ASTM D7043-10
(Test Method)Standard Test Method for Indicating Wear Characteristics of Petroleum and Non-Petroleum Hydraulic Fluids in a Constant Volume Vane Pump
Standard Test Method for Indicating Wear Characteristics of Petroleum and Non-Petroleum Hydraulic Fluids in a Constant Volume Vane Pump
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
This test method is an indicator of the wear characteristics of non-petroleum and petroleum hydraulic fluids operating in a constant volume vane pump. Excessive wear in vane pumps could lead to malfunction of hydraulic systems in critical applications.
SCOPE
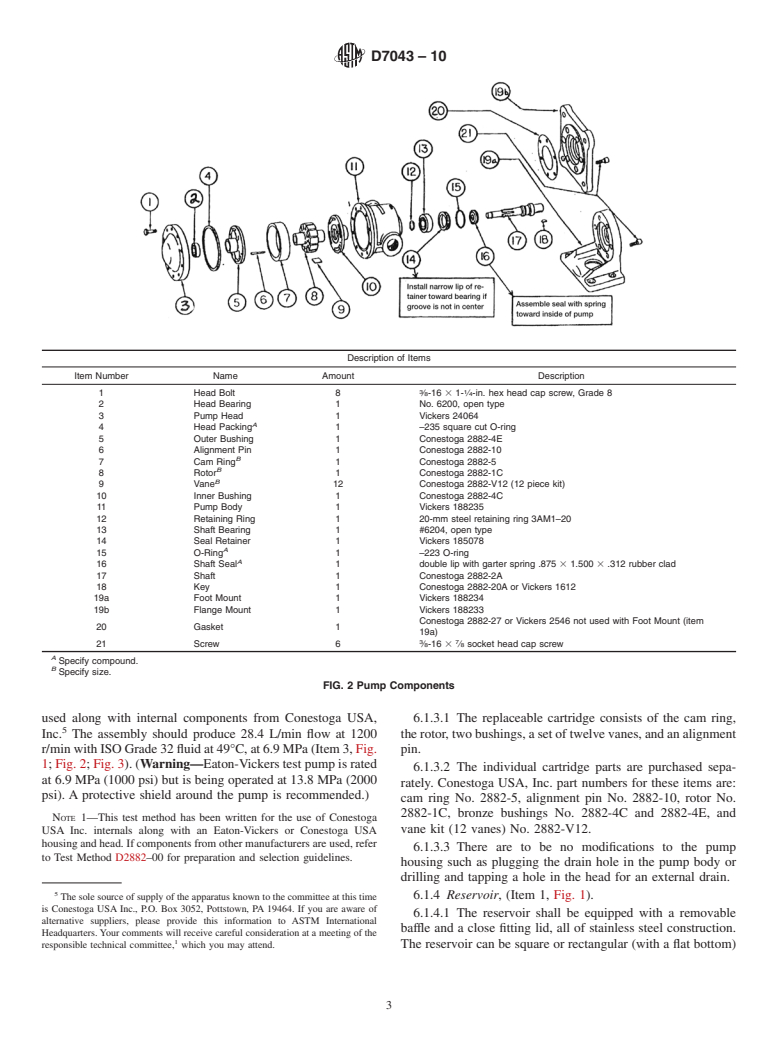
1.1 This test method covers a constant volume vane pump test procedure operated at 1200 rpm and 13.8 MPa.
1.2 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as standard. No other units of measurement are included in this standard.
1.2.1 Exception—There are no SI equivalents for the inch fasteners and inch O-rings that are used in the apparatus in this test method.
1.2.2 Exception—In some cases English pressure values are given in parentheses as a safety measure.
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
General Information
Relations
Buy Standard
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Designation:D7043–10
Standard Test Method for
Indicating Wear Characteristics of Non-Petroleum and
Petroleum Hydraulic Fluids in a Constant Volume Vane
1
Pump
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D7043; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision.Anumber in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval.A
superscript epsilon (ϵ) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope* 3.1.1 flushing, v—processofcleaningthetestsystembefore
testing to prevent cross-contamination.
1.1 This test method covers a constant volume vane pump
3.1.2 torquing, v—process of tightening the pump head
test procedure operated at 1200 rpm and 13.8 MPa.
bolts to achieve a uniform clamping force.
1.2 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as
standard. No other units of measurement are included in this
4. Summary of Test Method
standard.
4.1 An amount of 18.9 6 0.5 L of a hydraulic fluid are
1.2.1 Exception—There are no SI equivalents for the inch
circulated through a rotary vane pump system for 100 h at a
fastenersandinchO-ringsthatareusedintheapparatusinthis
pump speed of 12006 60 r/min and a pump outlet pressure of
test method.
13.8 6 0.3 MPa (2000 6 40 psi). Fluid temperature at the
1.2.2 Exception—InsomecasesEnglishpressurevaluesare
pump inlet is 66 6 3°C for all water glycols, emulsions, and
given in parentheses as a safety measure.
other water containing fluids and for petroleum and synthetic
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the
fluids of ISO Grade 46 or lighter. A temperature of 80 6 3°C
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
is used for all other synthetic and petroleum fluids.
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
4.2 The result obtained is the total mass loss from the cam
priate safety and health practices and determine the applica-
ringandthetwelvevanesduringthetest.Otherreportedvalues
bility of regulatory limitations prior to use.
are initial flow rate and final flow rate.
2. Referenced Documents 4.3 Thetotalquantityoftestoilrequiredforarunis26.5L.
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
5. Significance and Use
D2882 Test Method for Indicating Wear Characteristics of
5.1 This test method is an indicator of the wear character-
Petroleum and Non-Petroleum Hydraulic Fluids in Con-
3 istics of non-petroleum and petroleum hydraulic fluids operat-
stant Volume Vane Pump
ing in a constant volume vane pump. Excessive wear in vane
D6300 Practice for Determination of Precision and Bias
pumps could lead to malfunction of hydraulic systems in
Data for Use in Test Methods for Petroleum Products and
critical applications.
Lubricants
E691 Practice for Conducting an Interlaboratory Study to
6. Apparatus
Determine the Precision of a Test Method
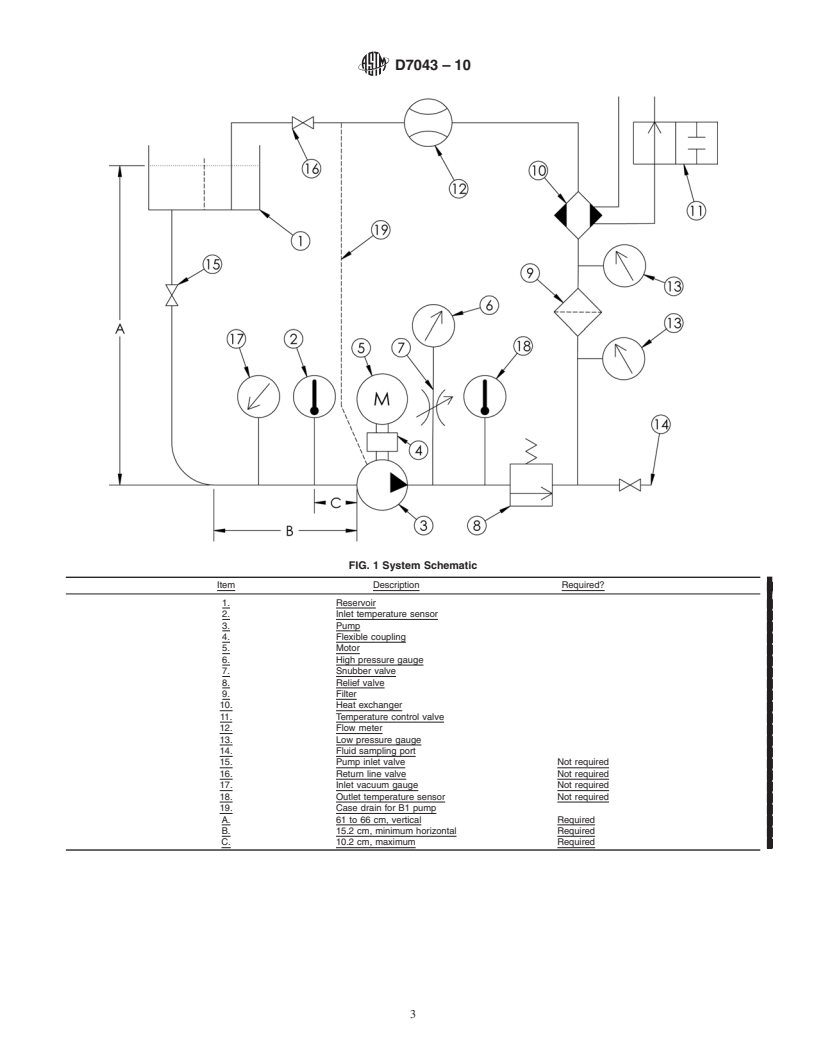
6.1 The basic system consists of the following (see Fig. 1):
3. Terminology 6.1.1 AC Motor, 1200-rpm, or other suitable drive, with 11
kw (15 hp) as suggested minimum power requirement (Item 5,
3.1 Definitions of Terms Specific to This Standard:
Fig.1).Themotormusthaverighthandrotation(counterclock-
wise rotation as viewed from the shaft end).
6.1.2 Test Stand Base, with appropriate, rigid mounting for
1
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D02 on
the motor, pump, reservoir, and other components.
PetroleumProductsandLubricantsandisthedirectresponsibilityofSubcommittee
6.1.3 Rotary Vane Pump, replaceable cartridge type. A
D02.N0.07 on Lubricating Properties.
4
Vickers V104C or V105C or Conestoga USA B1 housing is
Current edition approved May 1, 2010. Published September 2010. Originally
approved in 2004. Last previous edition approved in 2004 as D7043–04a. DOI:
10.1520/D7043-10.
2
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
4
contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM Previously available, this apparatus was made obsolete in 2000 by Vickers,
Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on which is part of Eaton Hydraulics Group USA14615 Lone Oak Road Eden Prairie,
the ASTM website. MN55344.Ifyouareawareofalternativesuppliers,pleaseprovidethisinformation
3
Withdrawn. The last approved version of this historical standard is referenced to ASTM International Headquarters. Your comments will receive careful consid-
1
on www.astm.org. erationatameetingoftheresponsibletechnicalcommittee, whichyoumayattend.
*A Summary of Changes section appears at the end of this standard.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959, United States.
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
D7043–10
Item Description Required?
1. Reservoir
2. Inlet temperature sensor
3. Pump
4. Flexible cou
...
This document is not anASTM standard and is intended only to provide the user of anASTM standard an indication of what changes have been made to the previous version. Because
it may not be technically possible to adequately depict all changes accurately, ASTM recommends that users consult prior editions as appropriate. In all cases only the current version
of the standard as published by ASTM is to be considered the official document.
Designation:D7043–04a Designation:D7043–10
Standard Test Method for
Indicating Wear Characteristics of Non-Petroleum and
Petroleum Hydraulic Fluids in a Constant Volume Vane
1
Pump
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D7043; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision.Anumber in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval.A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope*
1.1 This test method covers a constant volume vane pump test procedure operated at 1200 rpm and 13.8 MPa.
1.2The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as standard. The values in parentheses are provided for information only.
1.2 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as standard. No other units of measurement are included in this standard.
1.2.1 Exception—There are no SI equivalents for the inch fasteners and inch O-rings that are used in the apparatus in this test
method.
1.2.2 Exception—In some cases English pressure values are given in parentheses as a safety measure.
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility
of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory
limitations prior to use.
2. Referenced Documents
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
D2882 TestMethodforIndicatingWearCharacteristicsofPetroleumandNon-PetroleumHydraulicFluidsinConstantVolume
Vane Pump Test Method for Indicating Wear Characteristics of Petroleum and Non-Petroleum Hydraulic Fluids in Constant
Volume Vane Pump
D6300 Practice for Determination of Precision and Bias Data for Use in Test Methods for Petroleum Products and Lubricants
E691 Practice for Conducting an Interlaboratory Study to Determine the Precision of a Test Method
3. Terminology
3.1 Definitions of Terms Specific to This Standard:
3.1.1 flushing, v—process of cleaning the test system before testing to prevent cross-contamination.
3.1.2 torquing, v—process of tightening the pump head bolts to achieve a uniform clamping force.
4. Summary of Test Method
4.1 An amount of 18.9 6 0.5 L (5 6 0.13 gal) of a hydraulic fluid are circulated through a rotary vane pump system for 100
h at a pump speed of 1200 6 60 r/min and a pump outlet pressure of 13.8 6 0.3 MPa (2000 6 40 psi). Fluid temperature at the
pump inlet is 66 6 3°C (150 6 5°F) for all water glycols, emulsions, and other water containing fluids and for petroleum and
synthetic fluids of ISO Grade 46 or lighter.Atemperature of 80 6 3°C (175 6 5°F) is used for all other synthetic and petroleum
fluids.
4.2 The result obtained is the total mass loss from the cam ring and the twelve vanes during the test. Other reported values are
initial flow rate and final flow rate.
4.3 The total quantity of test oil required for a run is 26.5 L (7 gal). L.
5. Significance and Use
5.1 This test method is an indicator of the wear characteristics of non-petroleum and non-petroleumpetroleum hydraulic fluids
1
This test method is under the jurisdiction ofASTM Committee D02 on Petroleum Products and Lubricants and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee D02.N0 on
Hydraulic Fluids.
Current edition approved Dec.May 1, 2004.2010. Published January 2005.September 2010. Originally approved in 2004. Last previous edition approved in 2004 as
D7043–04.D7043–04a. DOI: 10.1520/D7043-04A.10.1520/D7043-10.
2
ForreferencedASTMstandards,visittheASTMwebsite,www.astm.org,orcontactASTMCustomerServiceatservice@astm.org.For Annual Book of ASTM Standards
volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on the ASTM website.
*A Summary of Changes section appears at the end of this standard.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959, United States.
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
D7043–10
operating in a constant volume vane pump. Excessive wear in vane pumps could lead to malfunction of hydraulic systems in
critical applications.
6. Apparatus
6.1 The basic system consists of the following (see Fig. 1):
6.1.1 AC Motor, 1200-rpmMotor, 1200-rpm, or other suitable drive, with 11 kw (15 hp) as suggested minimum power
requirement (Item 5, Fig. 1). The motor must have right hand rotation (counterclockwise rotation as viewed from the shaft end).
6.1.2 Test Stand Base, with appropriate, rigid mounting for the motor, pump, reservoir, and other compo
...








Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.