
Subcommittee F08.64 on Natural Playing Surfaces.
3.13 Water—shallbedistilledordemineralized,andbrought
Current edition approved Sept. 1, 2010. Published December 2010. Originally
to the temperature that is expected to prevail during the
approved in 1995. Last previous edition approved in 2003 as F1632–03. DOI:
10.1520/F1632-03R10.
sedimentation process. If air temperatures are expected to
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
fluctuate, cylinders should be placed in a constant temperature
contactASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. ForAnnual Book ofASTM
water bath, and the distilled or demineralized water brought to
Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on
the ASTM website. the temperature of the water bath.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
F1632 − 03 (2010)
3.14 Dissecting Microscope, 25 to 50× power. cylinder with waxfilm, a stopper, or watch glass. Place the
cylinder into a water bath, or allow it to stand until the
TEST METHOD 1—PROCEDURE FOR PARTICLE
temperature of the suspension is the same as the water bath or
SIZE ANALYSIS
the air temperature, respectively.
4.3.2 After the temperature is constant, resuspend the silt
4. Procedure
and clay by one of the two following methods: (a) stir
4.1 Dispersion of Sample:
thoroughly with a hand stirrer, using an up and down motion
4.1.1 Weigh 100 65 g of air-dried rootzone mix to the
for at least 30 s; or (b) stopper the cylinder and shake end over
nearest 0.1 g and place in mixing cup (Test MethodA) or flask
end for 1 min.
(Test Method B). Place a duplicate sample into a drying oven
4.3.3 Use Tables 1 and 2 or appropriate calculations using
set at 105 6 5°C for correction to oven dried basis.
Stoke’s Law to determine sampling depths and times for the
4.1.2 Add100mLofdispersingagent.Stirorswirluntilthe
suspension temperature.
rootzonemixisthoroughlywet.Allowtostandfor4h.Ifusing
4.3.4 Turn on the vacuum and withdraw a 25 mLsample in
Test Method B, place the flasks or bottles on the shaker and
about 12 s. Rate of withdraw is important.
shake for 16 h or overnight.
4.3.5 Discharge the sample into a tared beaker or drying
4.1.3 Test Method A—Add about 100 mL of water to the
dish.
mixing cup and place onto the mixer. Mix for 5 min on low
4.3.6 Towashoutanyresidualmaterialinthepipetdraw25
speed.
mLof water into the pipet, and discharge into the same drying
4.2 Determination of the Sand (2.0 to 0.05 mm) Fractions dish.
and Gravel (material >2 mm): 4.3.7 Evaporate the water and dry the clay at 105 6 5°C.
4.2.1 PlaceataredNo.270sieveontoalargefunnelheldby 4.3.8 Cool in a desiccator and weigh to the nearest 0.001 g.
astandoverasedimentationcylinder.Pourthesuspensiononto
5. Determination of Correction for Dispersing Solution
thesieve.Rinseremainingsandmaterialoutofthecuporflask
with water onto the sieve. Wash the collected sand and gravel
5.1 Dispense 100 mL of dispersing solution into 1 L
with misted water to wash any remaining silt or clay particles
container.
through the sieve into the cylinder.
5.2 Add distilled or demineralized water to 1 Lvolume, stir
4.2.2 An alternative for collecting sand and gravel is to
or swirl until thoroughly mixed.
separate following the sampling for clay (4.3). In this case the
suspension is poured and washed onto a No. 270 sieve after 5.3 Draw 25 mLand dispense into a tared beaker or drying
dish.
pipeting has been completed. The sample is then washed until
only sand and gravel remain on the sieve. Then continue the
5.4 Draw 25 mL of water and dispense into same dish.
procedure at 4.2.3. If this alternative method is used, the
5.5 Evaporate in an oven at 105 6 5°C.
volumeofsiltplusclaysuspensionatpipetingtimeislessthan
1000 ml due to the presence of sand and gravel. Thus the clay 5.6 Weigh the sediment in the beaker (W ) to the nearest
D
percentage as calculated in 6.1 must be corrected.Assuming a 0.001 g.
particle density of 2.65 g/cc for sand and gravel, conversion
6. Calculation for Test Method 1
factors for various sand plus gravel weights in the cylinder are
as follows:
6.1 Calculate percent clay as follows:
Sand and Gravel Conversion Factor to
in Cylinder, g Correct % Clay in 6.1
TABLE 1 Settling Velocities and Settling Times (at 10-cm depth)
68 to 92 0.97
for 5 g/L HMP Solutions and Particle Density of 2.65 g/cc when
93 to 100 0.96
Sampling for Clay (<2 microns) at Various Temperatures
Temperature, °C Settling Velocity
...







Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.