ASTM F397-02
(Test Method)Standard Test Method for Resistivity of Silicon Bars Using a Two-Point Probe (Withdrawn 2003)
Standard Test Method for Resistivity of Silicon Bars Using a Two-Point Probe (Withdrawn 2003)
SCOPE
This standard was transferred to SEMI (www.semi.org) May 2003
1.1 This test method covers the measurement of the resistivity of single-crystal bars having cross sections that are uniform in area and square, rectangular or round in shape, and having resistivity between 0.0009 and 3000 Ω·cm. The resistivity of a silicon crystal is an important acceptance requirement.
1.2 This test method is intended for use on single crystals of silicon of either n- or p-type for which the uniformity of the crystal cross section is such that the area can be accurately calculated. The specimen cross-sectional area shall be constant to within 1 % of the average area as determined by measurements along the crystal axis (see 12.2).
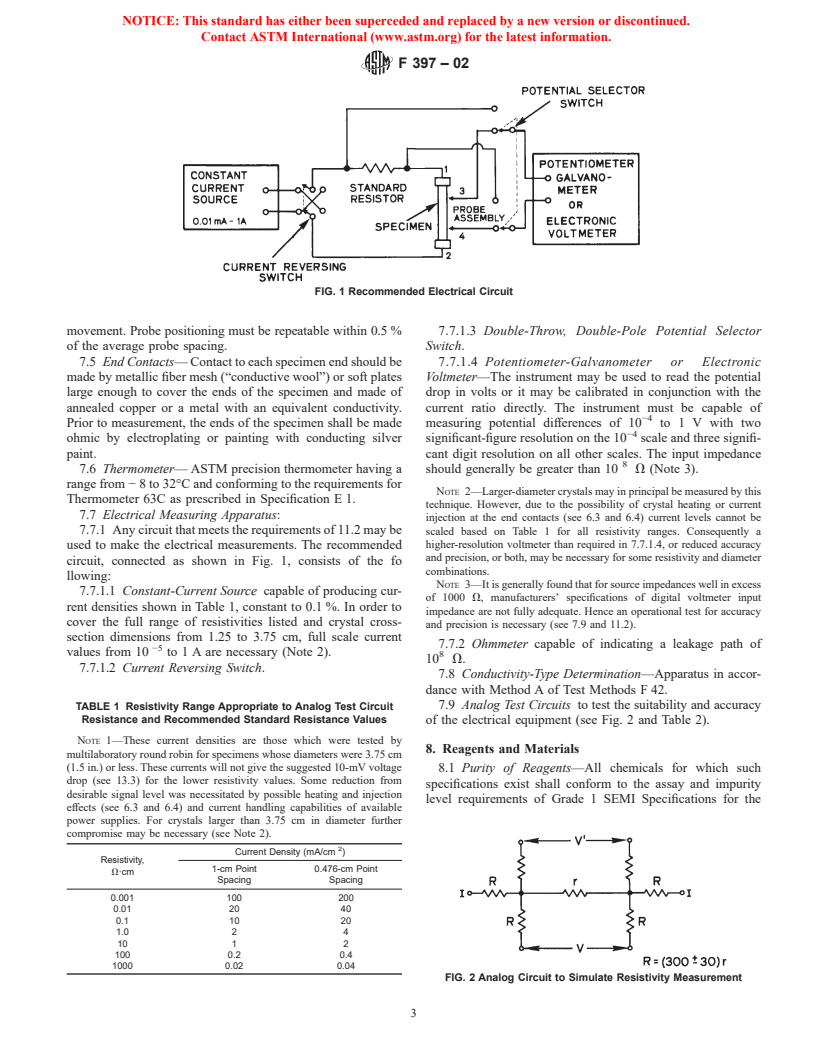
1.3 The ratio of the length to the maximum dimension of the cross section of the specimen shall not be less than 3:1 (see 12.1). The largest diameter tested by round robin was 3.75 cm (1.5 in.), and this is the largest diameter that can be measured by this method. The specimen shall normally have a surface finish of 0.4 m (16 in.) rms or less (see ANSI B46). Other surface finishes may be used if mutually acceptable; however, the multilaboratory precision figures of this test (see 16.1) then may no longer apply.
1.4 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use. Specific hazard statements are given in Section 9.
General Information
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superceded and replaced by a new version or discontinued.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information.
DIN 50430
Designation: F 397 – 02
Standard Test Method for
1
Resistivity of Silicon Bars Using a Two-Point Probe
This standard is issued under the fixed designation F 397; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (e) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope D 5127 Guide for Ultra Pure Water Used in the Electronics
3
2
and Semiconductor Industry
1.1 This test method covers the measurement of the resis-
4
E 1 Specification for ASTM Thermometers
tivity of single-crystal bars having cross sections that are
F 42 Test Methods for Conductivity Type of Extrinsic
uniform in area and square, rectangular or round in shape, and
5
Semiconducting Materials
having resistivity between 0.0009 and 3000 V·cm. The resis-
2.2 Other Standard:
tivity of a silicon crystal is an important acceptance require-
6
ANSI B46 Surface Texture
ment.
2.3 SEMI Standards:
1.2 This test method is intended for use on single crystals of
7
C19 Specification for Acetone
silicon of either n-or p-type for which the uniformity of the
7
C28 Specifications and Guidelines for Hydrofluoric Acid
crystal cross section is such that the area can be accurately
7
C31 Specification for Methanol
calculated. The specimen cross-sectional area shall be constant
7
C35 Specifications and Guidelines for Nitric Acid
to within 61 % of the average area as determined by measure-
ments along the crystal axis (see 12.2).
3. Terminology
1.3 The ratio of the length to the maximum dimension of the
3.1 Definitions of Terms Specific to This Standard:
cross section of the specimen shall not be less than 3:1 (see
3.1.1 resistivity, r[V·cm]—of a semiconductor, the ratio of
12.1). The largest diameter tested by round robin was 3.75 cm
the potential gradient (electric field) parallel with the current to
(1.5 in.), and this is the largest diameter that can be measured
the current density.
by this method. The specimen shall normally have a surface
finish of 0.4 μm (16 μin.) rms or less (see ANSI B46). Other
4. Summary of Test Method
surface finishes may be used if mutually acceptable; however,
4.1 A direct current is passed through ohmic contacts at the
the multilaboratory precision figures of this test (see 16.1) then
ends of a bar specimen and the potential difference is deter-
may no longer apply.
mined between two probes placed along the current direction
1.4 This standard does not purport to address all of the
(see 7.3.1). The resistivity is calculated from the current and
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
potential values and factors appropriate to the geometry. This
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
test method includes procedures for checking both the probe
priate safety and health practices and determine the applica-
assembly and the electrical measuring apparatus.
bility of regulatory limitations prior to use. Specific hazard
4.1.1 The spacing between the two probe tips is determined
statements are given in Section 9.
from measurements of indentations made on a polished single-
2. Referenced Documents crystal surface.
4.1.2 The accuracy of the electrical measuring equipment is
2.1 ASTM Standards:
tested by means of an analog circuit containing a known
resistance together with other resistors which simulate the
1
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee F01 on resistance at the contacts between the probe tips and the
Electronics and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee F01.06 on Silicon
semiconductor surface.
Materials and Process Control.
Current edition approved Dec. 10, 2002. Published February 2003. Originally
published in 1974 as F 397 – 74T. Last previous edition approved in 1993 as
3
F 397 – 93(1999). Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 11.01.
2 4
DIN 50430 is an equivalent method. It is the responsibility of DIN Committee Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 14.03.
5
NMP 221, with which Committee F01 maintains close technical liaison. DIN 50430, Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 10.05.
6
Testing Inorganic Semiconductor Materials: Measurement of the Specific Electrical Available from American National Standards Institute, 25 West 43rd St., 4th
Resistance of Bar-Shaped Monocrystals of Silicon or Germanium by the Two-Probe Floor, New York, NY 10036.
7
Direct Current Method is available from Beuth Verlag GmbH, Burggrafenstrasse Available from the Semiconductor Equipment and Materials International,
4-10, D-1000 Berlin 30, Federal Republic of Germany. 3081 Zanker Road, San Jose, CA 95134 (www.semi.org).
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959, United States.
1
...








Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.