ASTM D7993-15(2019)
(Guide)Standard Guide for Analyzing Complex Phthalates
Standard Guide for Analyzing Complex Phthalates
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
5.1 The regulatory candidate list classifies substances by CAS number. Complex branched phthalates, such as DINP or DIDP, manufactured with a defined alcohol distribution and registered by CAS number with a chemical description of the composition, shall be considered a single substance with that composition as described.
5.2 It is possible for the alcohols used in the manufacture of complex branched phthalates to vary in isomer composition. Care must be used to ensure a representative standard is used to the quantitation of the level of a complex branched phthalate.
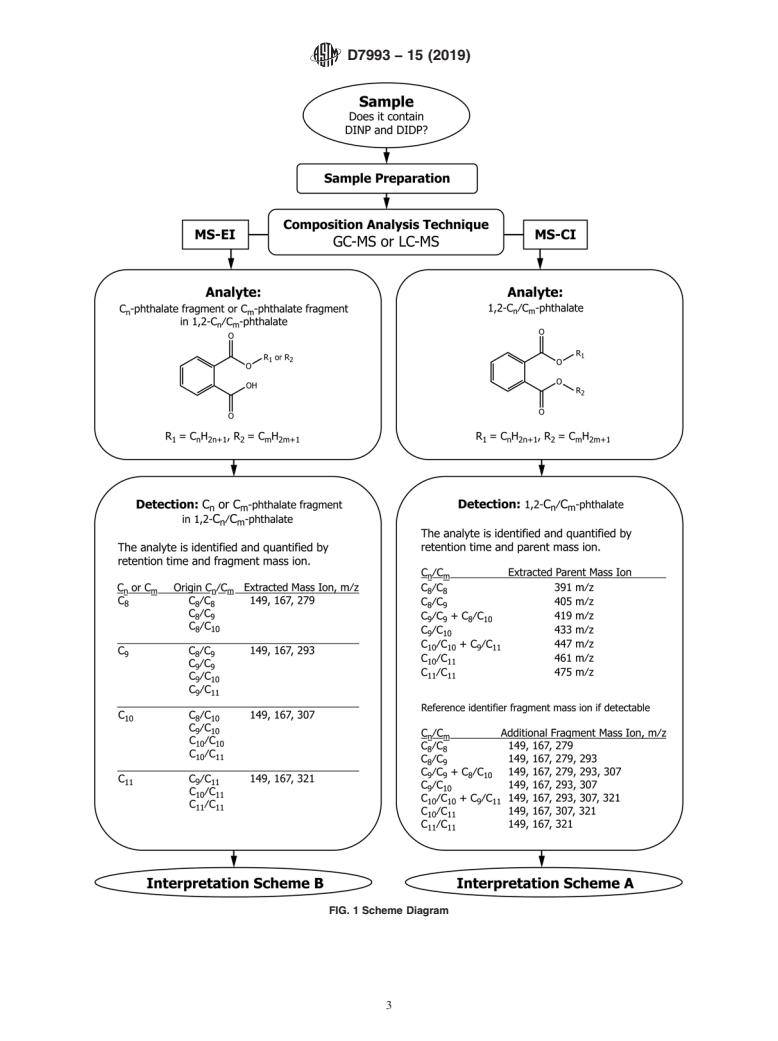
5.3 This guide is intended to provide a method on how to interpret and determine data from an analysis involving complex branched phthalates with defined CAS numbers. The test procedure employed shall be used to provide speciation information to assist use of the schematic flow diagram.
Note 3: A discussion on analytical challenges in complex branched phthalate analysis is found in: “Analytical Challenges in Detecting Regulated Phthalates in Flexible PVC Products,” SPI Flexible Vinyl Products Division, 23rd Annual Compounding Conference, July 17, 2012.
SCOPE
1.1 This guide is established in response to regulatory requirements for the determination of complex branched phthalates by CAS numbers. This guide is intended to provide information on how to interpret and analyze data from a chromatographic analysis involving complex phthalates with defined CAS numbers.
1.2 This guide provides a logical approach to determine levels of complex branched phthalates meeting regulatory and CAS number requirements.
1.3 The specific complex phthalates covered within this guide are DINP and DIDP.
1.4 Limitations—This guide does not recommend any specific test method. In some cases, it is necessary to deduce the quantity of substance present through the analysis and quantification of its components. Although this approach is routinely used some degree of uncertainty exists in the final result due to the reduced accuracy of the method.
1.5 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as standard. No other units of measurement are included in this standard.
1.6 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety, health, and environmental practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
1.7 This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization established in the Decision on Principles for the Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
General Information
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization established in the Decision on Principles for the
Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
Designation: D7993 − 15 (Reapproved 2019)
Standard Guide for
Analyzing Complex Phthalates
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D7993; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope 2. Referenced Documents
1.1 This guide is established in response to regulatory 2.1 ASTM Standards:
requirementsforthedeterminationofcomplexbranchedphtha- D883 Terminology Relating to Plastics
lates by CAS numbers. This guide is intended to provide D1600 Terminology forAbbreviatedTerms Relating to Plas-
information on how to interpret and analyze data from a tics
chromatographic analysis involving complex phthalates with D3465 Test Method for Purity of Monomeric Plasticizers by
defined CAS numbers. Gas Chromatography
D7083 Practice for Determination of Monomeric Plasticiz-
1.2 This guide provides a logical approach to determine
ers in Poly (Vinyl Chloride) (PVC) by Gas Chromatogra-
levels of complex branched phthalates meeting regulatory and
phy
CAS number requirements.
D7823 Test Method for Determination of Low Level Phtha-
1.3 The specific complex phthalates covered within this
lates in Poly (Vinyl Chloride) Plastics by Thermal
guide are DINP and DIDP.
Desorption—Gas Chromatography/Mass Spectrometry
E355 Practice for Gas Chromatography Terms and Relation-
1.4 Limitations—This guide does not recommend any spe-
cific test method. In some cases, it is necessary to deduce the ships
E594 Practice for Testing Flame Ionization Detectors Used
quantity of substance present through the analysis and quanti-
fication of its components.Although this approach is routinely in Gas or Supercritical Fluid Chromatography
IEEE/ASTM SI-10 Practice for Use of the International
used some degree of uncertainty exists in the final result due to
the reduced accuracy of the method. System of Units (SI), the Modernized Metric System
2.2 Spectral Library:
1.5 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as
NIST/EPA/NIH Mass Spectral Library
standard. No other units of measurement are included in this
2.3 SPI Association Publication:
standard.
“Analytical Challenges in Detecting regulated Phthalates in
1.6 This standard does not purport to address all of the
Flexible PVC products” SPI Flexible Vinyl Products
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
Division 23rdAnnual Compounding Conference, July 17,
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
priate safety, health, and environmental practices and deter-
mine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use. 3. Terminology
1.7 This international standard was developed in accor-
3.1 Definitions—For definition of plastic terms used in this
dance with internationally recognized principles on standard-
test method, see Terminologies D883 and D1600.
ization established in the Decision on Principles for the
3.2 For units, symbols, and abbreviations used in this test
Development of International Standards, Guides and Recom-
method refer to Practices E355, E594,or IEEE/ASTM SI-10.
mendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical
Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
3.3 Acronyms:
3.3.1 CAS—Chemical Abstract Services
This guide is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D20 on Plastics and
is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee D20.70 on Analytical Methods. For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
Current edition approved Aug. 1, 2019. Published August 2019. Originally contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
approved in 2015. Last previous edition approved in 2015 as D7993 - 15. DOI: Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on
10.1520/D7993-15R19 the ASTM website.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
D7993 − 15 (2019)
3.4 Compounds and Instrumentation: composition, shall be considered a single substance with that
3.4.1 (DINP) 1,2-Benzenedicarboxylicacid, di-C - composition as described.
8-10
branched alkyl esters, C -rich CAS #68515-48-0
5.2 It is possible for the alcohols used in the manufacture of
3.4.2 (DINP) 1,2-Benzenedicarboxylicacid, 1,2-diisononyl
complex branched phthalates to vary in isomer composition.
CAS #28553-12-0
Care must be used to ensure a representative standard is used
3.4.3 (DIDP) 1,2-Benzenedicarboxylicacid, di-C -
9-11
to the quantitation of the level of a complex branched phtha-
branched alkyl esters, C -rich CAS #68515-49-1
late.
3.4.4 (DIDP) 1,2-Benzenedicarboxylicacid, 1,2-diisodecyl
5.3 This guide is intended to provide a method on how to
CAS #26761-40-0
interpret and determine data from an analysis involving com-
3.4.5 GC Gas Chromatography
plex branched phthalates with defined CAS numbers. The test
3.4.6 GC-MS Gas Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry
procedure employed shall be used to provide speciation infor-
3.4.7 LC-MS Liquid Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry
mation to assist use of the schematic flow diagram.
3.4.8 PVC Poly(Vinyl Chloride)
3.4.9 Complex branched phthalates are phthalate diesters/
NOTE 3—A discussion on analytical challenges in complex branched
phthalate analysis is found in: “Analytical Challenges in Detecting
coesters based on alcohols with a variety of branched isomers.
Regulated Phthalates in Flexible PVC Products,” SPI Flexible Vinyl
NOTE1—DINPandDIDP,usedinvariousPVCorformulationsinother
Products Division, 23rdAnnual Compounding Conference, July 17, 2012.
matrix are technical mixtures. When preparing the phthalate calibration
standard, technical grade material shall be used. Specific information on
6. Substance List
examplesoftechnicalgradeDINPandDIDPcanbelocatedontheinternet
search engine.
6.1 Each of the four substances listed in Table 1 is a unique
NOTE 2—Branched phthalates have ranges of degrees and positions in
substance by manufacture defined by its CAS number. Its
branching. Example: Branched C phthalates have ranges of Slightly
unique chemical name defines its specific chemical composi-
Branched (primarily monomethyl-1-octyl- and dimethyl-1-heptyl-), Mod-
tion as shown in Table 2. Since the same diesters and coesters
erately Branched (primarily dimethyl-1-heptyl), and Highly Branched
can be found in
...







Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.